

4th July 2024 (10 Topics)
Context
This year, the Pantanal, the world’s largest tropical wetland, has experienced unprecedented fires due to severe water loss. A recent study highlighted that the area covered by water in 2023 was 61% below average, significantly affecting the ecosystem.
Key Points:
- Pantanal's Water Loss: In 2023, only 2.6% of the Pantanal was covered by water, a drastic reduction compared to previous years. This has led to extreme dry conditions, making the region prone to wildfires.
- Impact on Biodiversity: The Pantanal is renowned for its biodiversity, hosting species like jaguars and capybaras. The drying has endangered these species and their habitats.
- Amazon and Other Biomes: The Amazon also faced challenges with a reduced water surface, impacting fish and dolphin populations due to severe droughts. The Pampa grasslands and the Cerrado showed mixed results in water surface changes.
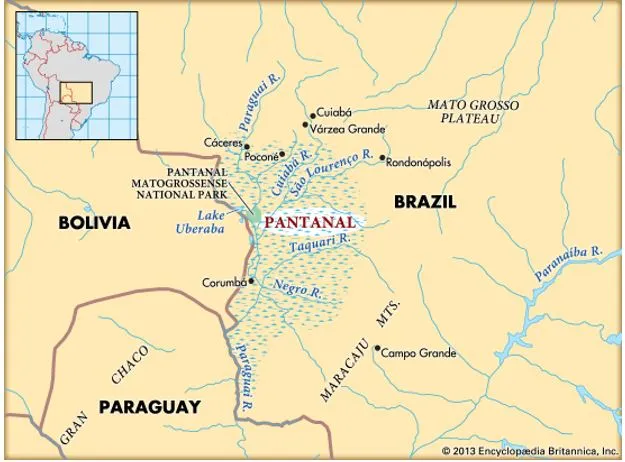
About Pantanal (Brazil, South America)
- The Pantanal is the world’s largest freshwater wetland, a seasonally flooded plain fed by the tributaries of the Paraguay River. At 68,000 square miles, it is more than 20 times the size of the Everglades.
- Location:Located in the upper Paraguay River basin, the Pantanal straddles Brazil’s border with Bolivia and Paraguay. About 80 percent of the Pantanal is in Brazil. It sprawls across three countries—Bolivia, Brazil, and Paraguay.
- Major Habitat Type: Flooded Grassland Savanna
- The Pantanal is also one of the world’s most productive habitats.
- Flora and Fauna: Iconic species found in the Pantanal include the jaguar (the highest density in the world), giant otters, capybaras (the largest rodent species), anteaters, tapirs, caimans, and a diverse array of birds such as toucans and jabiru storks.
More Articles

