

Indian astronomers have found evidence of supernova remnants in a star-forming region called G351.7–1.2.
Context
Indian astronomers have found evidence of supernova remnants in a star-forming region called G351.7–1.2.
Abuot
More in News
- The Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT), operated by the National Centre of Radio Astrophysics in Pune was used in observation.
- The evidence of explosion observed by Indian Astronomers is in the form of a high-velocity jet of atomic hydrogen. It implies that the explosion should have resulted in a compact stellar object such as a neutron star or a pulsar or a black hole. However, there is no trace of either yet.
- Therefore, it is an evidence of a supernova explosion but could not find the leftover of the massive star.
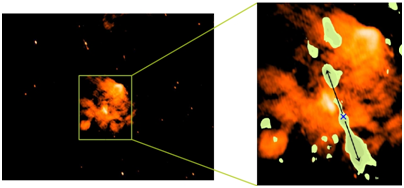
Figure 1: Pale green denotes the atomic hydrogen
Supernova - A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space. Supernovas are difficult to see in our own Milky Way galaxy because dust blocks our view.
Occurrence - Astronomers believe that about two or three supernovas occur each century in a particular galaxy. There are two different ways in which a supernova can occur:
- In a Binary Star System – One of the stars (white dwarf - a star near the end of its life that has used most or all of its nuclear fuel) steals matter from the companion star. Eventually, the white dwarf accumulates too much matter. Having too much matter causes the star to explode, resulting in a supernova.
- In a Single Star System - As the star runs out of nuclear fuel, some of its mass flows into its core. Eventually, the core becomes so heavy that it cannot withstand its own gravitational force. The core collapses, which results in the giant explosion of a supernova. The sun is a single star, but it does not have enough mass to become a supernova.

Past Observations
Supernovas can be observed through variety of telescopes. Some telescopes are used to observe the visible light from the explosion while others record data from the X-rays and gamma rays that are also produced during the explosion.
- In 1604, Johannes Kepler discovered the last observed supernova in the Milky Way.
- NASA’s Chandra telescope discovered the remains of a more recent supernova. It exploded in the Milky Way more than a hundred years ago.
Significance of Supernovas
- Supernovas play a key role in distributing elements throughout the universe. When the star explodes, it shoots elements and debris into space. Many of the elements we find here on Earth are made in the core of stars.
- Supernovas have shown scientists that we live in an expanding universe, one that is growing at an ever increasing rate.
- Supernovas help scientists in measuring distances in space.


