

9th May 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
DNA samples collected from two human skeletons unearthed at a necropolis of a Harappan-era city site in Haryana have been sent for scientific examination, the outcome of which might tell about the ancestry and food habits of people who lived in the Rakhigarhi region thousands of years ago.
About
- The skeletons of two women were found a couple of months ago at mound number 7 (named RGR 7 by the Archaeological Survey of India or (ASI), believed to be nearly 5,000 years old.
- Pots and other artefacts were also found buried next to them in a pit, part of the funerary rituals back in the Harappan Civilisation era.
Benefit of DNA Analysis:
- The outcome of the DNA analysis will help tell about the ancestry of the people who lived at this ancient city, whether they were native or had migrated from elsewhere to settle.
- Besides, samples taken from the teeth area would tell about their food habits, what kind of food they consumed and other anthropological patterns related to that human settlement which must have been one of the largest, dating from the Harappan Civilisation period.
- carbon dating would tell the age via scientific process, the excavation site at mound RGR 7, as per current status of the excavation, can be said to be tentatively dated close to the 3,000 BC period, making the site about 5,000 years old.
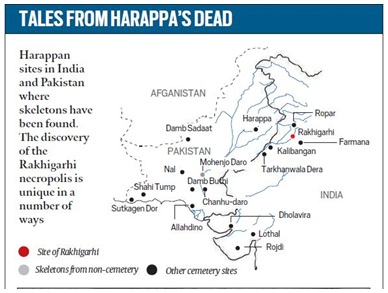
Rakhigarhi
- Representation of Harappan Culture: The site has yielded various stages of Harappan culture.
- It is by far one of the largest Harappan sites in India.
- Seven (07) mounds are located here.
- Collective Site: The ancient site of Rakhi-Khas and Rakhi-Shahpur are collectively known as Rakhigarhi.
- Location: It is located on the right bank of the now dried-up Palaeo-channel of Drishadvati (Saraswati basin).
- Some important discovered features:
- Infrastructure: paved roads, drainage system, large rainwater collection, storage system, terracotta bricks.
- Art: statue production, and skilled working of bronze and precious metals have been uncovered.
- Jewelry, bangles made from terracotta, conch shells, gold, and semi-precious stones.
- Fire altars and apsidal structures were revealed in Rakhigarh
|
Five places to be developed as “iconic sites”
|
|
Additional Information:
|
More Articles


