

30th December 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
Despite outlawing caste-based discrimination in 1950, Dalits still get discriminated against when applying for programs established to help them.
Challenges faced by Dalit Women
- Failure of policies: Dalit women continue to suffer from a high degree of poverty, gender discrimination, caste discrimination, and socioeconomic deprivation.
- Violence: Girls face violence at a younger age and at a higher rate than women of other castes.
- Caste System
- Exploitation by dominant castes
- Cases are withdrawn and lack of justice
- Workplace violence
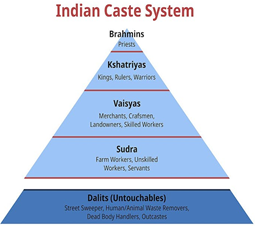
Rigid Occupational Hierarchy
- Caste is essentially the stratification of people into a rigid occupational hierarchy.
- The origins of India’s caste system go back thousands of years.
- It is deeply entwined with Hinduism.
Problem with microloans
- A microloan from a government bank:
- It was pioneered by economist Muhammad Yunus and the Grameen Bank in Bangladesh in the 1970s.
- In India, it is backed by the Reserve Bank of India.
- It is offered to people who lack the collateral that institutional lenders usually require.
- Role of RBI in Microloans:
|
Unsung Dalit women heroes
|
-
- Regulating the sector
- Guarantor of microloans given by banks
- Provision for Dalit women: The Reserve Bank of India underwrites incentives including interest rates about half that offered to other women.
- Poor Implementation: 66 per cent of rejected applications were from Dalit women.
- Discrimination at the branch level.
The problem faced while issuing Caste certificates
- To qualify for a program to assist Dalits, they had to prove they were Dalits by supplying a government-issued caste certificate.
- But this certificate then became the means for them to be identified as Dalits and discriminated against.
Initiatives Taken to Promote Transformation
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
- Skills Acquisition and Knowledge Awareness for Livelihood (SANKALP) Scheme
- Stand Up India Scheme
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana


