Reaching 70 is an extraordinary achievement for the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
Issue
Reaching 70 is an extraordinary achievement for the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation.
Background
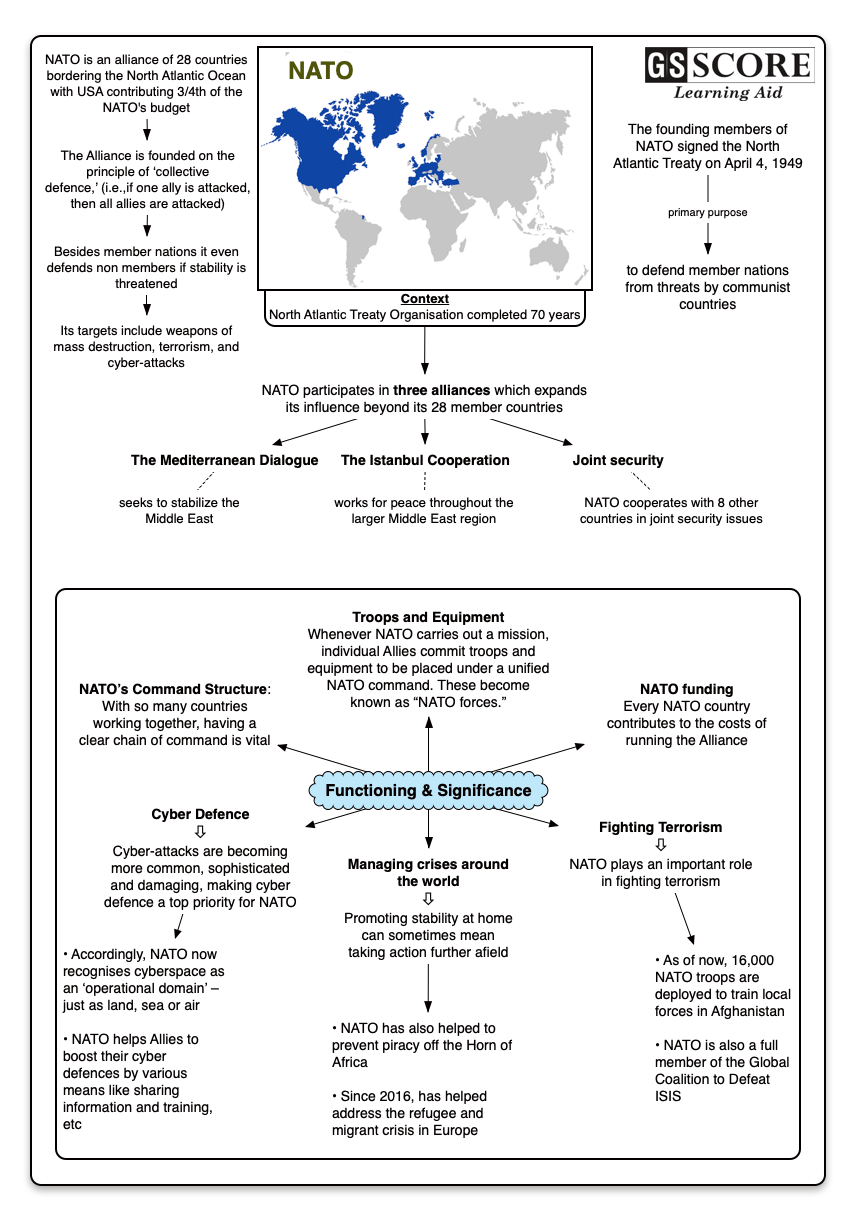
- NATO is an alliance of 28 countries bordering the North Atlantic Ocean.
- It includes the United States, most European Union members, Canada, and Turkey.
- NATO is an acronym for the North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
- The United States contributes three-fourths of NATO's budget.
- NATO's mission is to protect the freedom of its members. Its targets include weapons of mass destruction, terrorism, and cyber-attacks.
- If the stability is threatened, NATO would defend non-members.
- NATO's headquarters are located in Haren, Brussels, Belgium.
Member Countries
- NATO's 28 members are: Albania, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, Croatia, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Turkey, United Kingdom, and the United States.
- Each member designates an ambassador to NATO.
- They send the appropriate official to discuss NATO business. That includes a country’s president, prime minister, foreign affairs minister or head of the department of defense.
Analysis
- NATO participates in three alliances. They expand its influence beyond its 28 member countries.
- The Mediterranean Dialogue seeks to stabilize the Middle East. Its non-NATO members include Algeria, Egypt, Israel, Jordan, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia. It began in 1994.
- The Istanbul Cooperation Initiative works for peace throughout the larger Middle East region. It includes four members of the Gulf Cooperation Council. They are Bahrain, Kuwait, Qatar, and the United Arab Emirates. It began in 2004.
- NATO cooperates with eight other countries in joint security issues. There are five in Asia. They are Australia, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mongolia, and New Zealand. There are two in the Middle East: Afghanistan and Pakistan.
History
- The founding members of NATO signed the North Atlantic Treaty on April 4, 1949.
- It worked in conjunction with the United Nations, the World Bank, and the International Monetary Fund.
- NATO's primary purpose was to defend member nations from threats by communist countries.
Significance of NATO
- Collective defence: The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was founded in 1949 and is a group of 29 countries from Europe and North America that exists to protect the people and territory of its members. The Alliance is founded on the principle of ‘collective defence,’ meaning that if one NATO Ally is attacked, then all NATO Allies are attacked.
- Managing crises around the world: Promoting stability in our neighbourhood and protecting our people at home can sometimes mean taking action further afield. NATO has also helped to prevent piracy off the Horn of Africa and, since 2016, has helped address the refugee and migrant crisis in Europe.
- Fighting Terrorism: NATO plays an important role in fighting terrorism, contributing 16,000 NATO troops to train local forces in Afghanistan. NATO is also a full member of the Global Coalition to Defeat ISIS.
- Troops and Equipment: Whenever NATO carries out a mission, individual Allies commit troops and equipment to be placed under a unified NATO command. These become known as “NATO forces.”
- NATO’s Command Structure: With so many countries working together, having a clear chain of command is vital. Military and civilian personnel from all member states work together every day within NATO’s ‘Command Structure.’
- NATO funding: Every NATO country contributes to the costs of running the Alliance. By far the Allies’ biggest contribution comes in the form of taking part in NATO-led missions and operations.
- NATO funding: Every NATO country contributes to the costs of running the Alliance. By far the Allies’ biggest contribution comes in the form of taking part in NATO-led missions and operations.
- Cyber Defence: Cyber-attacks are becoming more common, sophisticated and damaging, making cyber defence a top priority for NATO. In fact, NATO now recognises cyberspace as an ‘operational domain’ – just as land, sea or air. NATO helps Allies to boost their cyber defences by sharing information about threats, investing in education and training, and through exercises. NATO also has cyber defence experts that can be sent to help Allies under attack.
Learning Aid