3rd February 2025 (12 Topics)
Context
The Budget introduces a massive income tax cut to spur consumer consumption and economic activity. The government estimates that Rs 1 lakh crore will be foregone in tax revenues, and this money is expected to flow back into the economy through higher consumption.
Key-highlights of the Tax Reform:
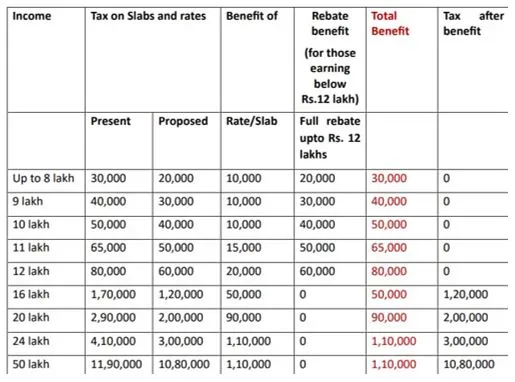
- The budget has proposed to exempt individuals with income (excluding incomes taxable at special rates like capital gains) up to Rs 12 lakhs from paying income tax from FY 2025-26 onwards.
- The annual limit for TDS on rent has been raised from Rs 2.40 lakh to Rs 6 lakh, benefiting small taxpayers receiving smaller payments.
- This Rs 1 lakh crore largesse has been given in the hope of driving consumption and GDP growth, thereof.
What are the potential impact of Tax Cut?
- The tax cut aims to increase disposable income for citizens, allowing them to spend more on goods and services.
- This is seen as a way to address the demand-side problem of the economy, as businesses are unlikely to invest without adequate consumer demand.
- Economic Theory Behind the Tax Cut:
- Multiplier Effect: Economists suggest that the multiplier effect of an income tax cut is 1.01. This means that for every rupee cut in income tax, the GDP could grow by Rs 1.01 due to increased consumption.
- Increased Savings and Lower Interest Rates: The additional income can also increase savings, which could lower interest rates and stimulate more borrowing and economic activity.
- However, experts caution that the Rs 1 lakh crore tax cut may not be sufficient to trigger a full economic recovery, as India's GDP is much larger, and the total private final consumption expenditure (PFCE) is around Rs 200 lakh crore.
Key Challenges and Potential Pitfalls
While the tax cut may have positive short-term effects, experts argue that a comprehensive strategy for sustained economic growth is still lacking.
- Limited Impact of Tax Cuts: Critics point out that a tax cut, while helpful in the short term, will not solve the fundamental issue of low income growth across the population.
- Income Inequality: Tax cuts benefit a small portion of the population (those who pay income taxes). Since only a small segment of the population pays income taxes, the broader effect of tax cuts on consumption might be limited.
- External Dependencies: If increased consumer spending focuses on imported goods or services, it could lead to higher imports and inflation, rather than boosting domestic industries.
- Increased Domestic Inflation: More money in circulation may lead to higher demand, which could push up prices, especially if supply doesn’t keep pace with demand.
More Articles