

25th November 2022 (6 Topics)
Context:
A movement built around the Burlang Yatra, a traditional festival of the ‘Kutia Kondh tribe’ of Odisha, has involved traditional millet crops in reviving their ancient food palate.
Background:
- In collaboration with Millet Network of India (MINI), a forum founded for the promotion of millet, NIRMAN started celebrating the Burlang Yatra on a large scale to increase awareness about millet.
- In the past, millet used to be the staple food for tribals in Odisha. When paddy and other foods reached their doorstep through the public distribution system and the expanding consumer market, tribals started treating millets as subsistence crops that they grew to use or eat for themselves rather than to sell.
- Some millet started to disappear from the tribal food basket.
|
In 2017, the Odisha government realized the importance of highly nutritious and climate-resilient millets in tribal society. The Odisha government has also started celebrating ‘Mandia Dibas’ (Millet Day) on November 10 to popularise the crop. |
Kutia Kondh tribe’:
- The Kutia Kondhs are particularly vulnerable tribal groups (PVTGs) in Kalahandi district, Odisha.
- They live in Lanjigarh, Thuamul Rampur, Madanpur Rampur, and Bhawanipatna blocks.
- The Kondhs worship ‘nature’ like many other tribal groups in the country.
- Kutia kondh are mostly dependent on shifting cultivation, cultivation of minor agriculture products, and collection of NTFP.
- The practice of youth dormitory is gradually losing its importance but is still prevalent among Kutia kondh villages.
- Dhap and Salap Baja are the essential musical instruments of Kutia Kondhs.

About:
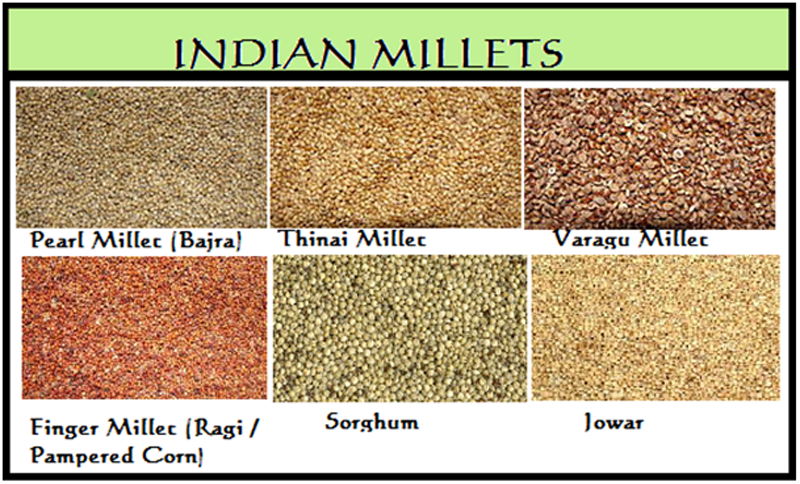
- Millet is a collective term referring to a number of small-seeded annual grasses that are cultivated as grain crops, primarily on marginal lands in dry areas in temperate, subtropical, and tropical regions.
- Some of the common millets available in India are Ragi (Finger millet), Jowar (Sorghum), Sama (Little millet), Bajra (Pearl millet), and Variga (Proso millet).

- The earliest evidence for these grains has been found in the Indus civilization and was one of the first plants domesticated for food.
- It is grown in about 131 countries and is the traditional food for around 60 crore people in Asia & Africa.
|
Do you know?
|
Significance of Millets:
Nutritionally Superior:
- Millets are less expensive and nutritionally superior to wheat & rice owing to their high protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals like iron content.
Gluten-free a low glycemic index:
- Millets can help tackle lifestyle problems and health challenges such as obesity and diabetes as they are gluten-free and have a low glycemic index (a relative ranking of carbohydrates in foods according to how they affect blood glucose levels).
Super Crop at Growing:
- Millets are Photo-insensitive, have less water consumption, and are capable of growing under drought conditions, under non-irrigated conditions even in very low rainfall regimes.
Initiatives by Tribals:
- Tribals grow interdependent crops in a single field and harvest them one after another, which helped millets and other crops survive.
- The tribals also managed to revive pulses, oilseed, and tubers which are regarded as companion crops. Now, the community has discovered four to five crop varieties from different villages.
Incidentally, two species of the mint family, supposed to belong to the Himalayan belt, have also been identified as traditional crops cultivated by tribals of the Kandhamal district in Odisha.
Other Initiatives at the Pan-India level:
- Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millet Promotion (INSIMP)
- Increase in Minimum Support Price (MSP): The government has hiked the Minimum Support Price of Millets, which came as a big price incentive for farmers.
- Further, to provide a steady market for the produce, the government has included millets in the public distribution system.
- Input Support: The government has introduced the provision of seed kits and inputs to farmers, building value chains through Farmer Producer Organisations and supporting the marketability of millets.
More Articles



