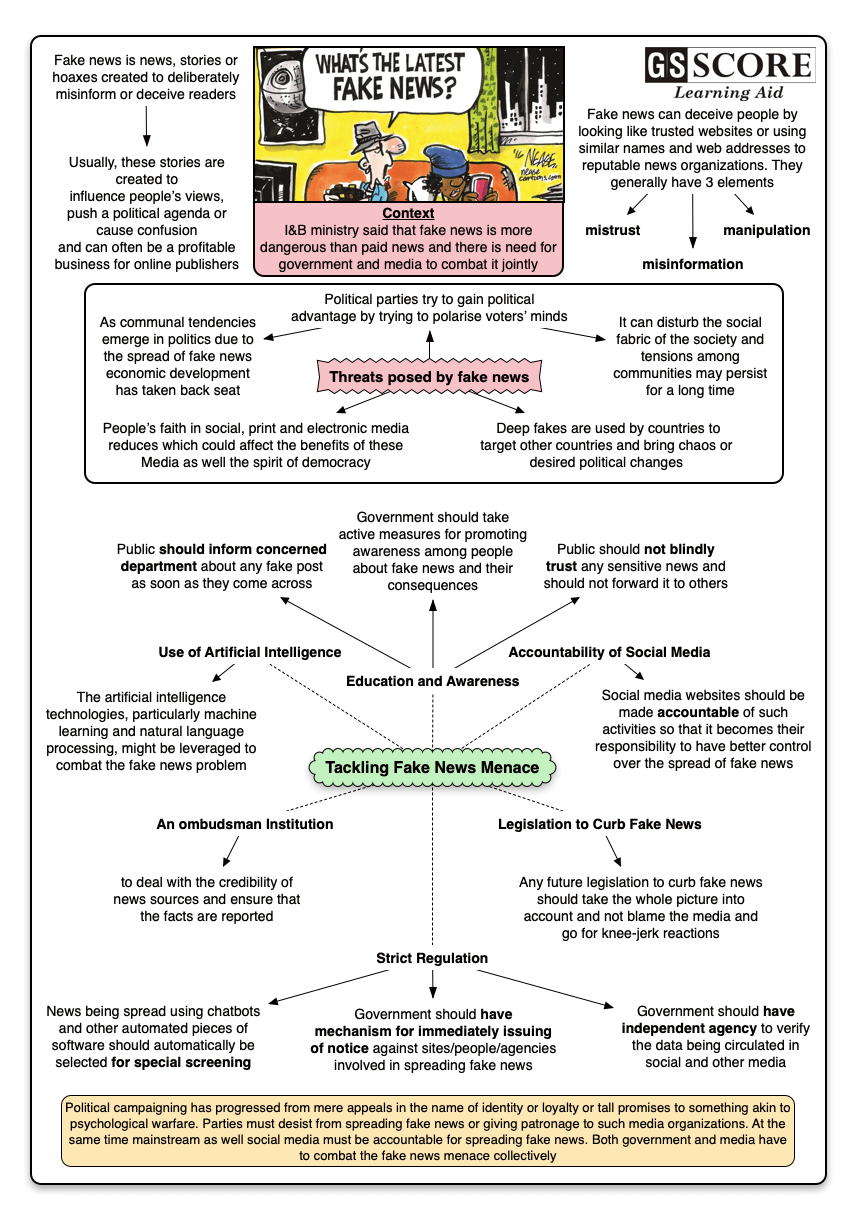
I&B ministry said that fake news is more dangerous than paid news and there is need for government and media to combat it jointly
Issue
Context
I&B ministry said that fake news is more dangerous than paid news and there is need for government and media to combat it jointly
Background
- Fake news is news, stories or hoaxes created to deliberately misinform or deceive readers.Fake news, defined by the New York Times as “a made-up story with an intention to deceive”
- Usually, these stories are created to influence people’s views, push a political agenda or cause confusion and can often be a profitable business for online publishers.
- Fake news stories can deceive people by looking like trusted websites or using similar names and web addresses to reputable news organizations.
- There are three elements to fake news; Mistrust, misinformation and manipulation.
- Popular Fake Examples from India:
- Muzzafarnagar riots of 2013: fake video fuelled communal passions
- UNESCO has declared ‘Jana Gana Mana’ best national anthem in the world (WhatsApp)
- Dying Woman Molested, Video shows (The Hindu Newspaper)
- Fatwa in Saudi Arabia; Men can eat wives when hungry (AajTak)
- GPS tracking nanochip in 2000 Rupee notes (Nov 2016)
- Child kidnapping rumours lead to lynchings by a mob in Jharkhand
- Missing JNU student Najeeb Ahmed has joined the ISIS
- Deep Fake
- It is dangerous than fake news. It is a technique for human image synthesisbased on artificial intelligence.
- It is used to combine and superimposeexisting images and videos onto source images or videos using a machine learning technique known as generative adversarial network.
- Because of these capabilities, deep fakes have been used to create fake celebrity pornographic videosor revenge porn. Deep fakes can also be used to create fake news and malicious hoaxes
Analysis
Causes for Rise in Fake News
- Internet and Social media: Many people now get news from social media sites and networks and often it can be difficult to tell whether stories are credible or not. Social media sites can play a big part in increasing the reach of these types of stories.
- Lack of Checking Authenticity: Everyone is busy in sharing/liking/commenting on news items without checking the authenticity of news.
- No codes of practice for Social Media: Traditionally we got our news from trusted sources, journalists and media outlets that are required to follow strict codes of practice. However, the internet has enabled a whole new way to publish, share and consume information and news with very little regulation or editorial standards.
- Stratified Organization of Fake News: Fake news is no longer being considered a rare or isolated phenomenon, but appears to be organized and shrewdly disseminated to a target population. It is believed that the high possibility of these organized bodies coming into existence with the help of political influence.
|
Laws Governing Fake News
|
- Vernacular Social Media Platforms:The immense popularity of vernacular social media platforms in India is exploited for the spread of fake news.
Dangers/Threats posed by Fake News
Political
- Political parties try to gain political advantages by polarizing the voter’s mind which further intensifies the tensions between different sections of society.
- Political campaigning has progressed from mere appeals in the name of identity or loyalty or tall promises to something akin to psychological warfare.
Economic: As communal tendencies emerge in politics due to the spread of fake news economic development has taken back seat. The problems faced by the problems are not solved by the government.
Society: It can disturb the social fabric of the society and tensions among communities persists for long times. It can lead to violence between two or more communities thereby creating enmity and hatred between them. It reduces the tendencies of cooperation between different communities.
International: Deep fakes are used by countries to target other countries and bring chaos or desired political changes. China and Russia are using deep fakes to target the hostile countries to gain political and trade benefits.
Faith in Media: People’s faith in social, print and electronic media reduces which could affect the benefits of these Media as well the spirit of democracy as media being the fouth estate of democracy. In its purest form, fake news is completely made up, manipulated to resemble credible journalism and attract maximum attention and, with it, advertising revenue.
How to tackle it?
- Education and Awareness
- The government must take the initiative to make all sections of the population aware of the realities of this information war and evolve a consensus to fight this war. It must also take strict action against the fake news providers.
- Government should take active measures for promoting awareness among people about fake news and their consequences.
- Italy, for example, has experimentally added ‘recognizing fake news’ in school syllabus. India should also seriously emphasize cybersecurity, internet education, fake news education in the academic curriculum at all levels.
- Strict Regulation:
- News being spread using chatbots and other automated pieces of software should automatically be selected for special screening.
- Government should have independent agency:to verify the data being circulated in social and other media. The agency should be tasked with presenting real facts and figures.
- An ombudsman Institution: It deals with the credibility of news sources and ensures that the facts are reported.
- Legislation to Curb Fake News:
- Any future legislation to curb fake news should take the whole picture into account and not blame the media and go for knee-jerk reactions; in this age of new media anyone can create and circulate new for undisclosed benefits.
- Government should have mechanism for immediately issuing of notice against sites/people/agencies involved in spreading fake news.
- Accountability of Social Media: Social media websites should be made accountableof such activities so that it becomes their responsibility to have better control over the spread of fake news.
- Help From Individuals and Civil Society:
- Public should not blindly trustany sensitive news and should not forward it to others.
- Public should inform concerned departmentabout any fake post as soon as they come across.
- They should act as active vigilant for maintaining peace and harmony in the society.
- NGO’s and other civil society groups can play important role in spreading awareness about the ill effects of fake news.
- Ordinary consumers of news can play a big role by, first, waking up to the reality that all they read on WhatsApp and Twitter is not the gospel truth, and then, by refusing to pass on what they cannot independently verify with other sources.
- Using Artificial Intelligence: The artificial intelligence technologies, particularly machine learning and natural language processing, might be leveraged to combat the fake news problem. AI technologies hold promise for significantly automating parts of the procedure human fact checkers use today to determine if a story is real or a hoax.
Conclusion
Political campaigning has progressed from mere appeals in the name of identity or loyalty or tall promises to something akin to psychological warfare. Parties must desist from spreading fake news or giving patronage to such media organizations. At the same time mainstream as well social media must be accountable for spreading fake news. Both government and media have to combat the fake news menace collectively.
Learning Aid
Practice Question:
Fake news menace has become a threat to media and democracy. In the light of this statement analyse how fake news can affect voting patterns in India?