18th February 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
The Ministry of Power notified the green hydrogen policy, also referred to as the green ammonia policy.
About
About National Hydrogen Mission (NHM):
- The National Hydrogen Mission (NHM), which would lay the roadmap for India to become a global leader in the production of hydrogen.
- Under the ambit of the mission, the government would support research, demand generation, infrastructure development and other parts of the process to ensure that India would be able to produce and use hydrogen as a fuel, especially in the transport sector.
What else will the National Hydrogen Mission cover?
- Under the mission the government would provide support in the form of free power transmission for 25 years, dollar-denominated bids, offer of land in renewable energy parks, and land allocation near ports for creating bunkers for green hydrogen or ammonia.
- The ultimate aim of the government is to bring down the cost of green hydrogen to $1 per kg and have five million metric tonnes per annum (MMTPA) green hydrogen capacity by 2030 in India.
What will be the green hydrogen policy?
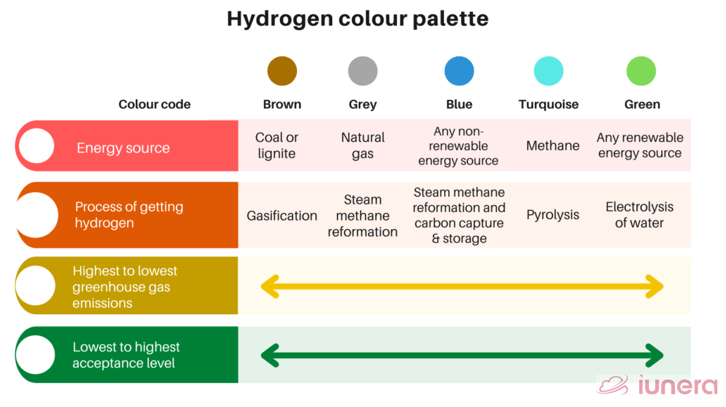
- The policy will set the roadmap to transition from the high-carbon-footprint grey hydrogen and grey ammonia to the zero-carbon process of extracting green hydrogen and green ammonia.
- The policy is not expected to include viability gap funding and mandates for producers under the hydrogen policy for green hydrogen and ammonia usage. These are likely to be added in the second phase.
Hydrogen:
- Hydrogen is the lightest and first element on the periodic table.
- It is the most abundant element in the universe. The sun and other stars are composed largely of hydrogen.
- Since the weight of hydrogen is less than air, it rises in the atmosphere and is therefore rarely found in its pure form, H2.
- Astronomers estimate that 90% of the atoms in the universe are hydrogen atoms. Hydrogen is a component of more compounds than any other element.
- Water is the most abundant compound of hydrogen found on earth.
Hydrogen fuel:
- Molecular hydrogen is not available on Earth in convenient natural reservoirs.
- Most hydrogen on Earth is bonded to oxygen in water and to carbon in live or dead and/or fossilized biomass. It can be created by splitting water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- At standard temperature and pressure, hydrogen is a nontoxic, nonmetallic, odorless, tasteless, colorless, and highly combustible diatomic gas.
- Hydrogen fuel is a zero-emission fuel burned with oxygen. It can be used in fuel cells or internal combustion engines. It is also used as a fuel for spacecraft propulsion.
- Hydrogen is being seen as the fuel of the future. Hydrogen has the potential to create limitless, emission-free, efficient energy.
There are several ways to produce hydrogen:
- Natural Gas Reforming/Gasification: Synthesis gas is a mixture of hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and a small amount of carbon dioxide is created by reacting natural gas with high-temperature steam.
- The carbon monoxide is reacted with water to produce additional hydrogen.
- This method is the cheapest, most efficient, and most common.
- Natural gas reforming using steam accounts for the majority of hydrogen produced in the United States annually.
- A synthesis gas can also be created by reacting coal or biomass with high-temperature steam and oxygen in a pressurized gasifier.
- This converts the coal or biomass into gaseous components, a process called gasification.
- The resulting synthesis gas contains hydrogen and carbon monoxide, which is reacted with steam to separate the hydrogen.
- Electrolysis:An electric current splits water into hydrogen and oxygen. If the electricity is produced by renewable sources, such as solar or wind, the resulting hydrogen will be considered renewable as well, and has numerous emissions benefits. Power-to-hydrogen projects are taking off, using excess renewable electricity, when available, to make hydrogen through electrolysis.
- Renewable Liquid Reforming:Renewable liquid fuels, such as ethanol, are reacted with high-temperature steam to produce hydrogen near the point of end use.
- Fermentation: Biomass is converted into sugar-rich feedstocks that can be fermented to produce hydrogen.