

27th June 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
Assam received 1,891.9 mm of rainfall from March 1 to June 24, just 347.5 mm less than the annual precipitation the State receives.
About
- Overall less: The country received 2% less rain this year than it usually does between June 1 and June 23 every year.
- Regional variations: The total rainfall was brought down by 34% over central India and 15% over peninsular India compared to the 32% more received by the east and northeast and 7% more by northwest India.
- Meteorologists said the recent episode of heavy rainfall underlined the presence of the east-west trough in the lower levels of the atmosphere over the region and the incursion of large-scale moisture due to strong southerly and south-westerly winds from the Bay of Bengal.
What are the factors determining rainfall pattern?
- Assam, which receives rainfall beyond the June-September monsoon phase, does not always get above-normal or excess rain.
- According to the IMD, Assam in 2022 received 41% above normal rainfall during the pre-monsoon season (March to May).
- Assam has received 71% more than normal rainfall up to June 25.
- Climate change is said to have increased the water and surface temperature of the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal by up to 2 degrees.
- This causes the frequent formation of low-pressure areas and cyclonic circulations, resulting in heavy rains.
- Rising black carbon emissions:
- A recent study by the IIT, Guwahati said aerosols, including black carbon, released by biomass burning, influence the western part of northeast India close to the Indo-Gangetic Plain the most.
- Rising black carbon emissions leads to a decrease in low-intensity rainfall while pushing up severe rain in the pre-monsoon season in northeast India.
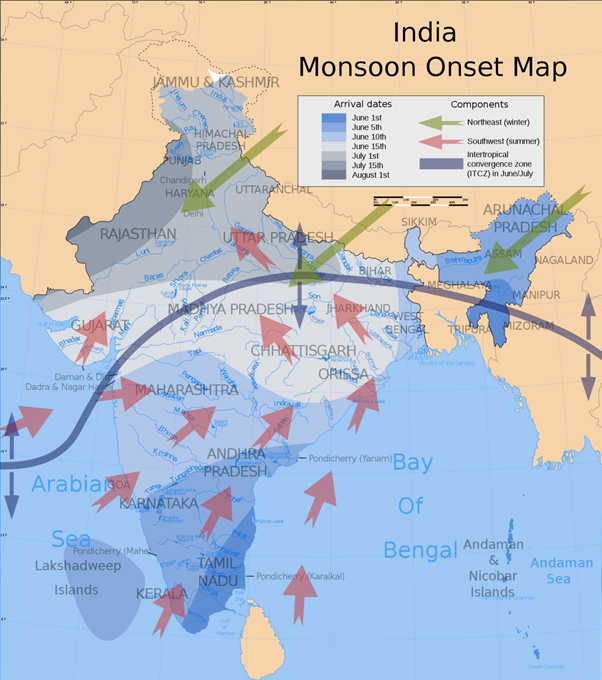
Monsoon in India:
- The seasonal monsoon winds are an extremely complex and intricate combinations of physical processes that operate not only in the atmosphere but also involve land and ocean.
- In India, June 1 is regarded as the date of arrival of the monsoon, which accounts for about 80% of the rainfall in the country.
- The key monsoon months are July and August and they bring nearly two-thirds of the monsoon rains.
- The monsoon in 2022 landed early in Kerala, three days ahead of the normal date, but then it turned sluggish on its western branch’s upward journey.
- Central India suffered a deficit, the east and north-eastern parts battled a diametrically opposite problem — excess rain — leading to widespread floods in Assam and Meghalaya.
- Synoptic Disturbances:
- The most important synoptic disturbances during the monsoons over India are disturbances (lows, depressions, etc.) that form mostly over the Bay of Bengal, move westwards or west north-westwards along the monsoon trough, and produce a large volume of rainfall.
- The other synoptic disturbance which affects monsoon rainfall significantly is the position of offshore trough or vortex along the west coast of India.
- Monsoon rainfall in India is known to be affected by global phenomena such as El Nino or La Nina — large-scale warming or cooling events of the sea surface.
- Other factors such as the Indian Ocean Dipole and Madden-Julian Oscillation also influence monsoon rainfall.
More Articles


