

Context
The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has announced a National Suicide Prevention Strategy, the first of its kind in the country to achieve a reduction in suicide mortality by 10% by 2030.
About
The National Suicide Prevention Strategy:
- The strategy is in line with the WHO’s South East-Asia Region Strategy for suicide prevention.
- Aim: The strategy broadly seeks to establish:
- Effective surveillance mechanisms for suicide within the next three years.
- Toestablish psychiatric outpatient departments that will provide suicide prevention services through the District Mental Health Programme in all districts within the next five years, and
- To integrate a mental well-being curriculum in all educational institutions within the next eight years.
- It envisages developing guidelines for:
- responsible media reporting of suicides, and
- restricting access to means of suicide with time-bound action plans and
- multi-sectoral collaborations.
- The stress is on developing community resilience and societal support for suicide prevention.
|
The South East-Asia Region Strategy:
|
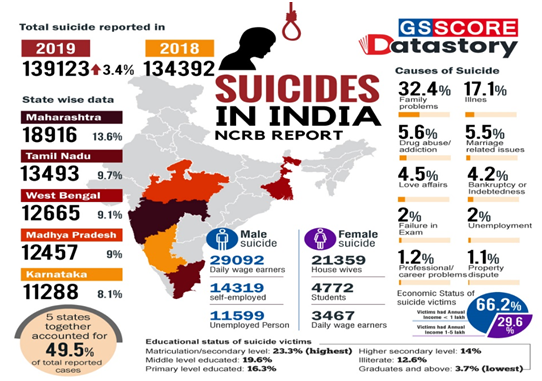
Suicide rates in India:
- According to the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) report 2021, the Suicide rate in India is increasing alarmingly.
- Delhi has recorded the highest number of (2,840) suicides.
- Reasons for Suicide:
- 2%: Family Problems (other than marriage-related problems)
- 8%: Marriage Related Problems
- 6%: Illness
- Daily wage earners accounted for 42,004 (25.6 per cent) of the total victims. One in four of the recorded 1, 64,033 suicide victims during 2021 was a daily wage earner.
- They were followed by self-employed people, unemployed people, and those involved in the farming sector were the top categories of people who died by suicide in 2021.
- The report certainly points out suicides as a critical public health issue in India and qualifies for a closer epidemiological assessment.
How is Suicide a Social Problem?
- Suicide is a serious social problem whose incidence varies between genders, age groups, geographical distribution, and the influence of the socio-political structure of society.
- Furthermore, suicide should be viewed as a multidimensional public and mental health issue, having complex interactions with the economic, social, cultural, psychological, and biological realms of individual and collective existence.
What are the challenges?
- Under-reporting of such cases due to fear of social stigma and sometimes to rescue from judicial procedures.
- Fear of legal action: Section 309 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) makes The fear of punitive action and added hassle of having to deal with police and courts often ‘Suicide a punishable offence’, results in a refusal to seek help.
- Social stigma:The social stigma associated with suicide results in the NCRB grossly under-reporting the true numbers of suicide.
Related Initiatives:
- Mental Healthcare Act, 2017
- KIRAN
- Manodarpan Initiative


