18th February 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
The Tamil Nadu government filed an affidavit in the Supreme Court stating that it would not permit the construction for the proposed Indian Neutrino Observatory at Bodi West Hills in Theni district.
About
About Neutrinos:
- Neutrinos were first proposed by Swiss scientist Wolfgang Pauliin 1930.
- It is the second most widely occurring particle in the Universe, after Photons (the particle which makes up light).
- Neutrinos are so abundant among us that every second there are > 100 trillion of them passing right through each of us.
- Properties of Neutrinos:
- They are subatomic part different from Neutrons. Leptons family. No charge.
- In 2015, Nobel Prize given to Takaaki Kajita and Arthur Mcdonald for discovering Neutrino Oscillations demonstrating that Neutrinos have mass (tiny mass).
- Not affected by electromagnetic forces which act on electrons.
- Neutrinos occur in 3 different types. They are separated in terms of different masses.
- “Electron neutrino” is associated with the electron
- “Muon neutrino”
- “Tau neutrino”
- They are least harmful of all as they almost never react with solid bodies.
- Sources: Sun, Black Hole, Nuclear explosion.
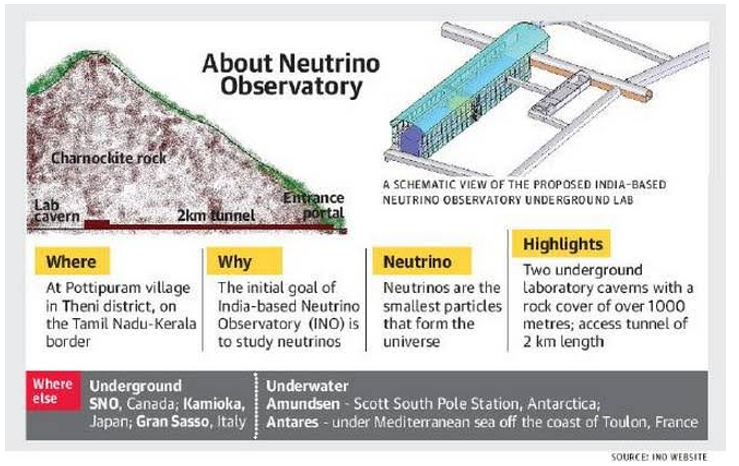
About the Indian Neutrino Observatory (INO) project:
- The India-based Neutrino Observatory (INO) Project is a multi-institutional effortaimed at building a world-class underground laboratory with a rock cover of approx. 1200 m for non-accelerator based high energy and nuclear physics research in India.
- The initial goal of INO is to study neutrinos.
- It is a mega-science project jointly funded by the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) and the Department of Science and Technology (DST).
The project includes:
- Construction of an underground laboratory and associated surface facilities at Pottipuram in Bodi West hills of Theni District of Tamil Nadu.
- Construction of an Iron Calorimeter (ICAL) detectorfor studying neutrinos.
- Setting up of National Centre for High Energy Physics at Madurai, for the operation and maintenance of the underground laboratory, human resource development and detector R&D along with its applications.
Objections to the project:
- It will affect the flora and fauna of the Periyar Tiger Reserve and Mathikettan Shola National Park in the Western Ghats.
- The tunnelling works for the proposed project involved blasting hard and composite rock in the Western Ghats.
- An enormous quantity of high-strength explosives will be required to break rocks.
- The tunnelling work will involve excavation of 600,000 cubic metres (m) of Charnockite rock from the hilly region.
- The tunnel and cavern of the project would be built at a depth of 1,000 m from a hilltop. But the construction work, vehicles and people required for it and the piling up of construction material in forest areas would adversely affect conservation activities.
- At a depth of 1,000 m, mountain rock would be under tremendous pressure and the vertical stress is expected to be greater than 270 kg per sq m. This will create problems like rock bust and roof collapse.
- The protection of the Western Ghats was supreme as they are a global biodiversity hotspot and a treasure trove of biological diversity.
- The proposed site formed part of the catchment of various streamlets and constituted a watershed that supported livelihoods in five districts of Tamil Nadu.
- The project site was located hardly 4.9 km from the Mathikettan Shola National Park of Kerala, which had enormous environmental importance. The area has many hill slopes that function as elephants and tiger corridors.
- The proposed project area links the Periyar Tiger Reserve in Kerala with Srivilliputhur Meghamalai Tiger Reserve.
- Quarrying and construction activities will upset wild animals which use the corridor for seasonal migrations.
- The project violated the Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972 and Forest (Conservation) Act of 1980.
More Articles