

2nd May 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) researchers has developed a portable desalination unit that can remove particles and salts to generate drinking water.
Background
About Portable Device:
- The suitcase-sized device requires less power to operate than a cell phone charger.
- It can also be driven by a small, portable solar panel.
- The device automatically generates drinking water that exceeds World Health Organization (WHO) quality standards.
- While other portable desalination units that require water to pass through filters, this device utilises electrical power to remove particles from drinking water.
- Eliminating the need for replacement filters greatly reduces the long-term maintenance requirements.
- This could enable the unit to be deployed in remote and severely resource-limited areas.
- It could also be used to aid refugees fleeing natural disasters or by soldiers carrying out long-term military operations.
How does it work?
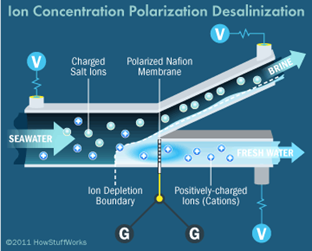
- The unit relies on a technique called ion concentration polarisation, which was pioneered by Han’s group more than 10 years ago.
- Rather than filtering water, the process applies an electrical field that causes positively or negatively charged particles — including salt molecules, bacteria, viruses — to be repelled as they flow past.
- The charged particles are funnelled into a second stream of water that is eventually discharged.
- The process removes solids, allowing clean water to pass through the channel.
About Desalination:
- Desalination is any process that removes excess salts and other minerals from water.
- In most desalination processes, feed water is treated and two streams of water are produced:
- Treated fresh water that has low concentrations of salts and minerals
- Concentrate or brine, which has salt and mineral concentrations higher than that of the feed water
- The feed water for desalination processes can be seawater or brackish water.
- Brackish water contains more salt than does fresh water and less than salt water.
- It is commonly found in estuaries, which are the lower courses of rivers where they meet the sea, and aquifers, which are stores of water underground.
Desalination technologies:
Two distillation technologies are used primarily around the world for desalination: thermal distillation and membrane distillation.
- Thermal distillation technologies are widely used in the Middle East, primarily because the region’s petroleum reserves keep energy costs low.
- The three major, large-scale thermal processes are multistage flash distillation (MSF), multi-effect distillation (MED), and vapor compression distillation (VCD).
- Another thermal method, solar distillation, is typically used for very small production rates.
- Membrane distillation technologies are primarily used in the United States.
- These systems treat the feed water by using a pressure gradient to force feed the water through membranes.
- The three major membrane processes are electrodialysis (ED), electrodialysis reversal (EDR), and reverse osmosis (RO).
More Articles


