

5th March 2025 (11 Topics)
Context
The Supreme Court of India directed State governments to consider framing guidelines to prevent private hospitals from overcharging patients for medicines, medical devices, implants, and consumables by forcing them to purchase from hospital-owned pharmacies. However, the court also cautioned against harsh regulations that could discourage private investment in healthcare.
Supreme Court’s Observations
- Need for Private Sector in Healthcare: The court acknowledged that States depend on private hospitals to provide basic and specialized healthcare services due to gaps in public health infrastructure.
- Until government facilities are strengthened, private hospitals play a crucial role in healthcare delivery.
- States Should Frame Guidelines: The court refrained from mandating strict rules but urged State governments to consider policies ensuring fair pricing.
- Caution Against Overregulation: States must balance consumer protection with the growth of private healthcare infrastructure.
Scenario of the Healthcare Sector in India
- India's healthcare industry is vast, covering hospitals, medical devices, clinical trials, telemedicine, medical tourism, health insurance, and medical equipment. The healthcare system is divided into:
- Public sector: Government-run Primary Healthcare Centres (PHCs) in rural areas and limited secondary and tertiary hospitals in key cities.
- Private sector: Dominates secondary, tertiary, and quaternary healthcare, mostly in metros, Tier-I, and Tier-II cities.
Private Healthcare in India
- Dominant role: Private spending makes up nearly 60% of total healthcare expenditure.
- Dispersed sector: Private healthcare is fragmented with rural-urban disparities, market failures, and income-based segmentation.
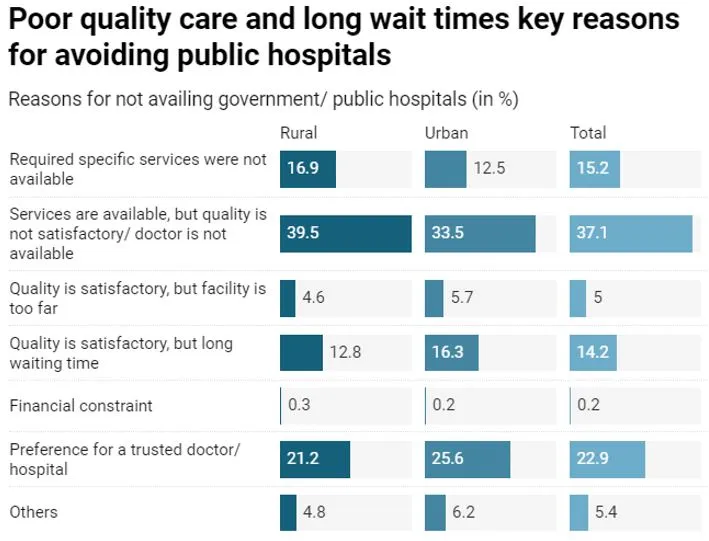
- Why is private healthcare not affordable in India?
- High-cost urban concentration of quality private healthcare.
- Fragmentation leading to uneven service delivery.
- Expensive insurance packages with limited benefits.
Key Challenges in Healthcare
- Limited Access to Basic Healthcare Shortage of medical professionals and quality assurance.
- Low government health spending leads to gaps in services.
- Lack of preventive care leads to high disease burden and costs.
- Low Budget Allocation: India spends only 1% of GDP on healthcare (2021-22). Developed countries like Japan, Canada, and France spend 10%. Even Bangladesh and Pakistan spend over 3%.
- Lack of Medical Research & Innovation: R&D in healthcare is Furthermore, there is limited focus on cutting-edge technology and new medical projects.
- Shortage of Healthcare Professionals: India lacks 600,000 doctors, as per government data. Nurses and paramedics are also in short supply.
- Poor Infrastructure & Resources: Overcrowded hospitals, inadequate staff, and lack of medicines.
Fact Box:
|
More Articles


