

13th September 2025 (11 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context:
Prime Minister inaugurated the ?8,000 crore Bairabi–Sairang railway line in Mizoram, connecting Aizawl to the national rail network for the first time, alongside several infrastructure projects across Northeast India.
From Frontier to Front-Runner: Northeast’s Transformation under Act East Policy
Historical Neglect vs. Contemporary Focus
- Earlier Status: The Northeast was long treated as a peripheral “frontier region” with weak connectivity and limited integration with the national economy.
- Shift in Approach: Post-2014, with the Act East Policy, the region is seen as central to India’s growth, connectivity, and strategic positioning.
Major Infrastructure Push
- Railways
- Railway budget for NE since 2014: ?62,477 crore, including ?10,440 crore in 2025–26.
- Bairabi–Sairang railway line: ?8,000 crore, 51 km, 143 bridges, 45 tunnels – engineering milestone, connects Aizawl to national rail grid.
- Ongoing projects worth ?77,000 crore (Jiribam–Imphal, Dimapur–Kohima).
- Highways and Roads
- 16,207 km of National Highways constructed till July 2025.
- PMGSY: 16,469 road works covering 80,933 km and 2,108 bridges completed.
- New road projects under NESIDS and PM-DevINE (e.g., Aizawl Bypass, Chhimtuipui River Bridge).
- Air Connectivity
- UDAN Scheme operational in NE – linking underserved airports and heliports.
- Digital Infrastructure
- BharatNet& Digital Bharat Nidhi initiatives improving Gram Panchayat-level internet access.
- Mobile towers established across remote districts.
Development Schemes and Investments
- PM-DevINE (?6,600 crore, 2022–26)
- Focus: Convergent infrastructure, social development, youth & women livelihood opportunities.
- North East Special Infrastructure Development Scheme (NESIDS)
- Roads: Gap funding for strategic and market-access roads.
- Others: Covers healthcare, education, power, water, waste management, industrial development.
- North Eastern Council (NEC) Schemes
- Promotes bamboo, piggery, tourism, higher education, healthcare, livelihood generation.
- Special Development Packages (2025)
- ?4,250 crore outlay (?4,000 crore for Assam, ?250 crore for Tripura).
- Rising Northeast Investors Summit 2025
- ?4.48 lakh crore investment interest in energy, agro-processing, textiles, healthcare, IT, logistics.
Strategic & Geopolitical Dimensions
- Act East Policy: NE as India’s gateway to ASEAN.
- Kaladan Multimodal Transit Project: Enhances connectivity to Myanmar and beyond.
- Security Dimension: Infrastructure strengthens border management and reduces alienation.
Socio-Economic Impact
- Agriculture & Local Produce: Improved freight corridors open markets for bamboo, horticulture, and tea.
- Tourism: Enhanced air, rail, road connectivity fosters eco-tourism and cultural tourism.
- Employment: Large construction projects and industrial clusters creating jobs.
- Social Integration: Enhanced mobility reduces isolation, supports nation-building.
Challenges
- Geographical Barriers: Difficult terrain, high cost of construction (bridges, tunnels).
- Insurgency and Security: Though reduced, still poses risks.
- Environmental Concerns: Deforestation, landslides, and ecological fragility.
- Implementation Gaps: Delays in land acquisition, inter-agency coordination.
Way Forward
- Sustainable Development: Balance infrastructure expansion with ecological safeguards.
- Skill Development: Train local youth for emerging opportunities in logistics, tourism, IT.
- Community Engagement: Ensure projects are inclusive, culturally sensitive.
- Cross-Border Integration: Maximise opportunities through BIMSTEC, BBIN, and ASEAN linkages.
- Resilience Planning: Climate-resilient infrastructure for floods, earthquakes, and landslides.


Mains Issues
Context:
Kerala will host the two-day ‘Blue Tides-Two Shores One Vision’ conclave on September 18–19, bringing together Indian and European stakeholders to promote a sustainable blue economy.
Blue Economy
Definition & Concept
- Blue Economy: Sustainable use of ocean, sea, and coastal resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and job creation, while protecting ocean ecosystems.
- World Bank: “Sustainable use of ocean resources for economic growth, improved livelihoods, and jobs while preserving the health of the ocean ecosystem.”
- European Commission: Covers “all economic activities relating to oceans, seas, and coasts” including established and emerging sectors.
Key Principles:
- Balance economic development with environmental sustainability.
- Address challenges: climate change, pollution, overfishing, marine biodiversity loss.
- Long-term goal: marine resilience and inclusive growth.
Objectives of Blue Economy
- Foster economic growth without degrading ocean health.
- Enhance employment, livelihoods, and food security through sustainable fisheries, tourism, and aquaculture.
- Promote innovation in marine biotechnology, ocean-based renewable energy, and coastal infrastructure.
- Minimise marine pollution and conserve biodiversity.
- Support climate-adaptive coastal infrastructure.
Blue Economy 2.0 (India)
- Focus: Climate-resilient development, restoration of coastal ecosystems, and sustainable expansion of aquaculture/mariculture.
- Policy Alignment:
- Interim Budget 2024 highlights Blue Economy 2.0.
- Linked to Vision 2025 and Deep Ocean Mission (2021).
- Key Components:
- Coastal Ecosystem Restoration: Mangroves, coral reefs, shoreline protection, beach nourishment.
- Sustainable Aquaculture &Mariculture: High-value marine species, seaweed farming, eco-friendly practices with funding & subsidies.
- Integrated Multi-Sectoral Approach: Coordination across shipping, ports, tourism, energy, biotech sectors using tech-driven planning.
Need for Blue Economy
- Vast Marine Resources: Oceans cover 75% of Earth, 97% of water, 99% of living space.
- Global Economic Significance: Oceans contribute 3–5% of global GDP (~USD 1.5 trillion; projected USD 3 trillion by 2030).
- Human Dependency: 40% of global population lives in coastal areas; 80% of trade via maritime routes.
- Climate Mitigation: Oceans absorb 30% of CO? emissions; sustainable management enhances carbon sink potential.
- Renewable Energy: Offshore wind, tidal, and wave energy for energy security and carbon reduction.
- Pollution Control: Plastic and chemical pollution mitigation; 33 billion pounds of plastic enter oceans annually.
Blue Economy in India
- GDP Contribution: ~4%.
- Key Sectors: Fisheries, aquaculture, shipping, tourism, offshore energy.
- Geography: 7,500 km coastline; 2.02 million sq km EEZ.
- Employment: Fisheries sector supports ~3.5 million directly, 30 million indirectly.
- Initiatives:
- Draft Blue Economy Policy
- Sagarmala Project: Modernise ports, enhance coastal industries & communities.
- Deep Ocean Mission: Scientific exploration & resource utilisation.
- O-SMART: Services, Technology, Resources, Observations, Science.
- India-Norway Task Force (2020): Sustainable blue economy cooperation.
- National Policy on Marine Fisheries (2017): Sustainable fisheries, MPAs, livelihood enhancement.
Importance
- Economic: Job creation, trade growth, marine biotech, shipping, fisheries, tourism.
- High ROI: $1 invested ? $5 return in key ocean activities.
- Environmental: Mitigates climate change, conserves marine biodiversity.
- Social: Supports SDG 14 “Life Below Water”.
- Strategic: Maritime security, coastal resilience, energy security.
Challenges
- Overfishing: 34% global fish stocks overexploited (FAO).
- Marine Pollution: ~8 million tonnes of plastic annually.
- Climate Change: Ocean warming, coral bleaching, species migration, acidification.
- Weak Governance: Insufficient enforcement of marine regulations
Way Forward / Strategic Measures
- International Cooperation: Strengthen regional partnerships (e.g., IORA).
- Sustainable Aquaculture: Ecosystem-based management.
- Infrastructure Investment: Ports, coastal facilities, renewable energy installations.
- Blue Finance Mechanisms: Blue bonds, climate finance, public-private partnerships.
- Marine Spatial Planning (MSP): Coordinated ocean use for fishing, tourism, shipping.
- Technology & Innovation: Ocean monitoring, marine biotechnology, climate-resilient coastal infrastructure.


Mains Issues
Context:
Heavy monsoon rains in August 2025 caused widespread flooding in Punjab, affecting over 4 lakh people across 2,200 villages, destroying crops, homes, and livelihoods.
Cause & Extent:
- Excess rainfall: Punjab received 7 mm in August 2025, 74% above normal (IMD data).
- Rivers in spate:Sutlej, Ravi, Beas overflowed, inundating low-lying areas, farmland, and villages across 18 of 23 districts.
- Immediate human impact:55 deaths, thousands displaced, 111 relief camps set up sheltering 4,600 people initially, with continued displacement in Fazilka and Gurdaspur.
Agricultural Losses:
- Paddy and Basmati crops submerged on ~1.91 lakh hectares.
- Winter wheat sowing expected to be delayed, reducing yield.
- Increased harvesting costs due to use of machinery suitable for moist land.
Relief & Rehabilitation Measures: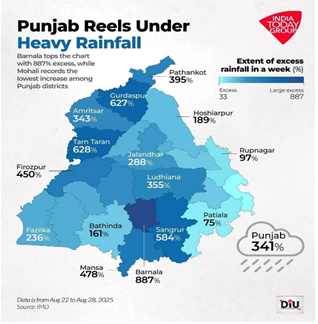
- Government response: 12,539 ration kits, 6,190 bags of cattle feed, fodder distribution, and temporary shelter in schools.
- Financial assistance: ?1,600 crore package announced by PM, while state parties highlighted the gap between actual losses (~?20,000 crore) and relief provided.
- Vulnerable populations: Daily wage laborers and landless farmers severely affected due to income and housing loss.
Policy & Administrative Significance:
- Demonstrates importance of State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) and coordination with central disaster funds.
- Highlights disaster preparedness, early warning systems, and riverine flood management.
- Draws attention to land tenure issues, as many displaced families lack formal land ownership, affecting relief eligibility.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Supreme Court directed the Union government to clarify whether meritorious candidates with disabilities are allowed “upward movement” to unreserved posts when they score above the unreserved category cutoff.
Legal Framework:
- Reservation for persons with disabilities is provided under Section 34 of the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPwD) Act, 2016.
- Purpose: To ensure mainstreaming and equal opportunities for persons with disabilities (PwDs).
Judicial Concern:
- Meritorious PwD candidates who qualify for unreserved seats are currently restricted to reserved posts, preventing upward movement.
- This denies opportunity to less meritorious PwDs who could otherwise fill reserved seats.
- Contrast with backward class candidates, who are automatically moved up to unreserved category if meritorious, freeing reserved seats.
Implications for Policy:
- Ensuring upward mobility aligns with the objective of reservation: creating inclusion while maintaining meritocracy.
- Calls for systematic procedural reforms in recruitment and promotions for PwDs.
- Recognizes disability as a lens to evaluate institutional inclusion, rather than a deficit requiring correction.


Prelims Articles
Context:
Retail inflation in India increased to 2.1% in August 2025, ending a nine-month declining trend.
Retail Inflation & Consumer Price Index (CPI)
- Retail Inflation: Also called CPI inflation, measures the change in retail prices of goods and services purchased by households for daily consumption.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): Index tracking the price level of a fixed basket of goods and services over time. The change in CPI over time reflects retail inflation.
Purpose of CPI
CPI provides insights into:
- Cost of Living: Indicates how expensive it is to maintain a certain standard of living.
- Purchasing Power: Helps assess the buying capacity of consumers.
- Price Level of Goods & Services: Tracks expensiveness of commodities and services.
- Value of Currency: Acts as an indicator of the Indian Rupee’s real value over time.
Calculation of CPI
- CPI compares the cost of a fixed basket of goods and services in the current year to a base year.
- Current Base Year: 2012 (India).
- Formula:
- CPI = (Cost of the market basket in the current year / Cost of the market basket in the base year) x 100
- Compiled by the National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- Scope: Provides All India as well as state-wise CPI for Rural, Urban, and Combined sectors.
Uses of CPI / Retail Inflation
- Macroeconomic Indicator:Reflects general price levels and inflation trends in the economy.
- Monetary Policy & Inflation Targeting:RBI uses CPI as a benchmark for monetary policy, including repo rates and interest rate adjustments and ensures price stability and manages inflation within the comfort band (2%-6%).
- Fiscal Policy & National Accounts:Used as a deflator in national accounts to calculate real GDP and economic growth.
- Wage & Pension Adjustments:Helps in indexing salaries, wages, and pensions to maintain real purchasing power.
- Currency Valuation & Purchasing Power:Indicates the real value of Indian Rupee in terms of domestic consumption.


Prelims Articles
Context:
SEBI has recommended to the Union Government to relax Minimum Public Shareholding (MPS) norms for large companies coming up with big IPOs, aiming to facilitate better primary market listings and investor participation.
Background:
- Minimum Public Shareholding (MPS): The minimum percentage of a listed company’s shares that must be held by the public. Currently, it is 25% of post-issue capital.
- Existing Norms: For issuers with post-issue market cap > ?1,00,000 crore, they must offer ?5,000 crore and at least 5% of post-issue market cap to public.
SEBI’s Recommendations:
- Scale-based relaxation: Large IPOs can list with a lower initial public float; MPS of 25% to be achieved gradually (up to 5 years).
- For companies with market cap ?50,000–100,000 crore: Minimum public offer of ?1,000 crore and at least 8% of post-issue market cap.
- Rationale:
- Large issuers face challenges in absorbing huge supply during IPOs.
- Avoid price overhang caused by mandatory dilution.
- Facilitate retail investor participation without affecting liquidity.


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Chief Justice of India (CJI) questioned why the firecracker ban is limited to Delhi-NCR and not implemented across India if pollution is a national problem, while also highlighting the need to protect industry workers.
Judicial Intervention on Pollution Control
- The Supreme Court has consistently intervened in environmental protection, citing Article 21 (Right to Life) which includes the right to pollution-free air.
- In this case, the CJI pointed out the selective ban on firecrackers in Delhi-NCR, asking why citizens elsewhere are not given the same protection.
Pan-India Policy Question
- The debate highlights the issue of unequal implementation of environmental laws across regions.
- If air pollution is a national problem, then the policy response must also be national in scope rather than region-specific.
Economic and Social Dimensions
- The firecracker industry employs lakhs of workers, mostly in Tamil Nadu (Sivakasi).
- The CJI stressed that any ban must also consider livelihood protection and explore alternatives like green crackers.
Role of Institutions
- National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (NEERI) is working on developing less-polluting “green crackers.”
- Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM) coordinates policy responses for air quality improvement, especially in NCR.
Constitutional & Policy Angle
- This issue reflects the conflict between Directive Principles (environmental protection, Art. 48A)and Fundamental Rights (Right to livelihood, Art. 19(1)(g)).
- Judicial scrutiny demands a balanced policy framework considering both public health and employment.
|
Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
Mandate & Jurisdiction
Powers
Composition
|


Prelims Articles
Context:
The Union Environment Ministry has approved the translocation of tigers from Tadoba-Andhari and Pench reserves to the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve in Maharashtra to revive the big cat’s population in the Western Ghats.
Background of Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (STR)
- Established in 2010 and spread over 1,165 sq. km.
- Encompasses parts of Kolhapur, Sangli, Satara, and Ratnagiri districts of Maharashtra.
- Formed by merging Chandoli National Park and Koyna Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Despite rich forest cover, tiger presence has remained transient and non-breeding.
Reason for Translocation
- STR has suitable forest and prey base but lacks a stable tiger population.
- Translocation aims to ensure long-term tiger survival in the Western Ghats, an ecologically sensitive and biodiversity-rich region.
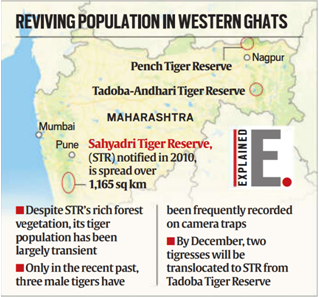
Implementation & Institutions Involved
- Approved by the Union Environment Ministry’s Wildlife Division.
- Wildlife Institute of India (WII) and State Forest Department are responsible for scientific planning and execution.
- The project had earlier been recommended by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) in October 2023.
Ecological Significance
- Strengthening tiger presence in STR ensures habitat connectivity between Western Ghats reserves and those in Goa and Karnataka.
- Helps maintain ecological balance and boosts conservation of prey species.
- Supports the long-term goal of landscape-level tiger conservation in India.


Editorials
Context:
The Supreme Court in Ram Charan&Ors. vs Sukhram&Ors. (2025) held that exclusion of daughters from ancestral property in tribal communities amounts to a violation of the fundamental right to equality.
Judicial and Constitutional Context
- Supreme Court Intervention: The Court equated denial of property rights to tribal daughters with negation of Article 14 and Article 15 guarantees of equality.
- Earlier Precedents: In Madhu Kishwar vs State of Bihar (1996), the Court refrained from striking down exclusionary customary laws, citing disruption risks.
- Progressive Shift: Recent rulings in Kamala Neti (2022) and Prabha Minz (2022) expanded recognition of tribal women’s property rights, moving toward gender parity.
Customary Laws and Exclusion
- Scheduled Areas Governance: Tribal communities in Scheduled V areas follow customary laws on marriage, succession, and adoption, often excluding women from inheritance.
- Gender Disparities in Landholding: According to Agriculture Census 2015-16, only 16.7% of ST women possess land compared to 83.3% of ST men.
- Justifications for Denial: Concerns of land alienation through inter-community marriages and the claim of communitarian ownership are used to deny women equal rights.
The Way Forward
- Codification of Tribal Succession: A separate Tribal Succession Act can provide clarity and statutory backing for gender-equal inheritance in tribal societies.
- Judicial Scrutiny of Custom: Courts can test customs on grounds of antiquity, continuity, and conformity with constitutional morality before recognition as law.
- Strengthening Gender Justice: Legal reforms must ensure that tribal women, who significantly contribute to agriculture and livelihoods, are not deprived of rightful property.
Practice Question
“Customary laws often restrict inheritance rights of tribal women, perpetuating gender inequality. Critically examine the constitutional, social, and legal dimensions of ensuring property rights for tribal women in India.” (250 words)


Editorials
Context:
The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act has amended Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act, diluting the scope of information disclosure and raising concerns over transparency and accountability.
Legal and Constitutional Dimensions
- Foundational Principle: The RTI Act is based on the idea that government information belongs to citizens, with exemptions narrowly defined under Article 19(2).
- Section 8(1)(j) Provision: Originally, personal information could be denied only if unrelated to public activity or an invasion of privacy, unless larger public interest justified disclosure.
- DPDP Amendment: The amendment shortens Section 8(1)(j) drastically, expanding the scope of “personal information” and enabling denial of most disclosures.
Practical Implications
- Ambiguity of Definition: With the DPDP Act’s expansive definition of “person” including firms, companies, and associations, almost all government data can be labelled as personal.
- Administrative Fear: Severe penalties under the DPDP Act (up to ?250 crore) incentivise Public Information Officers (PIOs) to deny information to avoid liability.
- Weakening Accountability: Routine documents like pension records, marksheets, and official orders risk being withheld, undermining citizens’ monitoring of governance.
Democratic and Governance Concerns
- Facilitation of Corruption: With denial becoming the norm, corruption cases linked to ghost employees, welfare leakages, and misuse of funds can remain hidden.
- Ineffectiveness of Safeguards; Although the “larger public interest” clause still exists, its application is rare, leaving little scope for meaningful transparency.
- Erosion of Citizen Rights: By prioritising data protection over disclosure, the amendment converts RTI into a “Right to Deny Information”, weakening democratic accountability.
Practice Question
“The recent amendment to Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act through the Digital Personal Data Protection Act has been criticised as transforming the Right to Information into a ‘Right to Deny Information’. Critically examine its constitutional, governance, and democratic implications.” (250 words)


Editorials
Context:
Nepal is witnessing youth-led protests triggered by deep-seated grievances over corruption, inequality, and the failure to implement promises made in the 2006 Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA).
Historical Background
- Comprehensive Peace Agreement (2006): The CPA was signed between the Maoists and the Nepalese government to end the 10-year-long civil war, creating hopes for peace, justice, and democracy.
- Democratic Transition: The monarchy was abolished, and the interim constitution (2007) paved the way for a new republican framework based on inclusiveness and human rights.
- Institutional Provisions: The CPA also mandated the formation of the Truth and Reconciliation Commission (TRC) and Commission on Disappeared Persons (CIEDP) to address conflict-era human rights violations.
Failure of Implementation
- Unfulfilled Commitments: Successive governments failed to deliver justice, truth-seeking, or reparations to victims, leaving CPA promises largely unimplemented.
- Constitutional Limitations: Although Nepal promulgated a new Constitution in 2015, political compromises diluted its inclusiveness, leaving marginalized groups disillusioned.
- Corruption and Inequality: Corruption scandals, elite capture of state resources, and widening socio-economic inequalities have fueled frustration among youth.
Contemporary Youth Protests
- Gen Z Mobilisation: Young protesters are rejecting corruption and demanding a more accountable, inclusive, and equitable political order.
- Economic Disparities: Nepal’s per capita income is only ?1.54 lakh, and unemployment remains high, with many youths forced to migrate for work.
- Quest for Justice: The protests highlight Nepal’s failure to utilize post-conflict peacebuilding resources effectively, instead squandering them on political patronage.
Practice Question
“Despite the Comprehensive Peace Agreement of 2006, Nepal continues to witness cycles of unrest and inequality. Analyse the structural failures of Nepal’s post-conflict peacebuilding and their implications for regional stability.” (250 words)




