

6th May 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
Salim Ali Centre for Ornithology and Natural History (SACON) in Coimbatore recently carried out a survey of slender loris populations in Tamil Nadu’s Dindigul forest division.
About
About Slender Loris:
- The gray slender loris (b) belongs to the family Loridae.
- It is a species of primate.
- Adult size: The average length of the Slender Loris is just 18-26 cm. It weighs 85-350 grams
- Natural Range: India and Sri Lanka
- Social life: Solitary nocturnal forager
- Habitat: Tropical forest, woodland and thorny scrub jungle
- The animal is largely found in the Eastern Ghats of the Karur and Dindigul Forest Divisions.
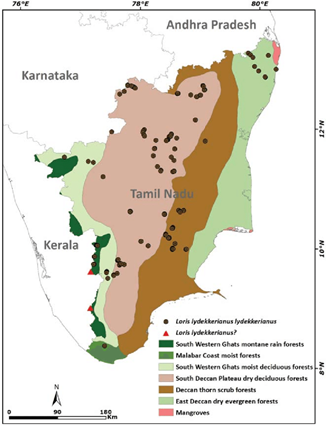
- The animal is largely found in the Eastern Ghats of the Karur and Dindigul Forest Divisions.
- Diet: Insects, young leaves, shoots, hard-rind fruits and flowers, occasional eggs and small vertebrates
- Habitat: Being arboreal, Slender Lorises spend most of their life on the trees.
- Though their movements are slow, they can climb up fast to the tree top when threatened.
- Among the strange habits they have is the urine washing of their face and limbs, which is said to soothe or defend against the sting of the toxic insects they prefer to eat.
- They are known to be very social at dusk and dawn, interacting with others of their own.
- Lifespan: The lifespan of Slender Loris is about 10 to 12 years in its natural habitat.
- Sexual maturity: 10-18 months
- Mating: Every 9.5 months
- Gestation: 166 – 169 days
- Number of young: 1 – 2 offspring every 9 – 10 months
- The two species of slender loris are: The red slender loris (Loris tardigradus) and the gray slender loris (L. lydekkerianus).
- Protection Status:
- IUCN: Endangered,
- Wildlife (Protection) Act of India, 1972: Schedule I
- CITES: Appendix II
- Threats:
- As it is believed that these animals have some medicinal properties, they are captured and sold.
- Since there is great demand for keeping these animals as pets, they are illegally smuggled.
- Habitat loss, electrocution of live wires and road accidents are other threats that have caused its populations to dwindle.

More Articles


