

12th April 2024 (9 Topics)
Context
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has achieved a significant milestone by practically eliminating orbital debris in Earth's orbit through its PSLV-C58/XPoSat mission. This accomplishment marks a crucial step towards mitigating the growing threat of space debris.
Key Highlights
Transformation of Fourth Stage:
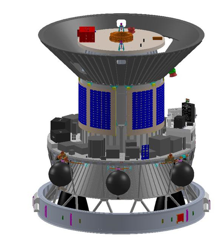
- POEM-3 Development: The last stage of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) used in the mission was transformed into the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3), serving as an orbital station.
- De-Orbiting Strategy: Instead of leaving the fourth stage to float in orbit after completing its mission, ISRO lowered POEM-3 from 650 km to 350 km, rendering it more susceptible to re-entry into the Earth's atmosphere.
- Passivation Measures: ISRO ensured the safe disposal of the stage by passivating it, meaning that its fuel was dumped to prevent the risk of explosion and the generation of small debris fragments.
Significance of POEM:
- Cost-effective Space Platform: Developed by the Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), POEM utilizes the spent fourth stage of a PSLV rocket as an orbital platform, facilitating scientific experiments and payload operations.
- Innovative Technology: Equipped with solar panels, a lithium-ion battery, and a navigation, guidance, and control (NGC) system, POEM represents a sustainable and resource-efficient approach to space exploration.
- Demonstration of Reusability: ISRO's successful demonstration of reusing the fourth stage of its rocket highlights its commitment to innovation and cost-effectiveness in space missions.
Addressing Space Debris Concerns:
- Rising Threat of Space Debris: With the proliferation of satellites and space missions, space debris has emerged as a critical concern, posing risks to operational spacecraft and future missions.
- Environmental Impact: Space debris, including defunct satellites and fragments of spacecraft, travels at high speeds and can cause collisions, potentially leading to cascading effects and further debris generation.
- International Mitigation Efforts: While there are currently no international space laws specifically addressing low Earth orbit (LEO) debris, spacefaring nations adhere to guidelines set forth by organizations like the Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC) to mitigate debris-related risks.
1: Dimension-Technological Advancements
- Space Debris Mitigation Technologies: ISRO's innovative approach to space debris mitigation underscores the importance of technological advancements in addressing space sustainability challenges.
- Reusable Space Platforms: POEM exemplifies the potential of reusing space hardware components to minimize waste and optimize resource utilization in space missions.
- Future Prospects: Continued investments in research and development of space technologies will be essential to enhance space situational awareness and develop effective debris mitigation strategies.
2: Dimension-Environmental Conservation
- Preserving Space Environment: Eliminating orbital debris contributes to preserving the space environment and ensuring the long-term sustainability of space activities.
- Mitigating Risks: By actively addressing the risks associated with space debris, space agencies play a crucial role in safeguarding critical space assets and reducing the likelihood of collisions.
- Global Cooperation: Collaboration among nations and international organizations is essential to develop comprehensive space debris mitigation frameworks and promote responsible space conduct.
3: Dimension-Policy and Governance
- Regulatory Frameworks: The absence of comprehensive international space laws necessitates the development of robust regulatory frameworks to govern space activities and address emerging challenges like space debris.
- Standardization and Compliance: Standardization of space debris mitigation practices and mechanisms for compliance monitoring are crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of mitigation efforts and promoting responsible space behavior.
- Diplomatic Initiatives: Diplomatic dialogues and multilateral agreements play a vital role in fostering cooperation and consensus-building on space governance issues, including debris mitigation and space sustainability.
Mains Practice Question
Q. Discuss the challenges and opportunities in addressing space debris concerns for sustainable space exploration.
More Articles

