7th September 2024 (8 Topics)
Context
Punjab and Haryana, two key states in India's Green Revolution history, are facing contrasting agricultural challenges. This issue is significant as both states have significantly shaped India's rice and wheat production.
Agricultural Patterns in Punjab
- Monoculture Dominance:
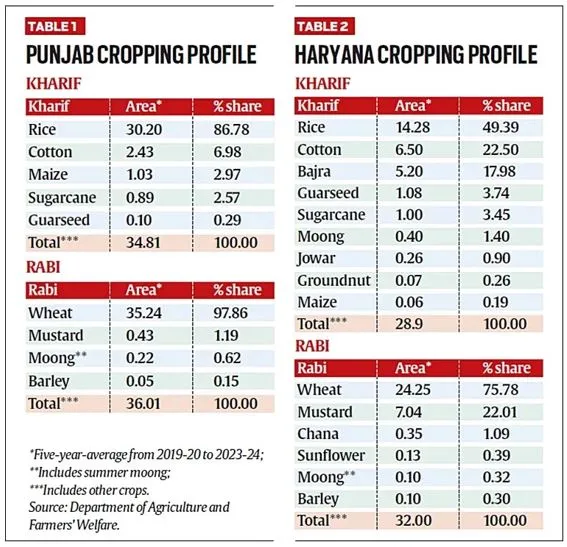
- Rice-Wheat Cycle: Punjab’s agriculture is heavily reliant on a monoculture system, focusing predominantly on rice and wheat. Rice is grown during the kharif season (monsoon), while wheat is cultivated in the rabi season (winter-spring).
- Crop Share: Over the past five years, rice has occupied about 86.8% of Punjab’s kharif crop area, and wheat has covered approximately 97.9% of the rabi area.
- Expansion and Challenges:
- Increased Area: The area under rice cultivation in Punjab has risen significantly from 20.2 lakh hectares in 1990-91 to 31.9 lakh hectares in 2023-24. Wheat cultivation has also increased, though less dramatically.
- Water Use and Groundwater Depletion: Rice is water-intensive, requiring about 25 irrigations compared to wheat's 4-5. This has led to severe groundwater depletion and fiscal issues related to grain procurement and storage.
Agricultural Patterns in Haryana
- Diversification Approach:
- Varied Cropping: Haryana exhibits a more diversified cropping pattern.
- Kharif season: Rice occupies less than half of the crop area, while crops like cotton, bajra (pearl millet), and guar (cluster bean) are also cultivated.
- Rabi season: Rapeseed-mustard, chickpea, and sunflower.
- Basmati vs. Non-Basmati Rice: Haryana’s rice cultivation includes a significant portion of basmati varieties (56.2% of rice area), which are less water-intensive and not subject to fixed minimum support prices (MSP), reducing surplus issues.
- Varied Cropping: Haryana exhibits a more diversified cropping pattern.
- Irrigation and Crop Mix:
- Irrigation Infrastructure: Haryana has an extensive canal network but faces irrigation constraints in southern districts. This limited irrigation leads to the cultivation of drought-resistant crops like bajra and guar in those areas.
- Challenges and Adjustments: Haryana’s government promotes crop diversification through MSP and the Bhavantar Bharpai Yojana (BBY) scheme to cover price differences for crops like bajra, mustard, and sunflower.
Environmental and Economic Impacts
- Punjab:
- Environmental Strain: The heavy reliance on rice has strained water resources and contributed to groundwater depletion.
- Economic Concerns: The surplus grain procurement has led to high fiscal costs and logistical challenges.
- Haryana:
- Balanced Approach: Haryana’s diversified cropping helps in managing water resources better and reduces reliance on a single crop.
- Promotion of Diversification: The state's policies and incentives aim to balance agricultural risk and economic stability by encouraging a range of crops.
More Articles