Context
China will launch three more astronauts to its newest space station in June after the latest crew returned recently following a six-month stay in orbit.
About
About China's space station – Tiangong:
- Tiangong is China's space station in low Earth orbit.
- Tiangong is a space station that the Chinese Manned Space Agency (CMSA) is building in low Earth orbit.
- In May 2021, China launched Tianhe, the first of the orbiting space station's three modules, and the country aims to finish building the station by the end of 2022.
- CMSA hopes to keep Tiangong inhabited continuously by three astronauts for at least a decade.
- The space station will host many experiments from both China and other countries.
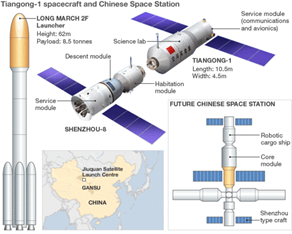
- Tiangong, which means "Heavenly Palace," will consist of Tianhe, the main habitat for astronauts, and two modules dedicated to hosting experiments, Mengtian and Wentian, both of which are due to launch in 2022.
- Shenzhou spacecraft, launching from Jiuquan in the Gobi Desert, will send crews of three astronauts to the space station, while Tianzhou cargo spacecraft will launch from Wenchang on the Chinese island of Hainan to deliver supplies and fuel to the station.
- Tiangong will be much smaller than the International Space Station (ISS), with only three modules compared with 16 modules on the ISS.
- Tiangong will also be lighter than the ISS, which weighs about 400 tons (450 metric tons) following the recent addition of Russia's Nauka module.