

Context
North Korea has dramatically ramped up missile tests this year and tested an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM).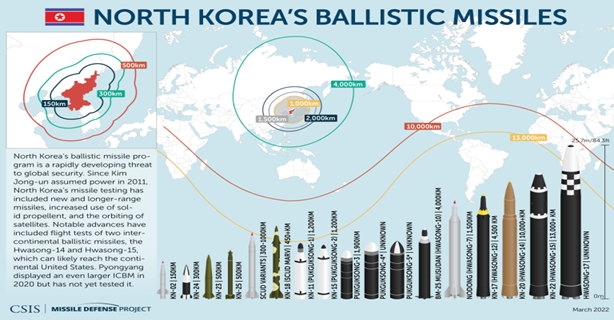
About
What are ICBMs?
- An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a missile with a minimum range of 5,500 kilometres primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery.
- Conventional, chemical and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs.
Important International Convention
- ICBMs are differentiated by having greater range and speed than other ballistic missiles.
- The International Code of Conduct against Ballistic Missile Proliferation (ICOC), now known as The Hague Code of Conduct against Ballistic Missile Proliferation (HCOC), is a political initiative aimed at globally curbing ballistic missile proliferation.
- India is a signatory to this convention.
- Established in April 1987, the voluntary Missile Technology Control Regime (MTCR) aims to limit the spread of ballistic missiles and other unmanned delivery systems that could be used for chemical, biological, and nuclear attacks.
- India has joined the MTCR in 2016.
Countries that have ICBMs:
- India, Russia, the United States, North Korea, China, Israel, the United Kingdom, and France.
- North Korea conducted the first successful test of its Hwasong-14 ICBM in July 2017.


