

Context
The Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) agreement, the world's largest free trade agreement, entered into force on January 1, 2022.
About
What is RCEP?
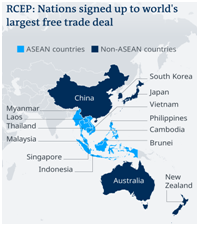
- RCEP is a free trade agreement between Asia-Pacific nations of Australia, Brunei, China, Cambodia, Japan, Indonesia, Laos, South Korea, Malaysia, New Zealand, Myanmar, Singapore, Thailand, the Philippines, and Vietnam.
- India and the United States are not members of RCEP.
- The 15-member grouping accounts for 30% of the world’s population and 30% of global GDP (2.2 billion people). Thus, it is the largest trade bloc in history.
- By comparison, the United States-Mexico-Canada trade agreement (USMCA) covers 28% of world trade, while the European Union's Single Market is a distant third at nearly 18%.
|
Background
|
Why did India opt out?
India was a member of the RCEP drafting committee from its inception in 2011, but in November 2019, it decided to opt out.
- Concerns regarding China: India did not join RCEP raising a concern that this deal would open it up to Chinese goods.
- Safeguarding domestic interest: Its decision was to safeguard the interests of industries like agriculture and dairy and to give an advantage to the country’s services sector.


