

Shinzo Abe advocated closer India-Japan ties, sought to move beyond Tokyo’s post-war pacifist worldview
Context
The unfortunate demise of Japan former PM and India’s ally Shinzo Abe has shocked the world. India remembered its friend, who has led the India-Japan relations to the new heights, announced one day of state mourning.
About
Mapping the evolving relations
- The friendship between India and Japan has a long history rooted in spiritual affinity and strong cultural and civilization ties.
- India and Japan established diplomatic relations on 28 April 1952. Japan is regarded as a key partner in India’s economic transformation.
- In the recent past, the India Japan relationship has transformed to a partnership of great substance and purpose.
- Japan’s interest in India is increasing due to a variety of reasons including India’s large and growing market and its resources, especially the human resources.
Shinzo Abe’s Vision for India
Shinzo Abe (21 September 1954 – 8 July 2022), was a Japanese politician who served as prime minister of Japan and President of the Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) from 2006 to 2007 and again from 2012 to 2020.
- He was the longest-serving prime minister in Japanese history.
- Abe sees India as the key to expanding Japan’s security options beyond its current US-centric framework, while Modi views Japan as central to the success of India’s ‘Look East’
- ‘Abenomics’ and ‘Modinomics’ are both geared to the same goal – reviving laggard growth — yet they need each other’s support for success.
- Economic strategy for Japan: Whereas Tokyo sees New Delhi as important to its own economic-revival strategy; India looks at Japan as a critical source of capital and commercial technology and a key partner to help upgrade its infrastructure and manufacturing base.
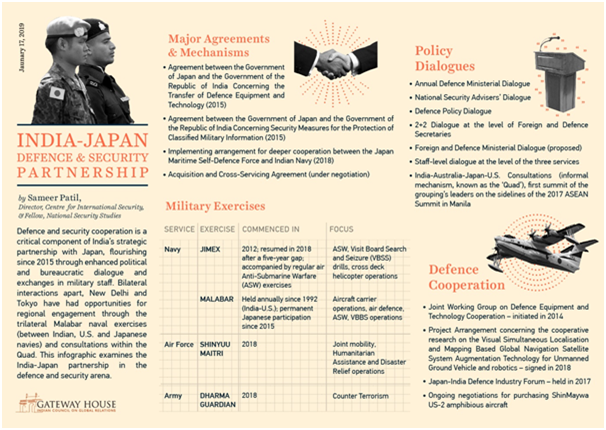
- Abe’s reassertion of the right of collective self-defence and his relaxation of Japan’s self-imposed arms export ban have opened the path to closer military cooperation with India, including co-production of weapon systems.
- Foreign investments: India — the biggest recipient of Japanese aid — has already become one of the largest destinations for Japanese FDI among major economies. Japan has a solid heavy manufacturing base, while India boasts services-led growth. India is a leader in software and Japan a leader in hardware.
- Attracting Demographic dividend: India has the world’s largest youthful population, while Japan is aging more rapidly than any other major developed country. Whereas Japan has financial and technological power, India has human capital and a huge market.

India Japan – Major Diplomatic Initiatives
- A Social Security Agreement (SSA)
- A bilateral swap agreement between the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Bank of Japan (BoJ).
- Political and security cooperation as mandated by the Action Plan of 2009 witnessed steady progress in 2012.
- A new Cyber Security Dialogue was held at Tokyo on 5 November 2012, while a newly established Maritime Dialogue.
- The 60th Anniversary of establishment of diplomatic relations between India and Japan was celebrated through various events both in India and Japan.
- QUAD grouping initiated by Japan.


