

The electronics exports have shown a rising tide amid slowdown in Indian economy and that is why it is in news.
Context
The electronics exports have shown a rising tide amid slowdown in Indian economy and that is why it is in news.
About
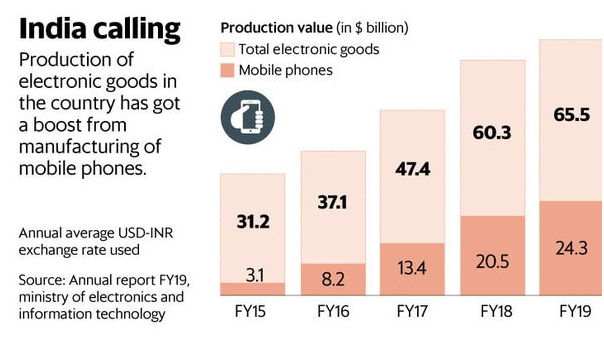
- Total value of production of electronic goods increased from $31.2 billion in FY15 to $65.5 billion in FY19
- Exports are led by mobile phones. India has become the 2nd largest producer of mobile phones, replacing Vietnam.
- India started to become an alternate production destination because
- Pull Factors include potential domestic demand and government policies to boost electronic exports.
- Push Factors include trade tensions between the US and China. This is expected that the positive trend in India’s electronic exports to continue.
Steps by Government to Boost Electronics Exports
- Schemes to boost local manufacturing of electronic goods: These include Phased Manufacturing Programme for mobile handsets and related sub-assemblies/components manufacturing, National Policy on Electronics 2019, Electronics Manufacturing Clusters scheme and Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme.
- Some countervailing duties were also announced to discourage imports of electronic goods.
Significance
Significance
- Avert BoP Crisis and control the stretched current account deficit (CAD)
- Transfer of technology
- Boost to manufacturing sector
- Employment generation
Government Schemes Promoting Electronics Sector
- National Electronics Policy (NEP), 2019
- Launched in 2019 and it replaced NEP, 2012.
- Vision
- To position India as a global hub for Electronics System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM) by creating an enabling environment for the industry to compete globally.
- Mission
- Promote domestic manufacturing in the entire value-chain of ESDM, including core components and materials to increase the domestic value addition and reduce dependence on import of electronic goods by focusing on scale, skill and technology.
- Strengthen India’s linkages with global trade, integrate with global value chains and build facilitative programmes and incentive framework to boost Indian ESDM exports.
- Develop capacities for manufacture in all sub-sectors of electronics, including semiconductor wafer fabrication and display fabrication (FAB) facilities and create a vibrant, dynamic and self-reliant Fabless Chip Design ecosystem in the country.
- Build a risk-management ecosystem to promote and create a framework for a comprehensive Start-up ecosystem with focus on development of products, key components and technologies based on emerging technological landscapes.
- Medical electronics, Defence Electronics, Automotive electronics, Industrial Electronics, Strategic Electronics, etc., and Fabless Chip Design.
- Become a global leader in the Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) segment by promoting progressively higher value addition in manufacturing of electronic products.
- Provide policy support and special package of incentives for highly capital intensive projects.
- Drive indigenization in the microchips used by strategic and critical infrastructure sectors viz., Defence, Space, Atomic Energy, Telecom, Aviation, Power, etc., through design and production of such microchips.
- Create specialized governance structures within the Government to cater to specific needs of the ESDM sector, in view of fast changes in technology and business models.
- Facilitate cost effective loans for setting up and expansion of electronics manufacturing units.
- Promote research, innovation and support to the industry in the areas of packaging, interconnects and micro photonics, as a long term measure to counter the problems posed by the continued use of Silicon, like the limit of scaling and dark Silicon.
- Promote research, innovation and support to industry for green processes and sustainable e-Waste management, including safe disposal of e-Waste in an environment friendly manner, development of e-Waste recycling industry and adoption of best practices in e-Waste management
- Strategy
-
- Creating eco-system for globally competitive ESDM sector
- Developing and Mandating Standards
- Ease-of-doing-Business
- Industry-led R&D and Innovation
- Human Resource Development
- Cyber Security
- Export Promotion
- Modified Special Incentive Package Scheme (M-SIPS)
- M-SIPS was launched in 2012 under NEP, 2012 and ended in 2018
- Aim
- To promote large-scale manufacturing in the Electronic System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM) sector
- Salient Features
- M-SIPS provides for 25% subsidy on capital investment along with a host of other incentives.
- It also provides for reimbursements of CVD/ excise for capital equipment for the non-SEZ units.
- The incentives are provided on reimbursement basis.
- The incentives were available for 29 electronic verticals.
- The investment threshold varies from Rs 1 Crore to Rs 5000 Crores depending upon a type of project. The incentives are available for 10 years from the date of approval. The scheme was initially opened for 3 years till 26-07-2015.The scheme was amended on August 3, 2015 and been extended up to31.12.2018.
- Electronics Manufacturing Clusters (EMC)
-
- Launched in 2012to overcome disadvantages due to infrastructure
- Encourages entities, including State Government entities, to provide good quality infrastructure within a cluster.
- Under the scheme, 50% of the project cost for Greenfield EMC and 75% for Brownfield EMC is given by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology as grant.
- Electronics Development Fund (EDF)
-
- In order to promote startups and innovation, a scheme called Electronics Development Fund (EDF) was launched.
- EDF is a fund of funds which invests in Venture funds, which in turn invests in ventures.
- At least 50% of the corpus has to be invested in Ventures working in ESDM sector.
- Under the scheme, 13 daughter funds have been approved with EDF commitment of Rs.857/crore. These funds are expected to invest Rs.6,951/- crore of corpus in startups.
- Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP)
-
- The Phased Manufacturing Programme (PMP) for mobile handsets and related subassemblies/ components manufacturing has been implemented with the objective of progressively increasing the domestic value addition for establishment of a robust Cellular mobile handsets manufacturing eco-system in the country.
- As a result, India has rapidly started attracting investments into this sector and Cellular mobile handsets manufacturing has emerged as a flagship sector in the electronics manufacturing space.


