Context
Taking a leap forward in the space research sector of India, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is all set to launch two back-to-back missions in a few months – Chandrayaan 3 and Aditya L1, both set to be launched in July 2023.
About the missions
-
Chandrayaan 3
- Chandrayaan 3 is the third moon mission set to be launched by ISRO, where a spacecraft will be launched into the lunar orbit of the moon for space research.
- It a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2 to demonstrate end-to-end capability in safe landing and roving on the lunar surface.
- It consists of Lander and Rover configuration. It will be launched by LVM3.
|
Previous Editions
|
-
Aditya L1
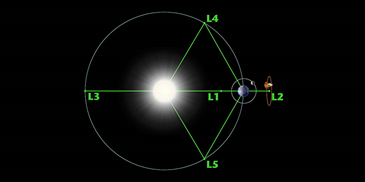
- Aditya L1 is set to be India’s first-ever space mission to the sun.
- Aditya L1 is a planned coronagraphy spacecraft to study the solar atmosphere and is a first-of-its-kind mission set to be carried out by ISRO.
- The main aim of the Aditya L1 mission is to insert the spacecraft in the halo orbit around the L1 point between the Earth and the Sun, through which it will be able to study the atmosphere of the Sun and the solar magnetic storms and its impact on the Earth.
|
Important Terms
|