

Tensions between India and Pakistan in 2019 have reduced the already low volumes of trade between the two countries to near zero.
Context
Tensions between India and Pakistan in 2019 have reduced the already low volumes of trade between the two countries to near zero.
Background:
- Following the terrorist attack on the CRPF convoy in Pulwama in February, India withdrew Most Favoured Nation(MFN) status for Pakistan and raised customs duty on Pakistani imports to 200% and, in April, suspended cross-LoC trade to stop the misuse of this route by Pakistan-based elements.
- Pakistan on its part closed its airspaceto India for a prolonged period.
- The decisions by both countries, while targeted at hurting the neighbour, have severely impacted the livelihoods of individuals and families involved in cross-border trading activities.
Analysis of trade:
- In 1948-49, about 56% of Pakistan’s exports were to India, and 32% of its imports came from India.
- From 1948-65, India and Pakistan used a number of land routes for bilateral trade; there were eight customs stations in Pakistan’s Punjab province and three customs checkposts in Sindh.
- India remained Pakistan’s largest trading partner until 1955-56.
- Between 1947 and 1965, the countries signed 14 bilateral agreements on trade, covering avoidance of double taxation, air services, and banking, etc.
- In 1965, nine branches of six Indian banks were operating in Pakistan.
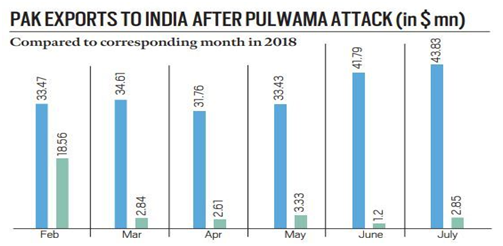
Scenario after attacks:
- Monthly average of trucks crossing from Wagah to Attari fell from 4,381 in April-November 2018 to 348 in the same period in 2019.
- Monthly average of trucks crossing from Attari to Wagah fell from 223 in April-November 2018 to 113 during the same period in 2019.
- It stopped altogether from September onwards.
Major items of exports and imports:
- Currently, there are two important trade routes between India and Pakistan:
- Sea route: Mumbai to Karachi
- Land route through Wagah border
- However, business is also done through Chakan Da Bagh in Poonch and Salamabad in Uri.
- Indian import from Pakistan
- India imports a total of 19 major products from Pakistan: dry food, fresh fruits (guava, mango and pineapple), cement, finished leather, spices, wool, rubber products, minerals and ores, inorganic chemicals, alcohol beverages, medical equipment, sporting goods, marine goods, plastic and raw cotton etc.
- Indian Export to Pakistan:
- Pakistan mainly imported tomato from India. However, Pakistan has banned the import of Indian tomato.
- After the Pulwama Attack India snatched the “Most Favoured Nation” status of Pakistan that is why India imposed 200% export duty on the tomato exported to Pakistan which increased the price of tomato up to Rs. 200 per kg in Pakistan.
- There are 14 items mainly imported by Pakistan from India: tea, sugar, oil cake, cotton yarn, tires, rubber, dye, petroleum oil, raw cotton and chemicals etc.
Conclusion:
Pakistan is geographically located at a strategic position between India and the energy-rich Gulf. It serves as a vital land link between South Asia and Central Asia. If India and Pakistan can make their relations friendly or at least trade-friendly the entire region can gain. It requires both the countries to engage in trade again and re-establish the trade ties. It will help to boot their economies.


