

19th June 2024 (10 Topics)
Context
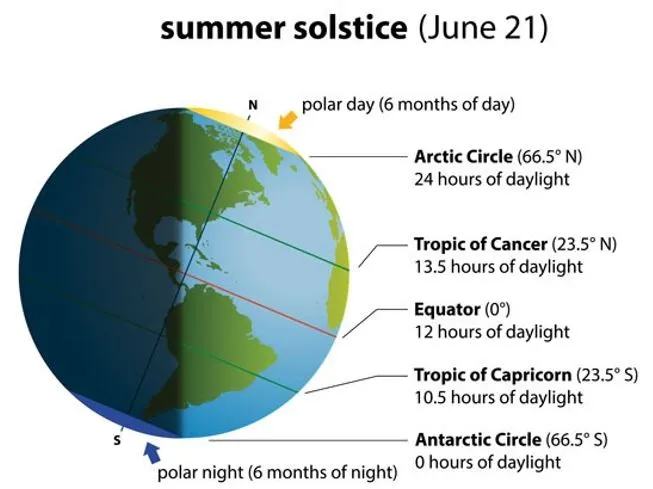
The Summer Solstice (June 21) is a significant astronomical event celebrated worldwide, marking the longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
What is the Summer Solstice?
- The term "solstice" describes the moment when the sun reaches its highest point in the sky, appearing to pause briefly before reversing its direction.
- This phenomenon signifies a pivotal moment in Earth's orbit around the sun, affecting daylight duration.
Why Does the Summer Solstice Occur?
- Earth's axis is tilted approximately 5 degrees relative to its orbit around the sun.
- Summer solstice: During the summer solstice, the Northern Hemisphere tilts closest to the sun, resulting in the longest day of sunlight for these regions.
- Winter solstice: Conversely, the Southern Hemisphere experiences its shortest day, marking the beginning of winter.
- Impact in India:
- In India, the Summer Solstice heralds the longest day of the year, characterized by extended daylight hours.
- The sun's rays fall directly overhead, creating the highest point of the sun in the sky.
- This alignment ensures more daylight than any other day of the year, marking the peak of summer and influencing various cultural and agricultural practices.
More Articles


