

2nd June 2022 (9 Topics)
Context
The first hydrogen-powered car was registered in Kerala in April 2022. With this, the southern state has become one of the select few states to allow the registration of such cars.
About
- The registration, entry and display of this car is part of a memorandum of understanding signed between International Centre for Automotive Technology (iCAT) and Toyota to study and evaluate fuel-cell electric vehicles.
- The car is not expected to ply on roads.
- It will be kept at a research organisation for studying India’s first fuel-cell electric vehicle (FCEV).
- Toyota Mirai is India’s first FCEV. The registered vehicle is exempt from taxation because it will be used for research and development purposes.
Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs):
- Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) run on hydrogen and are considered more efficient than conventional internal combustion engine vehicles and produce zero tailpipe emissions and only emit water vapour and air.
- Fuel cells are electrochemical devices to convert chemical energy into electrical energy.
- They offer over 40% higher electrical efficiency than the conventional ones.
- FCEVs are equipped with other advanced technologies to increase efficiency, such as regenerative braking systems that capture the energy lost during braking and store it in a battery.
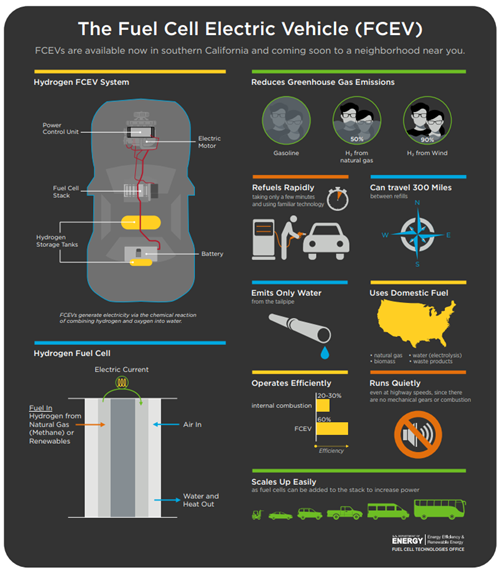
How Fuel Cells Work?
- The most common type of fuel cell for vehicle applications is the polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cell.
- In a PEM fuel cell, an electrolyte membrane is sandwiched between a positive electrode (cathode) and a negative electrode (anode).
- Hydrogen is introduced to the anode, and oxygen (from air) is introduced to the cathode.
- The hydrogen molecules break apart into protons and electrons due to an electrochemical reaction in the fuel cell catalyst.
- Protons then travel through the membrane to the cathode.
- The electrons are forced to travel through an external circuit to perform work (providing power to the electric car) then recombine with the protons on the cathode side where the protons, electrons, and oxygen molecules combine to form water.
|
Classification of EVs Globally, EVs are bracketed under three broad categories:
|


