

20th June 2022 (8 Topics)
Context
NASA’s Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) spotted a peculiarly-shaped cloud drifting across the Caspian Sea.
- The cloud had well-defined edges resembling something from a cartoon, or something painted onto the scenery, in sharp contrast with the typical diffused and dispersed cloud cover.
About
About:
- According to an atmospheric scientist at SRON Netherlands Institute for Space Research, the cloud is a small stratocumulus cloud.
- Cumulus clouds are detached “heaps” of “cauliflower-shaped” clouds that are usually found during good weather conditions.
- In stratocumulus clouds, these heaps are clumped together, forming a widespread horizontal layer of clouds.
- The stratocumulus cloud in the picture formed a layer that spans about 100 kilometres.
- These clouds typically form at low altitudes, generally between 600 and 2,000 metres above the ground.
- The one in the picture was probably hovering at an altitude of about 1,500 metres.
- Sharp edges are often formed when dry, warm air coming from land collides with colder moist air over the ocean, and the cloud forms at that boundary.

How are clouds formed?
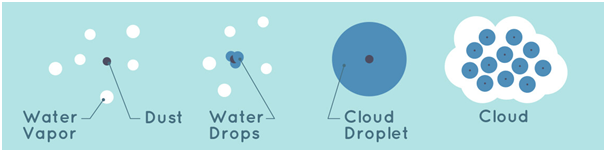
- A cloud is defined as 'a visible aggregate of minute droplets of water or particles of ice or a mixture of both floating in the free air'.
- Each droplet has a diameter of about a hundredth of a millimeter and each cubic meter of air will contain 100 million droplets.
- Because the droplets are so small, they can remain in liquid form in temperatures of -30 °C. If so, they are called supercooled droplets.
- Clouds at higher and extremely cold levels in the atmosphere are composed of ice crystals - these can be about a tenth of a millimeter long.
- Clouds form when the invisible water vapor in the air condenses into visible water droplets or ice crystals.
- For this to happen, the parcel of air must be saturated, i.e. unable to hold all the water it contains in vapor form, so it starts to condense into a liquid or solid form.
- There are two ways by which saturation is reached.
- By increasing the water content in the air, e.g. through evaporation, to a point where the air can hold no more.
- By cooling the air so that it reaches its dew point - this is the temperature at which condensation occurs, and is unable to 'hold' any more water.
Different types of clouds: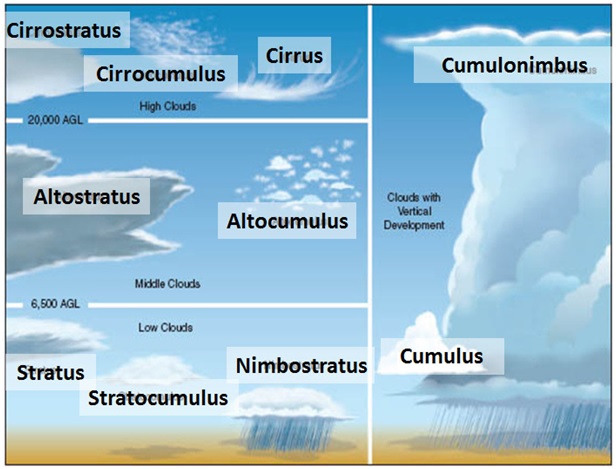
|
NASA’s MODIS:
|


