Introduction:
The increasing access to affordable data service has given rise to these faceless evil worldwide - young children, in particular teenagers, being the most vulnerable victims. One in every three young people has reported to be a victim of cyber bullying, according to a survey conducted by UNICEF in as many as 30 countries. The poll found that nearly one in five parents worldwide said their child had experienced cyber bullying at least once. And, according to a majority of respondents, social networks including Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat and Twitter are the most commonplace sites on which cyber bullying occurs.
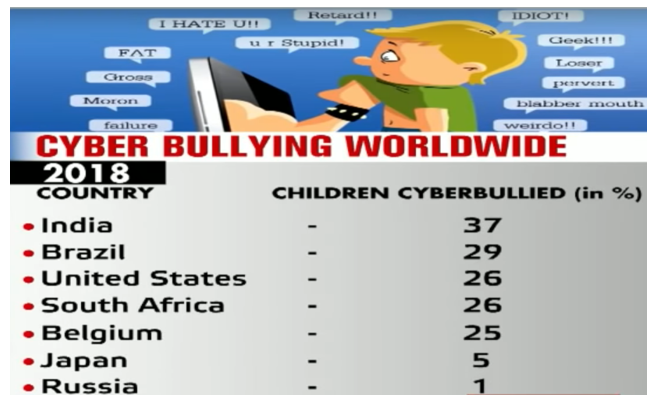
The problem is particularly bad in India which had the highest rate of parents confirming instances of cyber bullying. A total of 37% of parents across India said their child was bullied online, 14% among them said the bullying occurred on a regular basis. Studies show cyber bullying can cause profound harm as it can quickly reach a wide audience, and can remain accessible online indefinitely, virtually following its victims online for life.
Edited excerpts from the Debate:
Question: What is cyber bullying and how it is prevalent in world?
- Cyber bullying:
- It is bullying that takes place over digital devices like cell phones, computers, and tablets. Cyber bullying can occur through SMS, Text, and apps, or online in social media, forums, or gaming where people can view, participate in, or share content.
- It includes sending, posting, or sharing negative, harmful, false, or mean content about someone else. It can include sharing personal or private information about someone else causing embarrassment or humiliation. Some cyber bullying crosses the line into unlawful or criminal behaviour.
The most common places where cyber bullying occurs are:
- Social Media, such as Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, and Twitter.
- SMS (Short Message Service) also known as Text Message sent through devices.
- Instant Message (via devices, email provider services, apps, and social media messaging features)
Most of the cases of cyber bullying could be categorized in two main parts:
- Hate speech: Somebody wants to express its hatred towards a particular out of its particular grudge.
- A person harms a person through gossip and rumour.
Cyber bullying throughout world:
Question: What are the cyber bullying cases and how do the police tackle them?
- Cyber bullying does not qualify in the category of cognizable criminal offences. Only if it is in aggregated form for example, someone created fake profile of others and used that account for detrimental things that only qualifies as offence of impersonation.
- Most of the time the victim is a juvenile but at the same time the person who is committing this crime is also a juvenile and therefore this is covered under juvenile justice act. So the role of police authority in the conventional manner is limited hence registering an FIR and arresting the juvenile, these scenarios are not possible.
- In case bullies are not teenagers then the police deal with such perpetrators under the conventional provisions of the law and they will be treated as the ordinary criminals are treated.
Question: Do any of law in India explicitly define cyber bullying?
The term cyber bullying is neither mentioned in the Information Technology act 2000 nor in the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012. But there are certain provisions that tackle the problem of the same kind as that of cyber bullying
- Anti-ragging law: The central legislations keeps check on the practice of ragging in India through
- Indian Penal Code
- UGC Regulations On Curbing The Menace Of Ragging In Higher Educational Institutions, 2009
- And other institute specific regulations.
- If an act of person is an intimidation or threat, or somebody is threatening another person by making a video to make it viral just to disparate somebody’s reputation is also an act of cyber bullying which falls under Indian Penal Code (IPC).
- If an act of person is an identity theft then it goes under IT act.
These all are punishable offences up to 3 years imprisonment and fine.
|
Sections of Indian Penal Code:
|
Question: How does cyber bullying affects people?
Same kind of effects happens in cyber bullying as the case of physical bullying but the cyber bullying goes indefinitely and impacts mentally.
Effects of cyber bullying:
- Sleep can be affected.
- Increasing tensions and anxiety.
- Appetite disturbances.
- Inability to concentrate on studies.
- Many students can become fearful of the school environment.
Question: What are the challenges/concerns?
- Social stigma:
- Parents are proud that their children’s are on computer or mobile by thinking that their children’s are learning great knowledge. But that gives more room for exploration from children end which could lead toward pornography and other things.
- Many times parents don’t accept that their children are bullying the other child.
- The language and content of Web series: The certain shows running on amazon prime or Netflix are not appropriate for teenagers. Teenagers try to adapt that language used in the TV series or shows.
- Nuclear families and isolation of children: Most of the families in India are nuclear families and parents are going to their job regularly so the children’s get neglected and isolated. Therefore many are not able to identify what the child is going through.
- Law enforcing agencies: The problem is with the desk officers who do not even relate what the problem is. That is why most of the cybercrime cases get unnoticed. Not even 10% of cybercrime cases get registered.
Question: What are the government initiatives?
- Guidelines by NCERT: Because of lack of awareness about cyber bullying among the children’s, teachers as well as the parents, NCERT came up with three guideline booklets one for teachers one for school and one for students. For students it’s in the form of DO's & DON'Ts.
- For case reporting: Government of India is come up with ministry of home affairs Cybercrime reporting portal gov.in.
- For creating Awareness: For generating awareness in state of Delhi, Delhi police has come up with an initiative in which Police visits school administration to get aware of cyber bullying and also engage workshops for computer teachers.
Question: What should be done?
- Parental controls and checks:
- Setting up some guidelines or rules to control misuse of internet.
- Controlling browsing level and limiting the usage of WIFI etc.
- Net etiquettes: Child needs to tell what to watch and what not to watch.
- Parents itself need to restrict their abusive language.
- Children need to engage with real friends and real world instead in virtual things so that the proportion of being online gets balanced which will result in use of internet rather than misuse.
- Licencing like child licence and parents license can help restrict the content available for children.
- Knowledge sharing: Most of the people in the society don’t know about cyber bullying. So through seminars, advertisements and knowledge sharing platforms the awareness about it can be created.
- Use of Artificial intelligence:
- Tools can be developed which can analyse the behaviour of every internet user. So it can help prevent the user from falling into cyber bullying.
- Developing some mobile applications that can alert parents if the child is under threat of cyber bullying.
- Prevent malware attacks by tying up with antivirus agencies.
- Academic measures:
- The subjects related to cyber bullying and cyber security should be made mandatory instead of only guidelines.
- In school there should be cyber cell where one could report there grievances whether by its name or anonymously.
- Multipronged approach to handle cases: Need to handle the cases of cyber bullying through multipronged approach such as counselling through Psychiatrist, approaching police, etc.
- Use of Artificial intelligence:
Conclusion:
The cyber bullying is far more rampant and serious than we make out to be. The answer to online bullying and trolling is not to troll perpetrator because it will lead to vicious cycle. So we need to teach our children to stand up to bullying. But that does not mean flooding the wall of bullying with much more hate. It is the responsibility of society to report and prevent cyber bullying.
Practice Question: Cyber bullying is the major concern confronting children. What kind of cyber bullying is prevalent in the world? And what needs to be done to tackle the menace of cyber bullying?
More Articles