

Context
Amid tensions between Russia and Ukraine, pressure is mounting on Germany to stop the Nord Stream 2 gas pipeline project.
About
The original project
- The original Nord Stream pipeline, with an annual capacity of 55 billion cubic metres (bcm), was finished in late 2012.
- The pipeline system’s total capacity is set to double to 110 bcm following Nord Stream 2’s completion.
- Current status of project-: The pipeline falls in German and Danish Territory, and all but 150 km pipes for the project have already been laid.
|
Facts about Russia Energy Reserve-:
|
What is Nord Stream 2 Pipeline Project?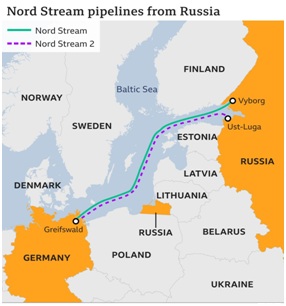
- Nord Stream 2 is an underwater twin pipeline that would transport natural gas from Russia directly to Germany.
- At a length of 1,230 kilometres, it is to follow the route of the existing Nord Stream twin pipeline underneath the Baltic Sea.
- It will carry 55 billion cubic meter of gas per year.
- The pipeline crosses into the exclusive economic zones of five countries: Russia, Germany, Denmark, Finland, and Sweden.
- It would transport natural gas from Russia directly to Germany.
- Nord Stream 2 is being built by Nord Stream 2 AG, a consortium incorporated in Switzerland.
- Moscow-based, state-owned Gazprom is the project’s sole shareholder.
|
Natural gas is a lower-carbon fuel that can replace other fossil fuels in the energy mix and deliver a reliable output to complement intermittent renewable energy. Largest natural gas fields in Russia
|
Objections
- Environmentalists argue that it will create further dependence of Germany on fossil fuels, which will impact its fight against climate change.
- The US says that the pipeline will make Europe further dependent on Russia for energy security. Russia could use it as a geopolitical weapon.
- Countries like Ukraine, Poland and Belarus are also opposing it as they will lose billions as transit fees due to bypassing.
- The US has threatened to impose sanctions on Nord Stream if Russia invades Ukraine. Germany has also said that it may be forced to impose sanctions.


