

21st November 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
A Report by the Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) to mark World Antimicrobial Awareness Week (WAAW) mentioned that Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a ‘silent pandemic’ and is a global public health threat.
|
World Antimicrobial Awareness Week (WAAW):
|
Key Points:
- The report has highlighted concern over the increasing use of antibiotics and infectious diseases are becoming difficult to treat.
- According to a study, some 4.95 million deaths were associated with, and 1.95 million deaths were directly attributable to bacterial AMR worldwide in 2019.
- Apart from health, AMR is also likely to heavily impact livelihood and economies.
- Waste from farms, factories, community, and healthcare settings contributes to the emergence and spread of AMR through environmental routes.
- Prevention implies the adoption of strategies and approaches that can reduce the need for antimicrobials.
- For example, in the human health sector, better sanitation, access to clean water, and appropriate hand hygiene can reduce the chances of infection and the need for antimicrobials.
- The Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) is also going to promote Ethnoveterinary medicine (EVM) for treating animals.
|
Ethnoveterinary medicine (EVM) involves the use of traditional/herbal preparations in treating diseases of cattle |
What is Antimicrobial Resistance?
- Antimicrobial Resistance is the resistance acquired by any microorganism (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites, etc.) against antimicrobial drugs that are used to treat infections.
- It occurs when a microorganism changes over time and no longer responds to medicines making infections harder to treat and increasing the risk of disease spread, severe illness, and death.
- The World Health Organisation (WHO) has identified AMR as one of the top ten threats to global health.
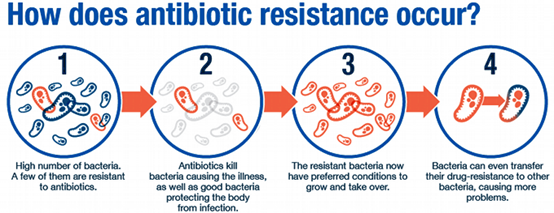
Factors Responsible:
- Antibiotic consumption in humans
- Access to antibiotics without prescription.
- Lack of knowledge about when to use antibiotics.
- Steroidal injection into Animals
- Anti-microbial drugs for animals
- Untreated disposal of sewage water bodies
Threats:
- Life-threatening Condition: The growth of AMR has proved to be a major challenge in the treatment of sepsis, which is a life-threatening condition, and, unfortunately, the failure of antibiotics is leading to deaths that are preventable.
- Reduction in Medical Advances: AMR is also undermining and undoing medical advances over decades, especially for high-burden diseases like tuberculosis and various cancers.
- Achievements of Goals: It is putting the gains of the Millennium Development Goals at risk and endangers the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals.
- Increase in Superbugs: Untreated wastewater from medical facilities is awash with chemical compounds that promote Superbugs.
- Expanding with Time: The concoction of self-medication and over-the-counter (OTC) antibiotic availability has led to one of the highest rates of antibiotic resistance in the world.
Recent Government Initiatives:
- National Programme on AMR containment: Launched in 2012. Under this programme, AMR Surveillance Network has been strengthened by establishing labs in State Medical College.
- National Action Plan on AMR: It focuses on the One Health approach and was launched in April 2017 with the aim of involving various stakeholder ministries/departments.
- AMR Surveillance and Research Network (AMRSN): It was launched in 2013, to generate evidence and capture trends and patterns of drug-resistant infections in the country.
- AMR Research & International Collaboration: Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has taken initiatives to develop new drugs /medicines through international collaborations in order to strengthen medical research in AMR.
- Antibiotic Stewardship Program: ICMR has initiated an Antibiotic Stewardship Program (AMSP) on a pilot project across India to control the misuse and overuse of antibiotics in hospital wards and ICUs.
- DCGI had banned 40 Fixed Dose Combinations (FDCs) which were found inappropriate.
Way forward:
- Addressing AMR requires a multipronged and multisectoral approach. The urgency to develop new drugs should not discourage us from instituting measures to use the existing antimicrobials judiciously.
- One Health Approach: AMR has the potential to return the world to a pre-antibiotic era when medicines could not treat even simple infections.
- Therefore, to contain AMR, there is a need for a One Health Approach through coherent, integrated, multi-sectoral cooperation and actions, as human, animal, and environmental health are integrated.


