

Art and Culture (GS-I)
Kati Bihu 2023

Assamese people celebrate Kati Bihu on the first day of the ‘Kati’ month, which usually falls in the middle of October.
- Kati Bihu 2023 falls on October 18 this year.
About:
- Kongali Bihu or Kati Bihu as it is commonly known derives its name from the month of Kartik which is traditionally known as Kati.
- Unlike Bohag Bihu, Kati Bihu is not a flamboyant festival and the festivities are more sombre in nature.
- This Bihu is celebrated during the time of relocation of the rice sapling during the month of October.
- The granaries of the farmers usually remain empty during this time, hence it is known as Kongali (poor) Bihu.
History (GS-I)
King Kulashekara Alupendra I
Recently, the Archaeologist discovers inscription announcing the death of King Kulashekara Alupendra I at Someshwara.
|
The Someshwara inscription is very significant in the study of Tuluva history and culture. |
About:
- The inscription was the first record of the Alupas that announced the death of a king.
- It also mentioned terms related to the Siri cult, such as Siri, Dalya and Chattara (Chatra).
- The Keerthi sthamba or pillar found in the inscription is a replica of the original pillar found in the premises of a church in Kulashekara, a suburb of Mangaluru.
Who was King Kulashekara Alupendra I?
- Kulashekara Alupendra I was a famous ruler of the Alupas of South Canara.
- He was responsible for the establishment of new city called Kulashekara in Mangaluru.
- He also laid down strict rules and regulations for temple administration, which are still followed in all temples in this region.
- He was the first ruler to give royal patronage to Tulu language and culture, ruling from both the capitals, Mangaluru and Barkuru.
The Soma Cult:
- The Soma cult was founded by one Soma Sharma of Gujarat in the 11th century AD and it spread across the country.
- The Someshwara temple at Someshwara was built during the time of Kulashekara Alupendra in honour of Soma and adorned with Nava Durgas.
- Independent Navadurga sculptures in sitting posture are found in the temple.
International Relations (GS-II)
CCI becomes member of International Competition Network's steering group

CCI joins the prestigious Steering group of International Competition Network (ICN) as a member at the ICN Annual Conference 2023 at Barcelona, Spain.
About International Competition Network (ICN) :
- The ICN comprises 140 competition agencies from 130 countries.
- The ICN provides competition authorities with a specialised yet informal venue for maintaining regular contacts and addressing practical competition concerns.
|
Competition Commission of India (CCI):
|
Polity and Governance (GS-II)
Gyan Sahayak Scheme

As Gujarat government has announced Gyan Sahayak Scheme to fill vacancies in government schools with the appointment of teachers on contractual basis till the process of regular appointments is complete.
About:
- Gyan Sahayak Scheme is for government and grant-in-aid schools, especially for Mission Schools of Excellence.
- The government had declared hiring on contract 15,000 Gyan Sahayaks in primary schools and 11,500 in secondary and higher secondary schools.
- A primary school Gyan Sahayak is eligible for a salary of Rs 21,000, secondary school Gyan Sahayak for Rs 24,000 and higher secondary school Gyan Sahayak for Rs 26,000 per month.
- The Gyan Sahayaks will replace the Pravasi Shikshaks, a scheme announced to serve the same purpose in 2015.
Polity and Governance (GS-II)
Digital crop survey

The Centre has asked states and Union Territories to digitise the process by adopting the Digital Crop Survey system from July 2024.
Guidelines for the survey:
- All states/ UTs were ordered to automate/digitise the process of area enumeration/girdawari of crops at field level, i.e. Digital Crop Survey, from 2024-25 Agricultural Year.
- The states and UTs shall use GPS enabled mobile application for collecting crop sown data of each plot for each season and share the village level aggregated data with DA&FW (Department of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare) through API only.
- The states have been asked to collect information on “basic parameters”, including
- Village name, year, season, farmer ID, farm ID, crop name (at farm plot level), crop variety, crop sown area (at farm plot level),
- Geotags of crop photos, geotags of farm boundary where the crop is sown, sowing/planting date (at farm plot level),
- Irrigation type (at farm plot level), and irrigation source (at farm plot level).
Polity and Governance (GS-II)
“Chakra-II” operation

The Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has launched Operation Chakra-II to fight against transnational organised cyber-enabled financial crimes in India.
About:
- It is aimed at combating and dismantling infrastructure of organized cyber-enabled financial crimes in India.
- CBI conducted it jointly with national and international agencies and private sector giants.
- Chakra-1 was conducted by the CBI in coordination with the Interpol, the FBI and police forces of multiple countries.
- Under Operation Chakra-2 that targets cyber criminals, the central probe agency had recently conducted searches at Bengaluru, Cochin and Gurugram, and these yielded substantial evidence, shedding light on the alleged activities of the shell companies' directors.
Polity and Governance (GS-II)
Project ‘Udbhav’
Recently, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh formally launched the Army's new initiative, "Project Udbhav,”.
About the project:
- Objective: The project seeks to harmonise India's time-honored strategic knowledge with contemporary military methodologies, aimed at addressing modern security challenges and preparing for future conflicts.
- Project Udbhav seeks to integrate ancient wisdom, such as the Arthashastra and Thirukkural, with contemporary military practices.
- It also emphasizes the study of prominent leaders and battles of the past.
- The initiative will serve as the foundation for indigenous strategic developments and a future-ready Indian Army.
Economy (GS-III)
Star rating programme for solar PV modules

Union Minister for Power, New and Renewable Energy has launched the initiative which provides ratings to Solar PV modules from 1-5 stars on the basis of the efficiency.
About the initiative:
- The Indian government has launched a star rating programme for solar photovoltaic modules, allowing consumers to choose panels with higher efficiency.
- The initiative provides ratings from 1-5 stars based on module efficiency, helping consumers make informed decisions when purchasing solar installations.
- Aim: This will also help build consumer confidence and give a push to solar installations in the country.
- Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), under Ministry of Power, promotes the use of energy-efficient processes, equipment, devices and systems.
- It takes various steps to encourage preferential treatment for the use of energy-efficient equipment or appliances.
Economy (GS-III)
Purple Economy

Recently, the b/Changemakers Award winner Shanti Raghavan has been in news for helping disable people making a view towards ‘Purple economy’.
What is Purple economy?
- It is also referred to as the care economy. It recognizes the importance of care work, empowerment and autonomy of women to the functioning of the economies, wellbeing of societies, and life sustainability.
- Care work can be paid or unpaid. Men’s involvement in unpaid caregiving and domestic work is significantly lower compared to women.
- According to the ILO, the value of unpaid care work would be 0.4 percent of the GDP for men and 3.1 percent of the GDP for women.
Economy (GS-III)
India to surpass Japan to become 2nd largest eco in Asia by 2030: S&P Global

As per S&P Global Market Intelligence, India is likely to overtake Japan to become the world’s third-largest economy with a GDP of USD 7.3 trillion by 2030.
About the Report:
- India’s gross domestic product (GDP) is expected to grow 2-6.3 per cent in the fiscal year ending in March 2024, being the fastest-growing major economy this fiscal year.
- Asia’s third-largest economy grew by a stellar 7.8 per cent in the April-June quarter.
- This rapid pace of economic expansion would result in the size of the Indian GDP exceeding Japanese GDP by 2030, making India the second largest economy in the Asia-Pacific region.
- By 2022, the size of the Indian GDP had already become larger than the GDP of the UK and also France.
- By 2030, India’s GDP is also forecast to surpass Germany.
|
Present Global GDP scenario:
|
Science and Technology (GS-III)
Fast Radio Bursts

A new study that documented the most distant "fast radio burst" mentions that, the FRBs can be used to measure the mass of the universe.
What are Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs)?
- Fast radio bursts (FRBs) are intense blasts of radio waves that can emit as much energy as the sun puts out in three day.
- Radio dispersion is imparted on each burst by intervening plasma, mostly located in the intergalactic medium.
|
The first fast radio burst to be described, the Lorimer Burst FRB 010724, was found in 2007 in archived data recorded by the Parkes Observatory on 24 July 2001 |
- The bursts last for several milliseconds (thousandths of a second). The bursts come from all over the sky, and are not concentrated on the plane of the Milky Way.
- Known FRB locations are biased by the parts of the sky that the observatories can image.
Science and Technology (GS-III)
Niemann-Pick disease
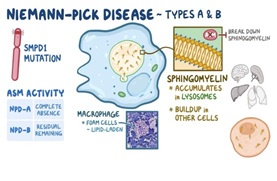
Families of two children diagnosed with the rarest of rare diseases — Infantile Hypophosphatasia and Niemann Pick — are struggling to get these genetic disorders included under the Centre’s National Policy for Rare Diseases (NPRD).
About the disease:
- Niemann-Pick disease refers to a group of inherited metabolic disorders in which abnormal amounts of lipids (fatty materials such as waxes, oils, and cholesterol) build up in the brain, spleen, liver, lungs, and bone marrow.
- Defective or insufficient amounts of enzymes are unable to break down lipids into smaller components to provide energy for the body.
- Symptoms may include:
- Ataxia (lack of muscle control during voluntary movements such as walking)
- Loss of muscle tone
- Brain degeneration
- Increased sensitivity to touch
Science and Technology (GS-III)
Gaganyaan Test Vehicle TV-D1

The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully conducted a test involving an in-flight abort demonstration and recovery of a crew module. The mission, known as the Gaganyaan Test Vehicle TV-D1.
About the Mission:
- The Gaganyaan Programme envisages undertaking the demonstration of human spaceflight to Low Earth Orbit (LEO) in the short-term.
- The overall programme co-ordination, systems engineering and implementation will be carried out by ISRO.
- The mission objectives of the TV-D1 launch were Flight demonstration and evaluation of Test Vehicle subsystems; flight demonstration and evaluation of Crew Escape System including various separation systems; crew module characteristics; and deceleration system demonstration at higher altitudes and its recovery.
Science and Technology (GS-III)
India Semiconductor Research Centre (ISRC)
![]()
The India Semiconductor R&D Committee handed over the report on the India Semiconductor Research Center (ISRC) to Union Ministry of State for Skill Development & Entrepreneurship and Electronics & IT.
About India Semiconductor Research Center (ISRC):
- The ISRC envisions the establishment of a world-class research institution focusing on;
- Semiconductor processes,
- Advanced packaging,
- Compound semiconductors and
- Fabless design and EDA tools.
- By fostering collaboration between industry, academia, and government, ISRC aims to nurture a vibrant semiconductor ecosystem.
- It is expected to facilitate seamless transfer from lab to fab, bridging the gap between research and manufacturing.
- The ISRC plans to invest strategically, focusing on achievable technology nodes and fostering collaborations with global research centres, academia and industry.
- The initiative aims to transform the centres of Excellence in India’s academic institutions into globally competitive entities, attracting global companies to India.
Science and Technology (GS-III)
Nuclear-powered lander for Saturn’s moon Titan

NASA is building a nuclear-powered lander for exploring ‘Titan’ — Saturn’s largest moon having a dense atmosphere and low gravity.
- The Lander is a part of Dragonfly spacecraft will be launched by 2027.
About:
- Titan is a major target in NASA’s quest to assess habitability and search for potential signs of life beyond Earth on worlds across the solar system.
- The lander, Dragonfly rotorcraft, is NASA’s only mission to the surface of another ocean world.
- Titan is also thought to have a subsurface ocean of water.
- The lander will be equipped with cameras, sensors and samplers to help examine swaths of Titan known to contain organic materials that may have come in contact with liquid water beneath the organic-rich, icy surface.
|
Titan: Saturn’s Largest Moon:
|
Species in News
Snow Leopard

Every year October 23 is celebrated as World snow leopard day to highlight the importance of the species.
About:
- Snow leopards live in the mountains across a vast range of Asia.
- They are insulated by thick hair—in shades of gray or creamy yellow and covered with grayish black spots—and their wide, fur-covered feet act as natural snowshoes.
- Habitat: They can be found throughout high mountain ranges, including the Himalayas and the southern Siberian Mountains in Russia.
- They can also be found in the Tibetan Plateau and across a range that stretches from China to the mountains of Central Asia.
- In India, their geographical range encompasses:
- Western Himalayas: Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh.
- Eastern Himalayas: Uttarakhand and Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
- Snow Leopard capital of the world: Hemis, Ladakh.
- Protection Status:
- The snow leopard is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN-World Conservation Union’s Red List of the Threatened Species.
- In addition, it is also listed in Appendix I of the Convention on International Trade of Endangered Species (CITES).
- It is listed in Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife (Protection) Act 1972.
Species in News
Saltwater crocodiles

Saltwater crocodiles (Crocodylus porosus) are also known as estuarine crocodiles.
- It is the largest of the 23 species of ‘extant’ or living crocodilians. This includes ‘true crocodiles’, alligators and caimans.
- It can also tolerate saltwater in the oceans and can travel long distances over the open ocean, making use of tidal currents.
- They are the largest living reptile, reaching up to seven metres in length.
- These crocodile species inhabit brackish waters of wetlands and marine intertidal environments from Sri Lanka, India, Bangladesh, and Myanmar east to the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu and south to Australia’s northern coast.
Found in India:
- They are found in three locations in India — the Sundarbans, Bhitarkanika National Park and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- It is one of the three crocodiles native to the Indian Subcontinent, along with the mugger crocodile (Crocodylus palustris) and the gharial (Gavialis gangeticus).
Species in News
Paintbrush swift butterfly

Under the Wild Bhattiyat Project initiated by the State Forest Department in 2022, a species of butterfly that is rare in the western Himalayas, the paintbrush swift butterfly has been documented for the first time in Himachal Pradesh’s Chamba district.
- It was first described by lepidopterist Frederic Moore more than 145 years ago.
About the Species:
- The paintbrush swift is a butterfly species of the Hesperiidae family.
- Scientific name: Baoris farri
- It is identified based on two separated spots in the upper forewing cell.
- The species’ larvae feed on bamboo and some other grass species.
- Habitat: Its habitat is distributed in northeast, central and south India, and rare in Uttarakhand.
- Threats: Habitat loss and scarcity of larval host plants are major causes of the decline in the butterfly population. An increase in pesticide use, deforestation, and climate change.
- Conservation status: This species is legally protected in India under Schedule IV of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.




