

6th May 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
The Delimitation Commission finalised the Delimitation Order for the Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir.
About
Important takeaways from the order of the delimitation panel:
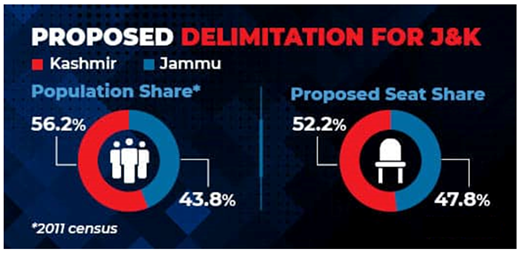
- The Delimitation Commission recommended seven additional constituencies; six for Jammu and one for Kashmir, taking the total number of seats in the UT to 90 from 83 earlier.
- This will increase the number of seats in the Jammu Division to 43 from 37 seats earlier, and that in the Kashmir Valley to 47 from 46 earlier.
- Reorganisation of the Parliamentary constituencies such that the five Lok Sabha seats now are made up of exactly 18 Assembly constituencies each, taking the total number to 90.
- Reservation of nine Assembly seats for Scheduled Tribes – six in Jammu and three in Kashmir
- Removal of the regional distinction between Jammu and Kashmir and treating it as one, as is reflected in the combining of Anantnag region in Kashmir with Rajouri and Poonch in Jammu to carve out Anantnag-Rajouri as a Parliamentary constituency.
- The panel also recommended that the Legislative Assembly of the Union Territory have at least two members – one of them a woman – from the Kashmiri migrant community with the right to vote at par with nominated members like in the Puducherry Assembly.
- Besides, it also recommended some representation to Persons displaced from Pakistan-occupied Jammu and Kashmir.
About Delimitation Commission:
- Delimitation literally means the act or process of fixing limits or boundaries of territorial constituencies in a country or a province having a legislative body.
- The job of delimitation is assigned to a high power body.
- Such a body is known as Delimitation Commission or a Boundary Commission.
- The Delimitation Commission is a commission established by the Government of India under the provisions of the Delimitation Commission Act to redraw the boundaries of the various assembly and Lok Sabha constituencies on a recent census.
- Under Article 82 of the Constitution of India, the Parliament enacts a Delimitation Act after every Census.
- Under Article 170, States also get divided into territorial constituencies as per Delimitation Act after every Census.
- The Central Government constitute the Delimitation Commission which consists of three members as follows:—
- one member, who shall be a person who is or has been a Judge of the Supreme Court, to be appointed by the Central Government who shall be the Chairperson of the Commission
- the Chief Election Commissioner or an Election Commissioner nominated by the Chief Election Commissioner, ex officio:
- Provided that after the nomination of an Election Commissioner as a member under this clause, no further nomination under this clause shall be made except to fill the casual vacancy of such member under section 6
- the State Election Commissioner of concerned State, ex officio
- In India, such Delimitation Commissions have been constituted four times—
- in 1952 under the Delimitation Commission Act, 1952
- in 1963 under Delimitation Commission Act, 1962
- in 1973 under Delimitation Act, 1972
- in 2002 under Delimitation Act, 2002
- The Delimitation Commission in India is a high power body whose orders have the force of law and cannot be called in question before any court.
- These orders come into force on a date to be specified by the President of India in this behalf.
- The copies of its orders are laid before the House of the People and the State Legislative Assembly concerned, but no modifications are permissible therein by them.
More Articles


