

19th June 2024 (10 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
RBI Governor Shaktikanta Das recently addressed inflation trends in India, noting that while overall inflation is easing, food inflation remains a significant challenge.
What is disinflation?
- Disinflation is the term used to describe a period of slowing inflation.
- In contrast to inflation which refers to price direction, disinflation refers to the rate of inflation change. Disinflation is not problematic, and it is different from deflation.
- Achieving disinflation is crucial for economic stability, as it helps maintain purchasing power and encourages investment.
- Current Inflation Trends
- Recent Figures: Retail inflation in May 2024 was at 4.75%, slightly down from 4.83% in April 2024, and lower than 4.31% in May 2023.
- Core Inflation: Stood at 3% in May 2024.
- Food Inflation: Remained high at 7.9% in May 2024.
Impact of Food Inflation on Disinflation
- Resistance to Disinflation: High food inflation is slowing the disinflation process.
- Supply-Side Factors: Weather conditions, including extreme heat, have affected the cultivation of pulses and vegetable production.
- Average Food Inflation: Stood at around 8% over the past six to seven months.
RBI's Policy and Projections
- Monetary Policy: The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee has kept the repo rate unchanged at 6.5% due to food inflation concerns.
- Future Policy Considerations
- Policy Stance: Governor Das indicated it is premature to change the policy stance of withdrawal of accommodation.
- Focus: The RBI aims to remain cautious and monitor inflation trends closely.
How Food Inflation Disrupts Disinflation?
India has been experiencing a slow pace of disinflation despite efforts to control inflation. A significant factor hindering this process is high food inflation.
- Persistent High Food Prices
- Food Inflation Rate: In May 2024, food inflation was at 7.9%, significantly higher than the overall inflation rate of 4.75%.
- Sticky Prices: Food prices have remained persistently high, with an average food inflation rate of around 8% over the past six to seven months.
- Supply-Side Constraints
- Weather Impact: Extreme weather conditions, such as the intense heat experienced last summer, have negatively impacted the cultivation of pulses and vegetables.
- Supply Disruptions: Adverse weather conditions lead to reduced agricultural output, causing supply shortages and driving up food prices.
Fact Box:
|


Mains Issues
Context
Prime Minister Modi recently honored over 30,000 women from Self Help Groups (SHGs) by granting them certificates as Krishi Sakhis. This initiative underscores the government's commitment to rural empowerment, particularly acknowledging women's pivotal role in agriculture.
About the Krishi Sakhi Convergence Programme (KSCP):
- The Krishi Sakhi Convergence Programme (KSCP) is a joint initiative led by the Ministry of Agriculture and Ministry of Rural Development.
- It aims to enhance the skills and contributions of rural women in agricultural activities and related businesses.
- Training and Certification: KSCP focuses on training rural women, termed Krishi Sakhis, as Para-extension Workers. These women undergo comprehensive training for 56 days, covering various aspects such as soil health, integrated farming systems, livestock management, and agroecological practices.
- Extension of 'Lakhpati Didi' Programme: KSCP is an extension of the government's ambitious 'Lakhpati Didi' initiative, which aims to empower women by creating opportunities for economic self-sufficiency.
- The programme aligns with the goal of elevating rural women to the status of proficient para-extension workers.
Significance of Krishi Sakhis as Para-extension Workers:
- Utilization of Expertise: Leveraging their existing knowledge and experience in agriculture, Krishi Sakhis serve as trusted community resources. They play a crucial role in disseminating agricultural best practices and promoting sustainable farming techniques among rural communities.
- Income Generation: After completing the certification course and passing a proficiency test, Krishi Sakhis can earn between ?60,000 to ?80,000 annually as para-extension workers. This income opportunity not only supports their livelihoods but also strengthens the rural economy.
- Expansion and Implementation: The programme is currently operational in 12 states across India, including Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, and others. Plans are underway to expand it to additional states in subsequent phases, aiming for broader coverage and impact.


Mains Issues
Context
The Indian government has proposed a significant infrastructure upgrade on Great Nicobar Island, encompassing an International Container Transshipment Terminal (ICTT), a greenfield international airport, a township, and a power plant. This initiative is part of a broader plan for the holistic development of the island, aimed at leveraging its strategic location in the Bay of Bengal.
About the project
- Project title: ‘Holistic Development of Great Nicobar Island at Andaman and Nicobar Islands’
- Cost: Rs 72,000 crore
- Implemented by: Andaman and Nicobar Islands Integrated Development Corporation (ANIIDCO).
- The project has four components –
- an International Transhipment Port (ITP)
- Greenfield International Airport
- a power plant
- a new township that could constitute a Special Economic Zone
- These four interlinked projects form the core of the new city and the holistic master plan.
Significance of the project:
- Great Nicobar Island holds strategic significance due to its proximity to major international maritime routes, including the Malacca Strait.
- The ICTT is expected to enhance India's participation in the global maritime economy and bolster regional connectivity.
- Additionally, the region's military upgrade aims to strengthen India's defense posture in response to geopolitical developments, particularly concerning Chinese naval activities in the Indo-Pacific.
Environmental Concerns and Opposition
- The proposed project has faced opposition from conservationists, wildlife experts, and local tribal councils, citing concerns over its environmental impact.
- Critics argue that the development could lead to deforestation, threaten marine ecosystems, and endanger vulnerable species like the Nicobar Megapode and leatherback turtles.
- There are also apprehensions about the potential disruption to the indigenous Shompen tribe's habitat and traditional way of life.
Steps were taken to mitigate the Losses:
- Building Coral population: Proposed mitigation measures to compensate for these damages include coral translocation and reef restoration in Galathea Bay.
- Compensatory Afforestation: Authorities plan to balance the loss of 12-20 hectares of mangroves here by ‘re-densifying’ existing mangrove patches and planting mangroves in non-forest areas.
- Declaring Protected areas: Mitigation measures also include intent to declare new protected areas, as well as the drawing up of monitoring and action plans to study threatened wildlife.


Mains Issues
Context
Himachal Pradesh (H.P.) is currently grappling with a severe spate of forest fires, with 1,684 incidents reported, affecting 17,471 hectares of forest land. These fires pose significant threats to wildlife and contribute to environmental degradation in the region.
Causes of Forest Fires
- Forest fires in Himachal Pradesh primarily occur during the pre-monsoon summer, exacerbated by moisture stress after snowmelt depletion.
- Human activities such as unattended campfires and discarded cigarettes also contribute to the outbreak of fires.
- Faulty forestry practices and a utilitarian approach to forest management further exacerbate the problem.
Impact on Environment and Climate
- Forest fires in the Himalayas
- release pollutants like black carbon
- Accelerates glacier melt
- negatively impacts regional climate patterns
- Historical transformations in Himalayan forests, driven by commercial interests, have reduced ecological resilience, making them more susceptible to fires.
Historical Transformation of Himalayan Forests
- Over the past two centuries, Himalayan forests have undergone significant transformations due to colonial-era forestry policies focused on commercial exploitation.
- The shift from Banj oak to commercially valuable Chir pine has altered forest ecosystems, affecting water retention and local livelihoods dependent on forest resources.
Challenges and Recommendations
- Challenges:
- Lack of community participation in forest management despite constitutional provisions.
- Curtailment of traditional forest rights, hindering local communities' ability to respond effectively to forest fires.
- Easy forest diversion for large-scale development projects like hydroelectricity and road infrastructure.
- Recommendations:
- Democratize forest management to involve local communities in decision-making processes.
- Restore traditional forest rights to enable effective forest protection and management.
- Implement mixed forestry approaches, reducing monoculture of vulnerable Chir pine.
- Integrate scientific knowledge with traditional practices for sustainable forest management.
- Establish local environmental services and infrastructure like check dams to revive water springs and mitigate fire risks.


Prelims Articles
Context
The Summer Solstice (June 21) is a significant astronomical event celebrated worldwide, marking the longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere.
What is the Summer Solstice?
- The term "solstice" describes the moment when the sun reaches its highest point in the sky, appearing to pause briefly before reversing its direction.
- This phenomenon signifies a pivotal moment in Earth's orbit around the sun, affecting daylight duration.
Why Does the Summer Solstice Occur?
- Earth's axis is tilted approximately 5 degrees relative to its orbit around the sun.
- Summer solstice: During the summer solstice, the Northern Hemisphere tilts closest to the sun, resulting in the longest day of sunlight for these regions.
- Winter solstice: Conversely, the Southern Hemisphere experiences its shortest day, marking the beginning of winter.
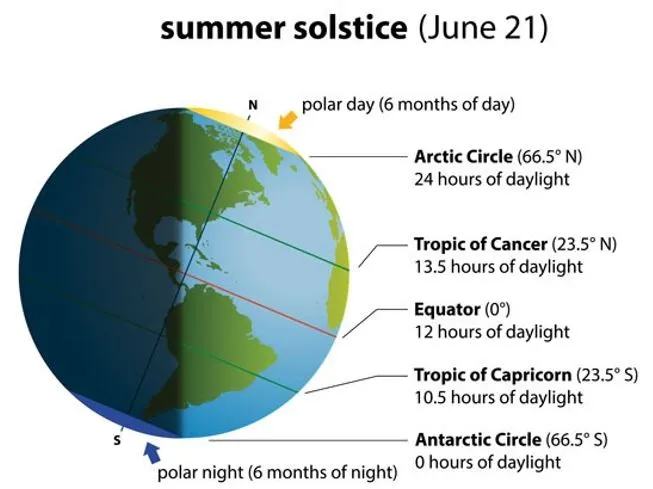
- Impact in India:
- In India, the Summer Solstice heralds the longest day of the year, characterized by extended daylight hours.
- The sun's rays fall directly overhead, creating the highest point of the sun in the sky.
- This alignment ensures more daylight than any other day of the year, marking the peak of summer and influencing various cultural and agricultural practices.


Prelims Articles
Context
Recently, K Suresh from the Congress party has been appointed as the pro-tem Speaker in the Lok Sabha. This appointment holds significance as it precedes the formal election of the Speaker of the House.
What is a Speaker pro-tem?
- Temporary Position: The Speaker pro-tem is appointed temporarily.
- Appointment: Appointed by the President of India, the pro-tem Speaker is traditionally the most senior member of the House.
- Duties: The pro-tem Speaker has several crucial responsibilities, including:
- Presiding over the first sitting of the Lok Sabha.
- Conducting the floor test to ascertain the government’s majority.
- Overseeing the vote to elect the Speaker and Deputy Speaker.
- Administering the oath of office to newly elected MPs: It is the pro-tem Speaker’s primary duty.
- Under Article 99 of the Constitution, “Every Member of the House shall, before taking his seat, make and subscribe before the President or some person appointed in that behalf by him, an oath or affirmation according to the form set out for the purpose in the Third Schedule of the Constitution.”
- Duration: The pro-tem Speaker’s tenure concludes once the new Speaker of the House is elected.
- The Constitution does not mention the post.
Fact Box: The Role of the Speaker
|


Prelims Articles
| S.N.O. | Term | About |
|
1. |
Disinflation |
It refers to a decrease in the rate of inflation over time. It is a situation where the general price level of goods and services in an economy is still rising, but at a slower rate compared to previous periods. Unlike deflation, where prices actually decrease, disinflation implies that the rate of price increases is slowing down. |
| 2. | Food Inflation |
It refers to the sustained increase in the prices of food items over time, impacting the cost of living and household budgets across the country. It is measured by tracking changes in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) for food items. |
| 3. | Global economic decoupling |
It refers to a phenomenon where the economic growth trajectories of different countries or regions become less synchronized or interdependent. |


Editorials
Context
The G-7 Outreach Summit hosted by Italy’s Prime Minister Giorgia Meloni invited leaders from the Global South, including Prime Minister Narendra Modi, emphasizing the need to move beyond the “West vs the Rest” mentality and addressing global issues in a broader, more inclusive manner.
G-7's Diminished Impact
- Pandemic and Conflict: The COVID-19 pandemic and Russia-Ukraine conflict have highlighted the G-7's diminished efficacy.
- Electoral Instability: Shaky electoral fortunes of G-7 leaders have weakened the group's impact.
- Unresolved Issues: The summit's communiqué failed to present strong action plans, particularly on the Ukraine war and Gaza ceasefire.
Focus on China and Infrastructure
- China's Influence: The G-7's focus on China's practices was prominent but lacked actionable plans.
- Trade Ties: It remains uncertain if member countries will reduce their trade with China.
- Infrastructure Projects: The communiqué reiterated commitment to infrastructure corridors, including the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, but execution remains doubtful.
India’s Participation
- Engagement Utility: India, attending for the eleventh time, may reassess the utility of G-7 engagement.
- Focus Areas: Prime Minister Modi emphasized elections as democratic victories, technology, AI, and the Global South.
- Preferred Platforms: Many of these issues might be better addressed within the larger, more representative G-20 format.
UPSC Mains Question
Q. Discuss the relevance of the G-7 in the current global power dynamics and the potential for India to leverage its participation in the G-20 for addressing global inequalities and development issues.


Editorials
Context
U.S. President Joe Biden's announcement in May to impose new tariffs on Chinese imports has reignited fears of economic decoupling between major global economies, influencing policymakers in Europe and highlighting geopolitical tensions.
Political Over Economic Considerations
- National Security Focus: The West's trade risk calculations with China are increasingly driven by national security concerns.
- Biden's Tariff Strategy: The new tariffs, especially on Chinese electric vehicles, are politically motivated to support domestic industries and unions.
- Medical Device Tariffs: Increased tariffs on Chinese medical devices aim to reduce dependence on China but could raise healthcare costs in the U.S.
Global Economic Impact
- Protectionism Consequences: The cycle of tit-for-tat tariffs exacerbates global protectionism, harming international trade.
- Green Transition Delays: Import restrictions on Chinese clean energy products could hinder global renewable energy goals.
- Multinational Challenges: Western companies dependent on China's consumer market face potential earnings declines due to China's economic slowdown.
Regional Effects
- Resource-Rich Countries: Countries like Australia and Brazil may suffer from reduced Chinese demand, impacting their exports and commodity prices.
- EU De-Risking: The EU's efforts to de-risk trade with China in raw minerals could backfire, giving China more control over supply chains.
- Southeast Asia and India: Southeast Asia and India may struggle to replace China as a manufacturing hub due to high dependency on Chinese technology and investment.
UPSC Mains Question
Q. Discuss the implications of the recent U.S. tariffs on Chinese imports for global trade dynamics and the potential impact on regional economies, with a focus on protectionism and economic decoupling.


Editorials
Context
The Indian Railways is under scrutiny after a freight train collided with a passenger train near Siliguri, West Bengal, on June 16, resulting in nine deaths and over 40 injuries. This incident is part of a troubling history of deadly train accidents in India, raising concerns about railway safety and efficiency.
Historical Context and Safety Issues
- Recurring Accidents: Since 1995, India has witnessed seven major train accidents, causing over 1,600 deaths.
- Safety Concerns: Frequent derailments and collisions highlight the persistent safety issues within Indian Railways.
- CAG Reports: Recent reports from the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) reveal high rates of asset failures, including signal failures and rail fractures, contributing to these accidents.
Declining Market Share and Performance
- Stagnant Traffic: Since 2010-12, Indian Railways has seen stagnation or decline in both freight and passenger traffic.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Road and air transport modes have grown 6-12% annually, while railways lag behind.
- Operational Speed: Despite claims of improvements, the average speed of trains has not increased significantly, undermining efforts like Mission Raftar.
Questionable Priorities and Future Outlook
- Misplaced Priorities: Investments in high-cost projects like bullet trains and dedicated freight corridors have not addressed core issues of safety and efficiency.
- Semi-High-Speed Trains: The introduction of Vande Bharat trains focuses more on luxury than on substantive speed improvements.
- Need for Review: A thorough review of priorities and strategies is essential to prevent the terminal decline of Indian Railways.
UPSC Mains Question
Discuss the current challenges facing Indian Railways, including safety issues, declining market share, and the impact of recent policy decisions. What steps should be taken to revitalize the railways and ensure it meets the needs of a densely populated, developing country like India?




