15th July 2022 (8 Topics)
Context
Recently, the Health Ministry said that the States should aware, alert, and ready to tackle other public health threats such as monkey-pox which is on the rise globally.
Background
- Monkey-pox (MPX) was first discovered in 1958 in colonies of monkeys kept for research, hence the name ‘monkey-pox.’
- The first human case of monkey-pox was reported in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) in 1970.
- Recently, an ongoing outbreak of the viral disease monkey-pox was confirmed in May 2022.
About Monkey-Pox:
- Monkey-pox (MPX) is a viral zoonotic disease with symptoms similar to smallpox, although with less clinical severity.
- It is a potentially serious viral illness that typically involves flu-like symptoms, swelling of the lymph nodes, and a rash that includes bumps that are initially filled with fluid before scabbing over.
- Illness could be confused with a sexually transmitted infection like syphilis or herpes, or chickenpox.
Mode of transmission:
- Human-to-human transmission is known to occur primarily through large respiratory droplets generally requiring prolonged close contact.
- It can also be transmitted through direct contact with body fluids or lesion material, and indirect contact with lesion material, such as through contaminated clothing or linens of an infected person.
|
Case fatality ratio
|
- Animal-to-human transmission: may occur by bite or scratch of infected animals like small mammals including rodents (rats, squirrels) and non-human primates (monkeys, apes) or through bush meat preparation.
What causes monkey-pox?
- It is a rare disease that is caused by infection with the monkey-pox virus.
- This virus belongs to the Ortho-pox-virus genus.
- It includes the variola (smallpox) virus as well as the vaccinia virus, which is used in the smallpox vaccine.
What are the symptoms of monkey-pox?
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Fever
- Headache
- Body aches
- Profound weakness
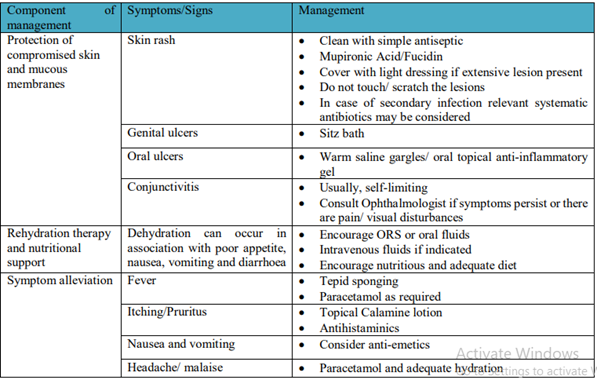
What is the treatment for monkey-pox?
- While there are no specific treatments for monkey-pox infections, antiviral drugs licensed for smallpox use are effective and can be used against monkey-pox.
- Monkey-pox is usually a self-limited disease with symptoms lasting from 2 to 4 weeks.
- Severe cases occur more commonly among children and are related to the extent of virus exposure, patient health status, and nature of complications.
- The extent to which asymptomatic infection occurs is unknown.
What is the monkey pox vaccine?
- Two vaccines licensed by the S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are available for preventing monkey-pox infection - JYNNEOS (also known as Imvamune or Imvanex) and ACAM2000.