10th May 2024 (15 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
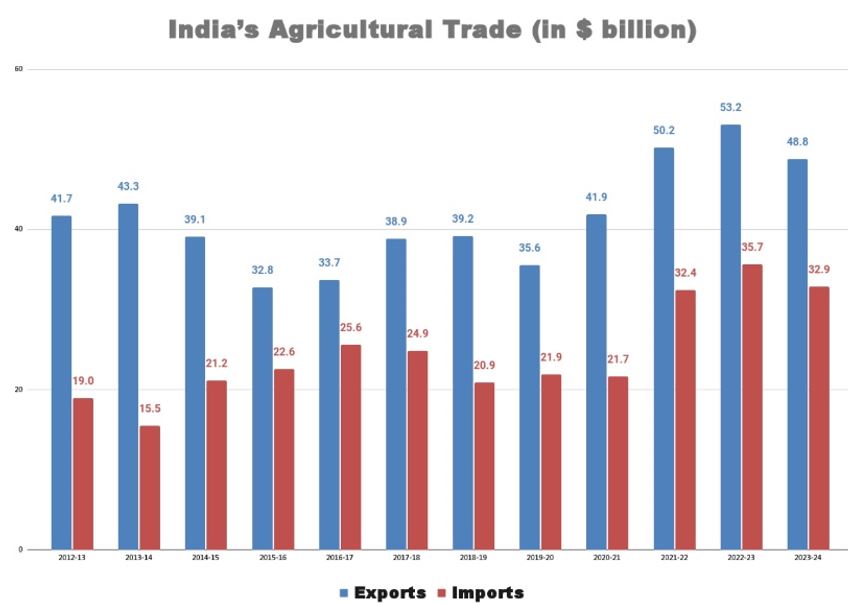
India's agricultural exports experienced an 8.2% decline, primarily due to restrictions on various commodities such as cereals, sugar, and onions. The total value of agricultural exports stood at USD 48.82 billion, a decrease from the record high of USD 53.15 billion in the previous fiscal year.
Factors Impacting Exports
- The decline in exports was led by sugar and non-basmati rice. Restrictions on sugar exports resulted in a significant drop in its export value, while a ban on non-basmati rice exports contributed to the overall decline in this segment.
- Wheat and onion exports were also affected by export restrictions imposed due to domestic shortages and rising prices.
- Discrepancy between government's objectives (promoting crop diversification) and its policies on import tariffs. While import duties on most pulses have been eliminated, promoting their cultivation, the low tariffs on certain imported items contradict the goal of reducing dependence on imports for items like pulses and edible oils.
Export Drivers and Import Trends
- Exports: Despite the overall decline, certain agricultural export items such as basmati rice and spices experienced growth. However, exports of oil meals, and raw cotton remained below their previous records.
- Imports: On the import side, the decrease in overall agricultural imports in 2023-24 was mainly due to a reduction in edible oil imports. Lower global prices led to a decrease in the import bill for vegetable oils. However, imports of pulses nearly doubled, reaching the highest levels since 2015-16.
Policy Implications
- There needs urgent recognition of importance of policy stability and predictability for farmers and agri-traders.
- Policies favoring consumers over producers, such as sudden export bans or restrictions, can have significant negative impacts on agricultural producers.
- A more predictable and rules-based policy approach, such as temporary tariffs instead of outright bans, is recommended.
- There is a need for a more rational export-import policy that balances the interests of producers and consumers, as well as short- and long-term goals for the agricultural sector. This may involve revisiting export and import restrictions and tariffs to ensure a more sustainable and equitable agricultural trade environment.
Fact Box:Agriculture in India
Schemes promoting Agricultural Export
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The Cook Islands is leading an effort to mine minerals from the ocean floor, particularly those used in electric car batteries.
About Cook Islands:
- The Cook Islands, consisting of 15 islands, became self-governing in 1965 after being a colony of New Zealand.
- Despite not being fully independent, the country began attracting international research vessels to explore its territorial waters, which span about 756,000 square miles, similar in size to Mexico.
- Researchers discovered the seabed in the Cook Islands covered with nodules, similar in size to avocados, containing cobalt and manganese. Each nodule grows as thick as a credit card approximately every million years. Until recently, technological limitations prevented the extraction of these rocks.


Prelims Articles
Context
The Batagay megaslump — a 3,250-foot-wide (990 meters) is "actively growing" by a massive amount every year, as per recent findings.
Characteristics of the Megaslump:
- Batagay megaslump, the world’s biggest permafrost crater, is located in the Russian Far East.
- It is a retrogressive thaw slump. Retrogressive thaw slumps belong to a class of terrain types called thermokarst that occur in areas underlain by permafrost.
- It was first observed on satellite images in 1991 after a section of hillside collapsed in the Yana Uplands of northern Yakutia, Russia.
- The collapse exposed layers of permafrost within the remaining hillside, which contains some of the oldest permafrost in Siberia and the world, dating back up to 650,000 years.
- From 1991 to 2018, the area increased by almost three times.
Fact Box: About Permafrost
|


Prelims Articles
Context
India has contributed $500,000 to the U.N. Counter-Terrorism Trust Fund, demonstrating its steadfast commitment to supporting global efforts in combating terrorism.
About United Nations Office of Counter-Terrorism (UNOCT):
- UNOCT was established in 2017 to address the growing threat of terrorism on a global scale.
- Functions of the Office of Counter-Terrorism:
- UNOCT provides leadership on counter-terrorism mandates entrusted to the Secretary-General by the General Assembly.
- It enhances coordination and coherence among the 38 Counter-Terrorism Implementation Task Force entities to ensure balanced implementation of the UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy's four pillars.
- The office strengthens the delivery of United Nations counter-terrorism capacity-building assistance to Member States.
- UNOCT improves visibility, advocacy, and resource mobilization for United Nations counter-terrorism efforts.
- It ensures due priority is given to counterterrorism across the United Nations system, with a focus on preventing violent extremism rooted in the Strategy.


Prelims Articles
Context
A new variant of COVID-19, called FLiRT, has become the dominant strain in the United States. FLiRT is a subtype of the Omicron JN.1 lineage and is characterized by two mutations, KP.2 and KP 1.1.
Key Points:
- FLiRT variant consists of two mutations, KP 1.1 and KP.2, both of which are spreading rapidly.
- It is characterized by various symptoms, and its rapid spread requires continued monitoring and appropriate public health measures.
- Symptoms: Sore throat, Cough, Fatigue, Nasal congestion, Runny nose, Headache, Muscle aches, Fever, Gastric issues


Prelims Articles
Context
A British toddler has had her hearing restored through a pioneering gene therapy trial, marking a significant development in treating deafness.
About DB-OTO Gene Therapy:
- The gene therapy, known as DB-OTO, targets children with OTOF mutations, a specific genetic cause of deafness.
- A harmless virus is used to deliver a functional copy of the OTOF gene into the patient's cells.
- Mechanism of Action:
- Auditory neuropathy, caused by a faulty OTOF gene, disrupts the production of otoferlin, a protein vital for ear cell communication with the hearing nerve.
- The DB-OTO therapy replaces the faulty DNA with a functional copy of the OTOF gene, allowing cells in the ear to produce otoferlin and restore hearing function.
- Innovative Approach: Developed by biotech firm Regeneron, this pioneering gene therapy delivers the working gene directly to the ear through an infusion.
About Gene Therapy
|
PYQQ . Consider the following statements : (2020)
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Solution: (d) |


Prelims Articles
Context
China's newest aircraft carrier, Fujian, recently completed its maiden sea trial after six years of construction.
Specifications:
- The Fujian, officially classified as a Type 003, was launched in 2022.
- It has a displacement of nearly 80,000 metric tons, making it bigger than China's two active carriers, Shandong and Liaoning.
- Unlike Shandong and Liaoning which rely on less advanced ski jump-style short take-off, barrier-arrested recovery (STOBAR) systems, Fujian is equipped with a Catapult Assisted Take-Off Barrier Arrested Recovery (CATOBAR) system for launching aircraft.
- Aircraft and Equipment: Fujian is expected to host Shenyang J-15 fighters, J-35s, JL-10 trainer jets, and Xian KJ-600 fixed-wing AEWC aircraft. It features an advanced deck coating.
- Despite its technological advancements, Fujian, is still conventionally powered rather than nuclear propulsion
Comparison:
- US Navy: Fujian is the first Chinese aircraft carrier equipped with CATOBAR, similar to systems used by the US Navy. Currently, only the US Navy operates aircraft carriers larger than 80,000 metric tons. Fujian's catapults are powered by an electromagnetic system similar to the U.S. Navy's Gerald R. Ford-class carriers.
- Indian Navy's Aircraft Carriers: The Indian Navy operates two aircraft carriers, INS Vikramaditya and INS Vikrant, which use the STOBAR system. China's Navy has become the largest with 355 warships and submarines, while India's total fleet strength is 130 vessels.


Prelims Articles
Context
Scientists have discovered a super-Earth in a nearby solar system, fulfilling the quest for rocky planets with an atmosphere conducive to life.
Characteristics of 55 Cancri e:
- Named 55 Cancri e, the super-Earth is twice as big as Earth and surrounded by a thick atmosphere.
- It is one of the few rocky planets outside solar system with a significant atmosphere, consisting mainly of carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide.
- It orbits its star, Copernicus, at a close distance, completing an orbit every 18 hours or so.
- Located 41 light years away from Earth, 55 Cancri e circles its star so closely that it experiences permanent day and night sides.
- A light-year is nearly six trillion miles (9.7 trillion kilometers), emphasizing the vast distance between Earth and the exoplanet.
- Comparison with Earth:
- Composition: While Earth's atmosphere comprises nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and other gases, the exact composition of 55 Cancri e's atmosphere remains unclear. The planet's atmosphere is likely rich in carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide, with possible traces of other gases like water vapor and sulfur dioxide.
- Size and Orbit: 55 Cancri e is eight times heavier and twice as big as Earth, making it a "super-Earth" larger than our planet but smaller than Neptune.


Prelims Articles
Context
Following the suspected deaths of a woman and two cattle after consuming Nerium Oleander flowers and leaves, the Travancore Devaswom Board has decided to exclude the flower from prasadas given to devotees.
Description of Oleander Plant:
- Oleander, known as 'Arali' in Malayalam, is an evergreen shrub that can grow 18-20 feet tall and produces fragrant blooms.
- Despite its deadly seeds and other parts, oleander flowers are commonly used in poojas due to their significance.
- Oleander, also known as "the desert rose," has a rich history dating back to ancient Mesopotamians, who believed in its healing benefits and used it as a remedy for hangovers.
- Romans and Arabs also utilized oleander for various health issues.
- Toxicity of Oleander:
- All parts of the oleander plant, including flowers, leaves, stem, and roots, contain toxic compounds called cardiac glycosides.
- Ingesting oleander can lead to severe health issues such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, irregular heart rhythm, and even death in severe cases.
- Medical Uses and Potential Benefits:
- Oleander contains oleandrin and nerioside, which have effects similar to digitalis, a medication used to treat heart conditions. Some studies suggest oleander extracts may have anti-cancer properties and be effective against asthma, epilepsy, malaria, and other ailments.


Prelims Articles
Context
Scientists at MIT are using machine learning to study sperm whale communication. Their study focused on whale vocalizations known as codas, short bursts of clicks similar to Morse Code.
Discoveries:
- Past research identified about 150 codas, but recent study reveals a complex language structure.
- After analyzing nearly 9,000 codas from Eastern Caribbean whales, researchers discovered a "sperm whale phonetic alphabet" where clicks form words with different meanings based on rhythm and tempo.
|
Fact Box: About Sperm Whale
|


Prelims Articles
Context
India's export landscape has witnessed notable developments, despite global economic uncertainties.
Export Destinations and Performance
- India exported to 115 countries out of 238 destinations in 2023-24, encompassing key markets like the US, UAE, China, and UK.
- Merchandise exports slightly declined to USD 437.1 billion, while services exports rose to USD 341.1 billion in 2023-24. India's share in world merchandise exports increased from 1.70% in 2014 to 1.82% in 2023 and rank in world merchandise exporters improved from 19th to 17th during the same period.
- Overall exports reached USD 778.2 billion in 2023-24, with a marginal growth of 0.23% compared to the previous year.
- Commodity-wise Performance: 17 items saw increased exports in 2023-24, constituting 48.4% of India's export basket. Notable decline in petroleum products (-13.66%) and gems and jewellery (-13.83%).
- Key Export Destinations: UAE emerged as the primary destination with a 12.71% growth, followed by Singapore, UK, and China. Significant growth rates were observed in countries like Russia, Romania, and Albania, indicating new market exploration.
- Regional Export Growth
- Exports to CIS, Oceania, and Europe witnessed expansion in 2023-24.
- Key export drivers in CIS region: Russia, Uzbekistan, Ukraine, Armenia, and Tajikistan.
- Major export growth in Oceania: Australia, Timor Leste, Samoa, Vanuatu, and Solomon Island.
- Notable export growth in Europe: UK, Romania, Albania, Netherland, and Greece.
Import Trends
- Imports declined from 124 countries in 2023-24.
- Top 10 source countries for imports include China, USA, Saudi Arabia, Indonesia, Russia, and Switzerland.
- Decline in imports from countries like UAE, Qatar, Kuwait, and Oman indicates the need for bolstering trade relations.


Prelims Articles
|
S.No. |
Term |
About |
|
1. |
Blue Corner Notice |
A Blue Corner Notice is issued to “collect additional information about a person’s identity, location or activities in relation to a criminal investigation”. The notice is sent to all countries via Interpol asking to identify and locate. |
|
2. |
Crater |
A crater is a bowl-shaped depression, or hollowed-out area, produced by the impact of a meteorite, volcanic activity, or an explosion. |
|
3. |
Genetic disorder |
A genetic disorder is a disease caused in whole or in part by a change in the DNA sequence away from the normal sequence. |
|
4. |
Rocky planet |
Rocky planet is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate, rocks or metals. Example: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. |


Editorials
Context
The global fight for women's rights has once again taken center stage, showcasing the resilience and determination of women worldwide. Despite facing repression and regression, women's movements continue to gain momentum, fueled by courageous activists like Manahel al-Otaibi in Saudi Arabia.
Global Women's Movements and Challenges:
- Activism and Solidarity: Despite repression, women's movements worldwide are gaining momentum, exemplified by the activism of individuals like Manahel al-Otaibi in Saudi Arabia and the solidarity shown by Iranian and Afghan women. Movements such as #MeToo and protests against gender-based violence in Chile underscore the global nature of the struggle for women's rights.
- Patriarchal Challenges: The narrative also addresses patriarchal obstacles, evident in instances like the rise of Harvey Weinstein and the political ascent of individuals like Brij Bhushan Singh in India, reflecting systemic challenges to women's empowerment and leadership.
- Empowerment and Leadership: The concept of "women's empowerment" is critiqued as a token gesture, emphasizing the need for women to strategically navigate within existing systems, especially in workplaces where sexual harassment remains a pervasive issue. The lack of women in leadership positions and the persistent gender disparities underscore the need for structural changes to achieve genuine gender equality.
Gender Disparities and Structural Changes:
- Gender Disparities in Leadership: Reports from UN Women highlight significant gender disparities in decision-making roles, labor force participation, and legal rights globally, underscoring the systemic barriers faced by women.
- Challenges Beyond Gender Divide: The narrative extends beyond gender disparities to address the broader battle of challenging normative behaviors and reversing societal norms, emphasizing the collective pushback needed from women to effect meaningful change.
- Call for Structural Reforms: To address these challenges, there's a call for structural reforms, including punitive measures against perpetrators of sexual harassment and greater representation of women in leadership roles, to ensure genuine progress towards gender equality.
Mains Question:
Discuss the challenges faced by women, and the need for structural reforms to achieve genuine gender equality.


Editorials
Context
A recent incident involving hackers using generative AI to extort money by impersonating kidnappers has raised concerns about the detrimental impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on cybersecurity, leading to discussions in the U.S. Senate and alarm regarding the erosion of human perception of reality in the face of AI-generated content.
Cybersecurity Challenges Posed by Generative AI:
- Rising Cyber Threats: The integration of generative AI into various sectors has led to a surge in cyberattacks, with phishing incidents and credential phishing witnessing exponential increases since 2022, highlighting the growing sophistication of cyber threats.
- Emergence of Novel Avenues for Attacks: Sophisticated cyber threats facilitated by generative AI include cognitive behavioral manipulation, endangering privacy and security through voice-activated devices, and real-time biometric identification systems posing threats to privacy.
- Challenges Faced by Organizations: Organizations are facing challenges such as undetectable phishing attacks, increased attack volumes, and growing privacy concerns due to the manipulation of generative AI, necessitating robust cybersecurity initiatives.
Global Collaborative Efforts and Institutional Responses:
- Bletchley Declaration: World leaders have initiated collaborative efforts to address the misuse of generative AI, as evidenced by the signing of the Bletchley Declaration at the AI Safety Summit by countries including China, the European Union, and the United States, aiming to understand and mitigate potential harms caused by advanced AI technologies.
- Policy-Led Initiatives: Stern policy-led efforts are crucial at the institutional level to combat cybercrimes facilitated by generative AI, including the development of frameworks for identifying AI-generated content and implementing realistic regulations with public feedback.
- Corporate Digital Awareness: Corporations need to prioritize digital awareness through media and literacy training sessions to enhance digital fluency among employees, enabling them to navigate the digital landscape effectively and identify credible sources.
Mains Question:
Discuss the rising concerns regarding the detrimental impact of generative artificial intelligence on cybersecurity.


Editorials
Context
Debate surrounding India's economic growth trajectory has garnered attention due to conflicting perspectives on the efficacy of current policies in sustaining growth post-pandemic.
Support for Current Policies:
- Continued Growth Trends: Robust growth, contained inflation, and poverty reduction post-pandemic.
- Revision of Growth Figures: Upward revisions contradict critics' claims, suggesting policy effectiveness.
- Countering Arguments: Challenges to current policies, like inflation measurement concerns, are rebutted by sustained growth and macroeconomic indicators.
Criticism and Skepticism:
- Questioning GDP Data: Critics raise doubts about data reliability, highlighting discrepancies between production-side and expenditure-side measurements.
- Fluctuating Growth Rates: Quarterly growth fluctuations attributed to seasonal and base effects, fostering skepticism about growth sustainability.
- Data Validity Challenges: Challenges to data validity, such as "smell tests" and selective evidence highlighting, fuel ongoing debates over growth measurement accuracy.
Policy Implications and Future Outlook:
- Concerns about Household Savings: Critiques point to challenges in household savings, investment, and current account deficits, calling for policy adjustments.
- Emphasis on Sustainable Growth: Proponents highlight healthy investment and credit-led growth supported by a robust financial sector and sustainable private capex.
- Importance of Policy Continuity: Need for balanced economic reforms and policy continuity stressed for long-term growth and development.
Mains Question:
Examine the complexities surrounding India's economic growth narrative, considering the interplay between policy effectiveness, data reliability, and the sustainability of growth trends.