

14th September 2022 (9 Topics)
Context
Later this month, NASA’s DART will intentionally crash into Dimorphos, the asteroid moonlet of Didymos.
- While the asteroid poses no threat to Earth, this is the world’s first test of the kinetic impact technique, using a spacecraft to deflect an asteroid for planetary defense.
Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART)
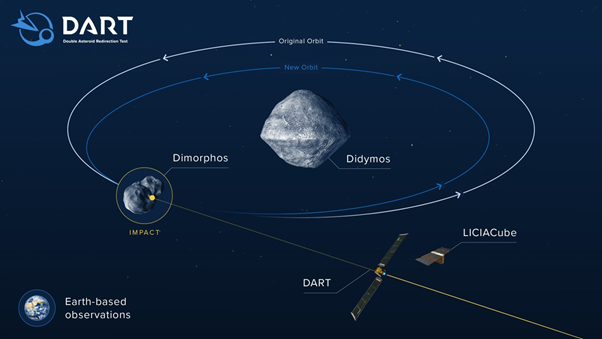
- DART is the first-ever mission dedicated to investigating and demonstrating one method of asteroid deflection by changing an asteroid’s motion in space through kinetic impact.
- This method will have DART deliberately collide with a target asteroid which poses no threat to Earth, in order to change its speed and path.
- DART’s target is the binary, near-Earth asteroid system Didymos, composed of the roughly 780-meter (2,560-foot) -diameter “Didymos” and the smaller, approximately 160-meter (530-foot)-size “Dimorphos,” which orbits Didymos.
- DART will impact Dimorphos to change its orbit within the binary system.
- DART is also carrying a cubesat that will film the larger spacecraft's impact and beam the footage back to researchers on Earth.
- At the time of DART's impact, Didymos will be visible enough to be a good candidate for study and distant enough to be no danger, at approximately 6.8 million miles (11 kilometers) away from Earth.
Key Objectives
- DART is a test of our ability to achieve a kinetic impact on an asteroid and observe the asteroid’s response.
- After DART’s kinetic impact with its target asteroid Dimorphos, an investigation team will measure how much the impact changed the asteroid’s motion in space using telescopes on Earth.
- This mission engages the international planetary science community and embraces worldwide cooperation to address the global issue of planetary defense.
- DART’s Mission Objectives:
- Demonstrate a kinetic impact with Dimorphos.
- Change the binary orbital period of Dimorphos.
- Use ground-based telescope observations to measure Dimorphos’ period change before and after impact.
- Measure the effects of the impact and resulting ejecta on Dimorphos.
|
What is an Asteroid?
Where asteroids are located?
|


