2nd April 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
The government recently introduced the ‘Antarctica Bill’ in the Lok Sabha that envisages regulating visits and activities to Antarctica as well potential disputes that may arise among those present on the continent.
About
Indian Antarctic Bill, 2022
Aims and objectives:
- To provide for national measures to protect the Antarctic environment and associated ecosystems and to give effect to the Antarctic Treaty
- To provide a harmonious policy framework for India’s Antarctic activities through a well-established legal mechanism
- Facilitate activities of the Indian Antarctic programme, including management of Antarctic tourism and sustainable development of fisheries
- To prohibit Indian expedition to Antarctica or carrying of certain activities in Antarctica without a permit or the written authorisation of another party to the protocol
- To provide for inspection in India by an officer designated by the Central government as an Inspector and to constitute an inspection team to carry out inspections in Antarctica.
Need for the Antarctic Legislation
- The growing presence of Indian scientists in Antarctica and the commitment to Antarctic research and protection prompted the government to adopt domestic legislation consistent with its obligations as a member of the Antarctic Treaty system.
- These laws will enable India’s courts to deal with disputes or crimes committed in parts of Antarctica, and help build credibility vis-à-vis India’s participation.
India and Antarctica:
- India is a signatory of the Antarctic Treaty, the Convention on the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources and the Protocol on Environmental Protection.
- India took its first expedition to Antarctica in 1982.
- The country maintains two research stations on Antarctica – Maitri (since 1989) at Schirmacher Hills and Bharati (2012) at Larsemann Hills – and has launched 41 expeditions to the continent thus far.
|
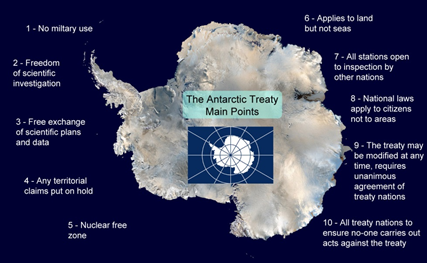
About Antarctic Treaty:
|