

Context
A recent study in the state of Rajasthan (the state that makes use of the second highest variety of Kisan Credit Cards (KCC)) has highlighted how the agriculture sector, together with Kisan Credit Cards (KCC), has confronted lots of challenges recently.
About
What is Kisan Credit Card (KCC)?
- The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme was introduced in 1998.
- Under the scheme, Kisan Credit Cards are issued to farmers based on their holdings for uniform adoption by the banks so that farmers may use them to readily purchase agriculture inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, etc., and draw cash for their production needs.
- Objective: The scheme aims to fulfill the needs as indicated below:
- To provide adequate and timely credit support from the banking system under a single window with flexible and simplified procedure
- To meet the short term credit requirements for the cultivation of crops
- Post-harvest expenses
- Produce marketing loan
- Consumption requirements of farmer household
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets and activities allied to agriculture
- Investment credit requirement for agriculture and allied activities
What about Bank loans?
- Agricultural credit disbursed by banks increased by 27% from 2016-17 to 2018-19 as a result of mandated priority sector lending(PSL) policies of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- However, the coverage is still not satisfying.
- In India, the RBI mandates banks that are unable to attain their PSL target to either purchase priority sector loans from other banks or contribute to the Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF).
What are the challenges faced by the sector?
- Small Holdings: In India, the bigger chunk is of small holdings of land, thus leaving a negative impact on, both output and earnings/incomes.
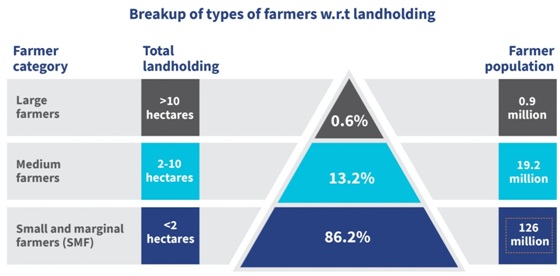
- Low Productivity: With a larger number of small and marginal farmers (86 percent), there have been the persisting problems of low productivity.
- Lower rate of participation: The participation rate in agriculture is on the decline as the agricultural sector has not been growing enough.
- Lack of finance: Lack of sufficient resources to buy or lease more land or invest in farm infrastructure such as irrigation, power, farm machinery.
- Prevalence of Informal Loans: Moneylenders providing farm loans at a higher rate exploit the farmers, which further pushes them to big distress.
- Unfair market regulation: Farmers are not getting fair prices of their produce due to the monopoly of the big traders as they bar farmers from selling directly to consumers.
- Climatic Variability: Indian agriculture is rain-fed, thus, delayed monsoon impacts the agricultural output. Due to his, most of the farmers get trapped under the agricultural loan.
- Others: Farmers face different sorts of challenges including floods, barren, natural calamities, insects attack, weather changes, scarcity of money, and whatnot.


