

10th December 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
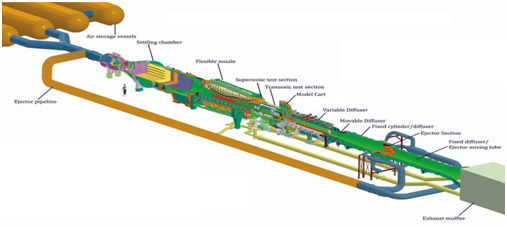
- A new trisonic wind tunnel was inaugurated by successfully conducting the first blow-down test at the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC).
About
What is a Trisonic Wind Tunnel?
- The trisonic wind tunnel is used to study the aerodynamic behaviour of flying objects, such as aeroplanes, artillery projectiles or missiles in all three-speed regimes:
- Subsonic
- Transonic
- Supersonic
- This is how it got its name, Trisonic Wind Tunnel.
- This system aids the aerodynamic design of rockets and re-entry spacecraft by characterizing a scaled model by evaluating forces, moments, load distribution, unsteady pressures, acoustic levels etc.
Specifications of the Trisonic Wind Tunnel:
- Maximum Length: 160 m
- Maximum cross section: 4 m
Uses:
- The tunnel can be used for testing various space vehicles in three flight regimes:
- below the speed of sound(Subsonic)
- at the speed of sound (Transonic)
- above the speed of sound (Supersonic)
- The tunnel can simulate flight conditions from 0.2 times the speed of sound (68 m/s) to 4 times the speed of sound (1360 m/s).
Significance:
- The trisonic wind tunnel was implemented through M/s Tata Projects India Ltd with the assistance of industries across the country.
- The trisonic wind tunnel is a major step towards India’s increasing self-reliance in the Aerospace sector.
- For years, ISRO had depended on the trisonic wind tunnel at the National Aerospace Laboratory (NAL), now it has its own.
National Aerospace Laboratory (NAL):
- National Aerospace Laboratories (NAL) in Bengaluru is the only industrial wind tunnel providing high-speed aerodynamic data for national aerospace programmes for:
- civil sectors
- military sectors
- The 1.2m trisonic wind tunnel was built by the CSIR between 1963 and 1967.
- It has recently commemorated its 55 years.
- The highest speed of this tunnel is Mach 4.0 which is four times the speed of sound.
- DRDO’s missiles such as Agni, Akaash, Prithvi, Pralay, SRSAM, LRSAM, ASTRA, NAG, LRAShM, BrahMos, Nirbhay, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, etc. were characterized in this facility.
- Aerodynamic characterisation of the ISRO’s launch vehicles such as ASLV, PSLV, SLV, SSLV, GSLV, RLV and GAGANYAAN programmes was carried out extensively.
More Articles


