Social Schemes: Revision Test
Ekam Fest” to Promote Craftsmanship & Products of Divyang Artisans and Entrepreneurs
Context
The week-long Exhibition-cum-Fair “EKAM Fest” organized by National Handicapped Finance Development Corporation (NHFDC) under M/o Social Justice& Empowerment began.
About
- Fest is hosting several activities like cultural extravaganza including performances by Divyang artists and well-known professionals.
- It is an effort for promoting entrepreneurship and knowledge among Divyangjan community, generating awareness among society about potentialities of PwDs & providing a major marketing opportunity to PwDs entrepreneurs.
- NHFDC is making efforts for the development of a brand and platform for the marketing of products of these determined entrepreneurs.
- Accordingly, the name of the brand has arrived at Ekam (Entrepreneurship, Knowledge, Awareness, and Marketing).
- The word Ekam also represents the inclusiveness, oneness and unity which appropriately describe the efforts being put in by NHFDC to develop the marketing platform and aggregation of the products through the promotion of entrepreneurship, knowledge sharing, Awareness creation and marketing initiatives amongst the Divyangjan.
- It is an opportunity for all to encourage these products made with extraordinary determination by the divyang crafts persons and entrepreneurs.
- Since women have contributed a lot in the embroidery work, NHFDC should encourage Divyangjan, especially women Divyangjan for entrepreneurship in this sector so that Divyangjan may get employment and self-employment.
The new initiatives of NHFDC launched in Fest are as follows
- NHFDC Swavalamban Kendra (NSK): NHFDC has taken an initiative to establish PWD owned micro skill training Centers throughout the country for skill training of PwDs. These NSKs will have the capacity to provide quality skill training to around 120 PwDs per year NSK. The PwD owner of the NSK is expected to earn around Rs 20,000 per month.
- Safe Cabs in Delhi and Indore: NHFDC has arranged with Sakha Cabs where the PwD owned commercial vehicles will be driven by the Women drivers to provide safe taxi option for the women, children and senior citizen commuters. Such Safe cabs are already in operation at New Delhi and Indore Airport. The vehicles here are financed by NHFDC under its scheme.
- Safe Drinking Water E Carts: NHFDC has recently agreed to finance E-carts fitted with RO water dispensing vending machines. These carts will sell water in paper glasses maintaining hygiene. The carts will be supported in operation by Bharat Jal. The PwD owner is expected to earn Rs 10,000/- to Rs 15,000/- per month in the operation of these carts.
Madhya Pradesh radio-tags first-ever Indian Pangolin
Context
In order to know the species’ ecology and develop an effective conservation plan, the Madhya Pradesh forest department has radio-tagged an Indian Pangolin (Manis crassicaudata) for the first time.
About
About Pangolins:
- Pangolins are uniquely covered in tough, overlapping scales. These mammals eat ants and termites using an extraordinarily long, sticky tongue, and are able to quickly roll themselves up into a tight ball when they feel threatened.
- Commonly known as ‘scaly anteaters’, the toothless animals are unique, a result of millions of years of evolution.
- Pangolins evolved scales as a means of protection. When threatened by big carnivores like lions or tigers they usually curl into a ball.
- Species: There are eight species of pangolins:
- Asia:Four are found is Asia and they're listed by the IUCN as critically endangered.:
- Chinese
- Sunda
- Indian
- Philippine
- Africa:The four African species and they are listed as vulnerable:
- the ground pangolin
- giant pangolin
- white-bellied
- black-bellied
Pangolin habitat map in India:
- India is home to two species of pangolin. While the Chinese Pangolin (Manis pentadactyla) is found in northeastern India, the Indian Pangolin is distributed in other parts of the countrys as well as Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and Pakistan.
- Both these species are protected and are listed under the Schedule I Part I of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 and under Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES).
- However, despite protective measures, pangolins in India are widely exploited and traded both domestically and internationally.
Rapid decline in population:
- When threatened by big carnivores like lions or tigers they usually curl into a ball. The scales defend them against dental attacks from the predators.
- However, this unique protection mechanism has now become the main cause of the pangolin’s disappearance. The scales are in high demand in China, where they are used in traditional Chinese medicine.
- Pangolins are currently the most trafficked wildlife species in the world. Pangolin meat is also in high demand in China and southeast Asia.
- Consequently, pangolins have seen a rapid reduction in population globally. The projected population declines range from 50 per cent to 80 per cent across the genus.
- All species face declining populationsbecause of illegal trade. In 2016, the 186 countries party to the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES), the treaty that regulates the international wildlife trade, voted to ban the commercial trade in pangolins.
The plan:
- The radio-tagging is part of a joint project by the department and non-profit, the Wildlife Conservation Trust (WCT) that also involves the species’ monitoring apart from other activities.
- The measure comes as the world gets ready to observe the ninth ‘World Pangolin Day’ on February 15, 2020.
- It is an international attempt to raise awareness about pangolins and bring together various stakeholders to help protect them from extinction.
This new initiative of radio tagging will hopefully ensure better survival rates of Pangolins in the wild and for sure, it will have a positive impact on the population of this endangered species.
How wide is the gender gap in science?
Context
Between 1901 and 2019, 334 Nobel Prizes have been awarded to 616 Laureates in Physics, Chemistry and Medicine, of which just 20 have been won by 19 women.
About
- February 11 was the International Day of Women and Girls in Science, established by the United Nations to promote equal access to and participation in science for women and girls.
- While some of the greatest scientists and mathematicians have been women, they remain under-represented in comparison to their male counterparts in higher studies involving science, as well as among the top scientific achievers.
Researchers and achievers
- According to a 2018 fact sheet prepared by UNESCO on women in science, just 28.8% of researchers are women.
- It defines researchers as “professionals engaged in the conception or creation of new knowledge”. In India, this drops to 13.9%.
- Between 1901 and 2019, 334 Nobel Prizes have been awarded to 616 Laureates in Physics, Chemistry and Medicine, of which just 20 have been won by 19 women.
- The double Laureate is Marie Curie, one of just three women who have won in Physics and one of just five in Chemistry, while 12 women have won the Medicine Nobel.
- In 2019, the American mathematician Karen Uhlenbeck became the first woman to win the Abel Prize, following 16 male mathematicians.
- The Fields Medal so far has also been awarded to only one woman mathematician, the late Maryam Mirzakhani of Iran, as opposed to 59 men since 1936.
Women in science courses
- UNESCO data from 2014-16 show that only around 30% of female students select STEM (science, technology, engineering and mathematics)-related fields in higher education.
- Female enrolment is particularly low in information technology (3%), natural science, mathematics and statistics (5%) and engineering and allied streams (8%).
- In India, a 2016-17 NITI Aayog report compared female enrolment in various disciplines over five years, until 2015-16.
- In 2015-16, 9.3% of female students in undergraduate courses were enrolled in engineering, compared to 15.6% across genders. Conversely, 4.3% of female students were enrolled in medical science, compared to 3.3% across genders.
- Then, a master’s and doctoral levels, female enrolment remained lower than overall enrolment, and also fell behind for medical science in three of the five years.
- “This reflects that moving up from UG to a higher degree and research programmes, the restricted presence of women in higher studies and research in science becomes evident for a broader range of disciplines.
- Broadly, women showed a preference for arts; however, female enrolment in science streams rose from 2010-11 to 2015-16.
- The report found that in over 620 institutes and universities, including IITs, NITs, ISRO, and DRDO, the presence of women was 20.0% among Scientific and Administrative Staff, 28.7% among Post-Doctoral Fellows, and 33.5% among PhD scholars.
Why the gender gap?
- Girls excel at mathematics and science-oriented subjects in school, but boys often believe they can do better, which shapes their choices in higher studies.
- In 2015, an analysis of PISA scores by OECD found that the difference in maths scores between high-achieving boys and girls was the equivalent of about half a year at school.
- But when comparing boys and girls who reported similar levels of self-confidence and anxiety about mathematics, the gender gap in performance disappeared — when girls were more anxious, they tended to perform poorly.
- The NITI Aayog report said, “The problem of entry of women in science is not uniform across disciplines. Interventions geared to popularising subjects such as Engineering or the Physical sciences or Chemistry among female students at the school level in both urban and rural areas might be helpful in changing mind-set.”
Miscellaneous
Schemes
1. Scholarships under National Overseas Scholarship Scheme for Scheduled Tribe Candidates
The eligibility criteria and age limit prescribed under the Scheme of National Overseas Scholarship for Scheduled Tribe candidates are as under: -
Minimum Qualifications
- For Post Doctoral: 55% marks or equivalent grade in relevant Master’s Degree and Ph.D.
- Experience: 5 years - Research/Teaching/ Professional in the concerned field is desirable. Candidates with experience would be given preference.
- For Ph.D.: 55% marks or equivalent grade in relevant Master’s Degree.
- Experience: 2 years - Teaching/ Research/ Professional / M. Phil Degree in the concerned field is desirable. Candidates with experience would be given preference.
- For Masters’ Degree: 55% marks or equivalent grade in relevant Bachelor’s Degree.
Experience: 2 years’ work experience in the concerned field is desirable. Candidates with experience would be given preference.
Age Limit:Below 35 years, as on first day of July of the relevant year of the award.
The scheme provides financial assistance to ST students selected for pursuing higher studies abroad in certain subjects at the Masters level, and for Ph. D and Post-Doctoral research programmes. A list indicating subjects/ courses of study which will qualify for consideration for award of scholarship is at Annexure-I. The prescribed financial assistance shall be provided till completion of the course/ research or the following period, whichever is earlier: -
- Post-Doctoral Research - 1& 1/2 years (One and a half year)
- Ph.D. - 4 years (four years)
- Master’s Degree -1/2/3 years (One/Two/three years) depending upon the duration of the Course.
The extension of stay beyond prescribed period for levels of courses as mentioned above, may be considered without financial assistance of any kind except the air passage to return to India, if and only if recommendation of the competent concerned authority in the educational institution/ university as well as the Indian Mission abroad is received certifying that such an overstay for a specified period, is absolutely essential for facilitating the candidate to complete the course. The final decision in this regard will, however, rest with the Government of India alone.
2. Strengthening Education among ST Girls in Low Literacy Districts
Objective
- The scheme aims to bridge the gap in literacy levels between the general female population and tribal women, through facilitating 100% enrolment of tribal girls in the identified Districts or Blocks, more particularly in naxal affected areas and in areas inhabited by Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs), and reducing drop-outs at the elementary level by creating the required ambience for education. Improvement of the literacy rate of tribal girls is essential to enable them to participate effectively in and benefit from, socio-economic development.
Coverage
- The scheme will be implemented in 54 identified Districts where the ST population is 25% or more, and ST female literacy rate below 35%, or its fractions, as per 2001 census.
- Any other tribal block in a district, other than aforesaid 54 identified districts, which has scheduled tribe population 25% or above, and tribal female literacy rate below 35% or its fractions, as per 2001 census, shall also be covered ( Blocks intimated by West Bengal and Karnataka so far. Such Blocks fulfilling the criteria in other States may also be considered as and when reported).
- In addition, the scheme will also cover areas below a Block level (e.g. Gram Panchayats) inhabited by the notified Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs).
- Out of all the aforesaid areas, the naxal affected areas shall be given priority
Implementing Agency
- The scheme will be implemented through Voluntary Organizations (VOs)/Non- Governmental Organizations (NGOs) and autonomous society/institutions of State Government/Union Territory Administration.
- The existing multidisciplinary “State Committee for Supporting Voluntary Efforts” (SCSVE) constituted by various States/Union Territories will be responsible for identification and scrutiny of the projects of Non-Governmental Organizations under this scheme also.
Eligibility of the Organizations
Organizations including autonomous society/institutions of State Government/Union Territory Administration shall maintain women project staff for the projects run under this scheme.
Voluntary Organization (VO)/Non-Government Organizations (NGOs) have to fulfill the following requirements (through certificates from the District or Panchayati Raj administration):
- Registered for at least three years for the conduct and promotion of social welfare of scheduled tribes.
- Experience of at least three years in successfully running and maintaining hostels and/or educational complexes.
- Financial viability to continue the work for limited periods in the case of delay or absence of assistance from the Ministry.
- Good reputation and credentials, especially for guaranteeing the security and safety of the hostellers.
- Networking with other institutions including Panchayati Raj for optimum utilization of resources allocated and assets created.
3. Development of primitive tribal groups (PTGS)
Objective
- There are certain tribal communities who are having low level of literacy, declining or stagnant population, and pre-agricultural level of technology and economically backward. 75 such groups in 15 States/UTs have been identified and have been categorized as Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs).
- State/UT-wise list of PTGs is at Annexure I. each of these groups is small in number, differentially developed with respect to one another, of remote habitat with poor administrative and infrastructure back up. Therefore, they are in need of priority to be accorded for their protection and development.
- Their problems and needs are quite different from other Scheduled Tribes. Since Primitive Tribal Groups constitute the most vulnerable among tribal groups, States/UTs have been requested to allocate requisite funds from Central Sector/Centrally Sponsored and State Plan schemes for their socio-economic development.
- However, there are items/activities, which though very crucial for the survival, protection and development of PTGs, are not specifically catered to by any existing scheme, the funds under this scheme would be used for these activities.
Scope
- The funds under the Central Sector Scheme for the development of Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs) would be available only for those items/activities which though very crucial for the survival, protection and development of Primitive Tribal Groups (PTGs), are not specifically catered to by any existing schemes, State or Central or by Guidelines governing the utilization of funds under Special Central Assistance to Tribal Sub-Plan and Article 275(1) of the Constitution.
- Such items/activities cannot be exhaustively identified at the Central level as they may differ from State to State and within a State from project to project.
- However, funds under the scheme could be used for helping the beneficiaries of the project to cope with extremely adverse pressures which threaten their survival and protect them against various forms of exploitation and thereby bringing them to a stage when they can demand and receive specific assets and services.
- The activities under the scheme may include measures such as awareness generation and confidence building, training for skill development of tribal youth organizations of self-help groups and provision of services/inputs not covered by any existing scheme. In terms of beneficiaries the scheme will cover only members of PTGs.
Implementing Agency
- The scheme will be implemented through Integrated Tribal development Projects (ITDPs)/Integrated Tribal Development Agencies (ITDAs), Tribal Research Institutes (TRIs) and Non-Governmental Organizations having capability and willingness.
- The State Government concerned will be responsible for proper execution, implementation, supervision and coordination of the scheme including selecting of NGOs.
- The ITDPs/ITDAs and TRIs should send their proposal in the prescribed Performa at Annexure II.
- The NGOs should submit their proposal in Performa II with recommendation of the State Govt./UT Admin as per Annexure IV and Annexure V.
Pattern of Funding
- It is Central Sector Scheme; therefore, financial assistance will be available on 100% basis. The optimum period for grant-in-aid to the implementing agencies will be for a period of 3 years.
Initiatives for the North East
4. Ishan Uday
- Special Scholarship Scheme for students of North East Region.
- The UGC has launched a special scholarship Scheme for students of North East Region from the academic session 2014-15.
- The Scheme envisages grant of 10,000 scholarships to students from North East Region whose parental income is below Rs. 4.5 lakh per annum and would be provided scholarship ranging from Rs. 3,500 to 5,000 per month for studying at under graduate level in Colleges/Universities of the country.
5. Ish?n Vik?s
- Ish?n Vik?s is a comprehensive plan to bring selected students from the school and college levels from the North-Eastern states into close contact with the IITs, NITs and IISERs during their vacation periods.
- A typical visit is envisaged for a period of ten days to one of these institutions, in the form of either an exposure or an Internship programme.
- Each school will send one teacher to accompany a group of about 32 students of class IX and X and 8 teachers.
- The college students would be organised in two groups in summer and in winter, consisting of 32 students each group.
- About 2016 college students and 504 teachers from N-E will be visiting premier Institutes, like IIT/NIT/ IISERs in an academic year. Or Centrally Funded Technological Institutes) with Stipends and Travel will be taken up. From 25 Institutions, about 250 students will be visiting 16 IITs and 6 NITs (to start with six NITs are being considered) per year.
ClearSpace-1 Mission

RISAT-2BR1

NAVIC as Allied System of US

Gold-Coated Fungi

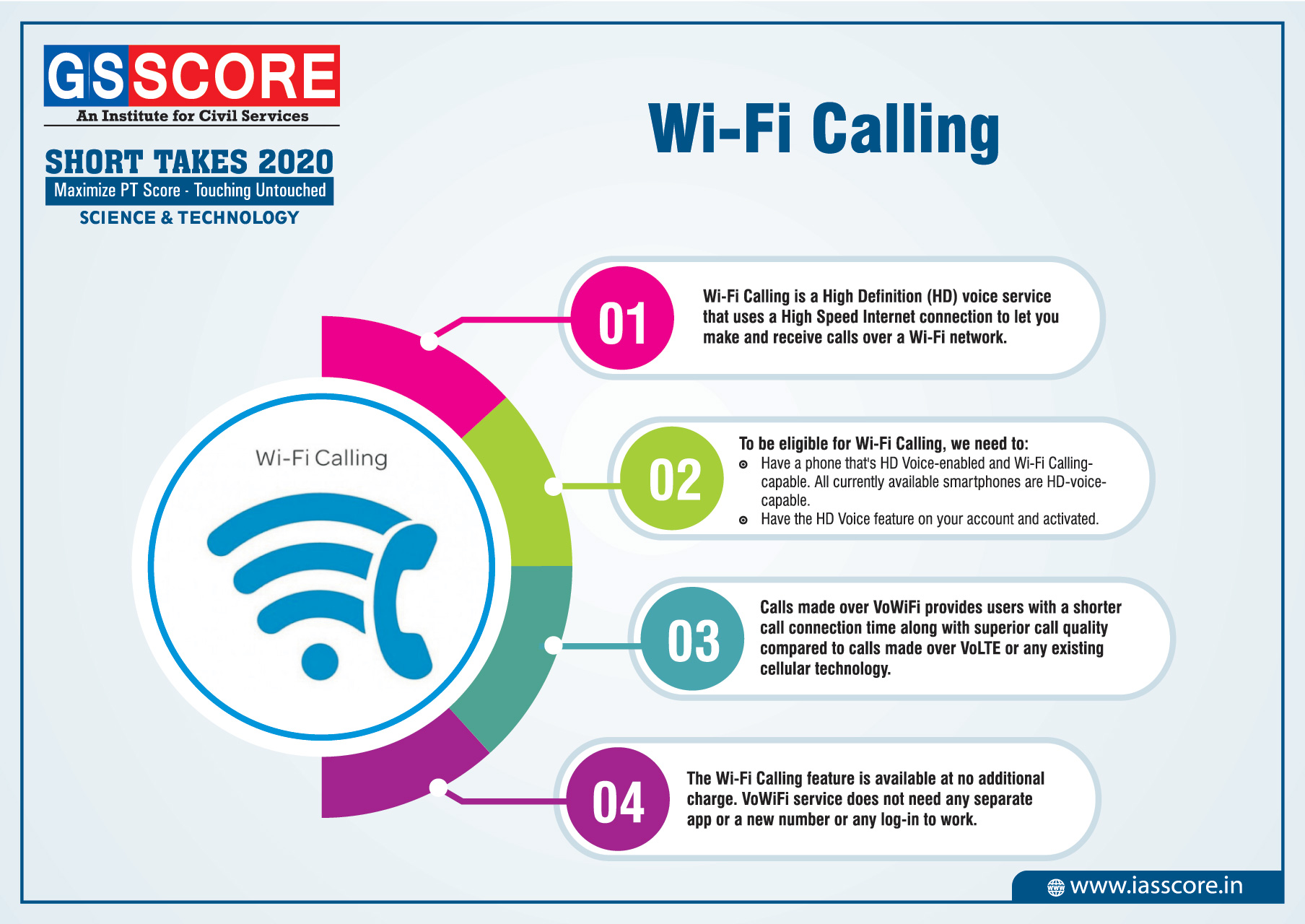
Wi-Fi Calling