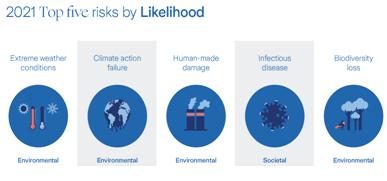
Infectious diseases topped the global risks chart, displacing climate change, according to the Global Risks Report, 2021.
Context
Infectious diseases topped the global risks chart, displacing climate change, according to the Global Risks Report, 2021.
About
What are Infectious diseases?
- Infectious diseases are caused by microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria, fungi and parasites.
-
- Microorganisms that cause disease are collectively called pathogens.
- Infectious diseases can be spread from one person to another, for example through contact with bodily fluids, by aerosols (through coughing and sneezing), or via a vector, for example a mosquito
What causes an infectious disease?
- Viruses: Viruses are tiny infectious agents that replicate only in the living cells of other organisms.
- Viruses have a very simple structure consisting of genetic material in the form of DNA or RNAwithin a protein
- They can infect all types of life forms, from animals to plants and bacteria to amoebae.
- Bacteria: Bacteria are single-celled microorganisms. They come in many shapes including ball-, rod- and spiral-shaped.
- Most bacteria are not harmful and some are actually beneficial. Less than one per cent of bacteria will actually make person ill.
- Fungi: Fungi are microorganisms characterised by cell walls made from a substance called chitin.
- Fungi reproduce by releasing spores that can be picked up by direct contact or even inhaled.
- Parasites: Parasites are organisms that live in or on another organism and benefit by getting nutrients at the expense of their host.
- Parasites can be found in many different body sites, for example in the blood, liver, digestive system, brain and even the eyes.
Key-highlights of the Report
- Five of the top 10 global risks in terms of impact and likelihood remain from the environmental category.
- Extreme weather is the top-most climate-related risk because of the failure of climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- For the first time, the report rates risks according to when respondents perceive they will pose a critical threat to the world.
- Infectious diseases pose the biggest livelihood and economic threat as witnessed during the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic.
- The category was ranked tenth in the previous report, which said extreme weather and failure of climate change mitigation and adaptation would be the most damaging for the planet over the next 10 years.
12 new risks
- In the wake of COVID-19, the 16th edition of the WEF annual report added 12 new risks to the previous list.
- They include the:
- collapse of systemically important industries
- social security systems or multilateral institutions
- deteriorating mental health
- mass youth disillusion
- prolonged economic stagnation
- fracturing international relations
- a ‘pervasive backlash’ against science
- digital inequality
- the failure of technology governance