

12th April 2025 (11 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar has called for accelerated trade deals with Western economies, following the US’s new import tariffs under the Trump Tariffs 2.0 policy. His remarks reflect India’s shift in strategic trade alignment and highlight the urgency in finalising free trade agreements (FTAs) with the US, EU, and UK amid rising US–China rivalry.
Why this shift is significant?
- For many years, India was more open to trading with countries in East and Southeast Asia (like China), but that openness led to cheap imports hurting Indian industries, especially small businesses.
- India is now accelerating trade negotiations with the US, EU, and UK, recognising that these economies offer rule-based systems, legal contract enforcement, and higher absorption for value-added exports.
- India has historically been hesitant on FTAs due to fears of import surges and industry backlash (e.g., RCEP withdrawal).
- But today’s shift is not ideological, it's strategic and necessity-driven, powered by:
- China’s overcapacity export model
- Fear of being excluded from Western supply chains
- The need to anchor domestic reforms to global competition
Why the timing is perfect for the shift?
- Disruption: Protectionist waves, supply chain vulnerabilities, and rising geopolitical competition have severely disrupted international trade in recent years.
- Bipolar Competition: The world is moving into a “US vs China” economic rivalry, and supply chains are shifting. India has a chance to replace China in some areas — but it must act fast. FTAs can help India become part of trusted global supply chains and reduce dependency on uncertain markets.
- Demography: India is entering its prime-age labour force boom (25–54 yrs), just as China’s workforce begins to shrink.
- Geopolitics: The West wants to de-risk supply chains away from China, and India is among the few with both scale and democracy.
- Technology: India has the human capital for semiconductors, AI, and clean tech manufacturing, but lacks global supply chain access — which FTAs can unlock.
Fact Box: Steps taken by India to diversify trade
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Odisha has rolled out a unified health insurance scheme aimed at expanding access to quality healthcare for its residents. This marks the first time Odisha has implemented the Central scheme, after years of running its own health program separately.
About the Scheme:
- The unified health coverage scheme aims to provide free and cashless healthcare to all eligible families in Odisha.
- The scheme integrates the Centre’s Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) with the state-sponsored Gopabandhu Jan Arogya Yojana (GJAY).
- Coverage:
- 03 crore families (3.46 crore people)
- Health cards for every family member
- Free treatment for over 23 lakh senior citizens
- Hospital Access: It is valid in over 29,000 hospitals in Odisha and across India.
- Special Focus: It combines the benefits of both state and central schemes to ensure universal and equitable health coverage.


Prelims Articles
Context
The United States’ "Returning Education to Our States Act," proposes the elimination of the U.S. Department of Education. This initiative aligns with the Trump administration's broader agenda to decentralize federal control over education, as outlined in the Project 2025 framework. In contrast, India's education system operates under a dual framework where both the Central and State governments play pivotal roles.
Key Provisions of the Bill:
- Abolition of the Department: The bill seeks to dismantle the Department of Education, redistributing its responsibilities to other federal agencies. ?
- Reallocation of Programs:
- The Department of Health and Human Services would assume control over programs under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act and Impact Aid.
- The Department of the Interior would manage the Office of Indian Education.?
- The Department of the Treasury would oversee federal student aid programs, including Pell Grants and federal student loans.?
- State-Controlled Block Grants: States would receive federal education funds through block grants, granting them discretion over the use of these funds for elementary, secondary, and postsecondary education. ?
- Civil Rights Oversight: The Department of Justice's Civil Rights Division would be responsible for enforcing federal civil rights laws applicable to these block grant programs and federal student aid programs.?
India's Dual Governance Structure in Education
|


Prelims Articles
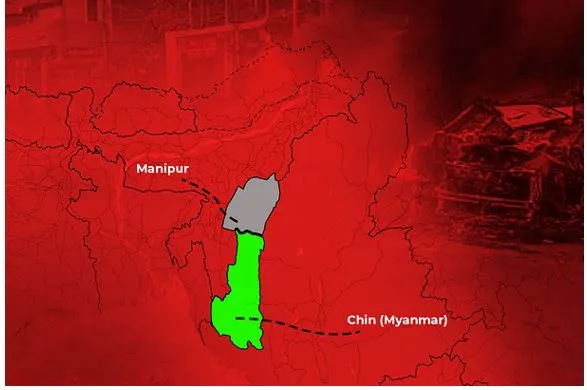
Context
The situation in Myanmar's Chin State is directly impacting India's northeastern region, particularly Manipur and Mizoram. The conflict in Chin State has led to an influx of refugees into these states, straining resources and escalating ethnic tensions.
About
- Chin State shares a 398-kilometer border with India's northeastern states, including Manipur and Mizoram.
- It is located in western Myanmar.
- Ethnically, the Chins are closely related to the Kukis of Manipur and the Mizos of Mizoram, forming part of the larger Zo ethnic group.
- The region has been embroiled in conflict since the military coup in Myanmar, with various ethnic armed organizations (EAOs) resisting the junta's rule.
- The Chin National Front (CNF) and its armed wing, the Chin National Army (CNA), have been at the forefront of this resistance.?
Fact Box: Manipur Conflict
|


Prelims Articles
Context
India’s Index of Industrial Production (IIP) growth slowed sharply to 2.9% in February 2025, marking the lowest expansion in six months. The slowdown was primarily driven by weaker performance in manufacturing and mining sectors. This data is crucial as it reflects the health of core industries and overall economic momentum.
Key Highlights
- Headline IIP Growth Slows: Industrial output grew by only 2.9% in February 2025, compared to 5.2% (revised) in January 2025. This is the lowest growth since August 2024, when IIP had registered zero growth.
- Sectoral Performance
- Manufacturing (77.6% weight in IIP): Grew by 9%, down from 5.8% in January.
- Mining (14.4% weight): Slowed to 6%, from 5.6%.
- Electricity (7.9% weight): Growth moderated to 6%, from 4.4%.
- Use-Based Classification Insights
- Consumer Durables: Grew by 8%, lowest in 15 months—indicating weak rural and semi-urban demand.
- Consumer Non-Durables: Contracted by -2.1%, third consecutive month of decline.
- Capital Goods: Strong growth of 2%, indicating continued investment momentum.
- Infrastructure/Construction Goods: Grew by 6%, showing steady construction sector activity.
- Primary Goods: Slowed to 8%, from 5.5% in January.
- Intermediate Goods: Slowed to 5%, from 5.3%—suggesting weaker production pipeline.
- What Does This Data Indicate?
- Uneven Growth: Capital and infra goods are holding up, but consumption-related sectors (durables, non-durables) are struggling.
- Volatile Momentum: Experts see a risk of stagnation in industrial recovery, especially with global headwinds and domestic consumption fatigue.
- Policy Relevance: Slowing industrial output may influence monetary and fiscal policy choices, especially as GDP growth targets remain ambitious.
Fact Box:About the Index of Industrial Production (IIP)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
In March 2025, India's mutual fund industry witnessed a notable shift in investor behavior. While the overall Assets Under Management (AUM) grew, equity mutual funds experienced a decline in net inflows, marking the third consecutive month of reduced investments in this category.
Key-highlights (India’s mutual fund industry)
- Overall Growth: The total Assets Under Management (AUM) rose by 23.11% year-on-year to Rs 65.74 lakh crore, indicating a growing investor base and market appreciation.?
- Equity Mutual Funds: Net inflows into equity mutual funds declined by 14.4% month-on-month to Rs 25,082 crore, marking the lowest in 11 months. This decrease is attributed to profit booking, year-end redemptions, and market volatility influenced by global tariff concerns.
- Systematic Investment Plans (SIPs): SIP contributions remained robust atRs.25,926 crore, showing a 34.53% year-on-year increase. However, there was a slight month-on-month dip from February'sRs.25,999 crore. The number of SIP accounts decreased marginally from 10.16 crore to 10.05 crore, with a stoppage ratio rising to 127.5% from 122% in February.
- Fund Categories Performance:
- Large-Cap Funds: Experienced net outflows ofRs.2,479 crore, despite an increase in AUM from Rs 3.25 lakh crore to Rs 3.59 lakh crore, primarily due to market gains.
- Mid and Small-Cap Funds: Continued to attract investors, with inflows of Rs 3,439 crore andRs.4,092 crore respectively, indicating sustained retail enthusiasm in these segments.
- Sectoral/Thematic Funds: Saw a significant drop in net flows toRs.170 crore fromRs.5,712 crore in February, possibly due to increased market volatility and underperformance in certain sectors.
- Gold ETFs: Recorded net outflows ofRs.77 crore, a reversal from theRs.1,980 crore inflows in February. This shift is largely attributed to profit booking and portfolio rebalancing strategies among investors.
Fact Box:Key Concepts
|


Prelims Articles
Context
US President Trump is facing insider trading allegations, an unprecedented development in US history, raising serious legal and ethical concerns.
What is insider trading?
- Insider tradingoccurs when someone with a vested interest in a company uses non-public information to make a trading decision.
- Insider tradingusually involves company executives or employees leveraging confidential company information to gain an advantage in the stock market.
- On the other hand, front-running typically involves brokers or fund managersexploiting knowledge of their clients' upcoming trades.
- In India, insider trading is prohibited under the SEBI Act, 1992.SEBI has established the SEBI (Prohibition of Insider Trading) Regulations, 2015, which outline the rules for prohibiting and restricting insider trading.
- These practices undermine investor confidencein the fairness and transparency of financial markets.


Prelims Articles
Context
The DRDO has successfully tested a new indigenous weapon – the Long-Range Glide Bomb (LRGB) named ‘Gaurav’, by releasing it from a Su-30 MKI fighter aircraft. These trials showed it can hit land targets with precision from around 100 km away.
About the Glide Bomb ‘Gaurav’:
- “Gaurav” is a 1,000-kg class glide bomb (heavy-duty bomb) designed and developed indigenously by the
- DRDO has developed two glide bombs - Gaurav and Gautham.
- While the winged version of LRGB Gaurav weighs around 1,000 kg, the non-winged Gautham weighs 550 kg.
- With a diameter of 0.6 mentre, both the bombs are four metre long and the wingspan of Gaurav is 3.4 metre.
- Range: It can strike targets up to 100 km away
- Precision: Pin-point accuracy, even from long distances
- Launch Platform: It can be launched from Su-30 MKI aircraft
- Made in India: It is designed by DRDO labs (like Research Centre Imarat), with support from Indian companies like Adani Defence and Bharat Forge

What is a Glide Bomb?
|


Editorials
Context
The National Education Policy (NEP) 2020, approved in July 2020, aims to overhaul India's education system, with a significant focus on transforming higher education to foster multidisciplinary and cross-disciplinary learning. ?
Transitioning to Multidisciplinary Institutions
- University Restructuring: The NEP proposes converting single-stream institutions into multidisciplinary campuses by adding diverse departments or forming university clusters, promoting a broad-based education. ?
- Establishing New Universities: To achieve widespread access, the policy advocates setting up new multidisciplinary universities, aiming to have at least one in or near every district by 2030. ?
- Administrative Considerations: Implementing these changes requires careful planning to address administrative challenges and ensure effective integration of disciplines. ?
Advancing Cross- and Interdisciplinary Education
- Curriculum Integration: Encouraging students to engage in courses across various departments fosters a cross-disciplinary approach, enhancing their problem-solving skills. ?
- Research Collaboration: Promoting interdisciplinary research involves integrating insights from multiple disciplines to address complex real-world issues.
- Faculty Development: Developing faculty expertise in cross- and interdisciplinary methods is crucial for nurturing a culture of collaborative teaching and research. ?
Practice Question:
Q. Critically evaluate the National Education Policy 2020's strategies for transforming India's higher education system, focusing on the promotion of multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary approaches.


Editorials
Context
On April 2, 2025, President Trump declared "Liberation Day," announcing a 10% baseline tariff on all imports and higher "reciprocal" tariffs targeting specific countries, including a 26% tariff on Indian goods. This move, invoking the International Emergency Economic Powers Act (IEEPA), aims to address the U.S. trade deficit and perceived unfair trade practices. ?
Strategic Underpinnings of Trump's Tariff Policy
- Invocation of National Emergency Powers: President Trump utilized the IEEPA to impose a universal 10% tariff on imports, citing a national emergency due to persistent trade deficits and unfair trade practices by other nations. ?
- Targeted Reciprocal Tariffs: Beyond the baseline tariff, higher rates were imposed on countries with significant trade surpluses with the U.S., such as a 26% tariff on India and up to 49% on Cambodia. ?The Economic Times+2PBS:
- Political and Economic Motivations: The tariffs are seen as a strategic move to counter China's long-term economic ambitions and assert U.S. economic sovereignty, rather than purely economic measures to balance trade.?
Implications for India
- Temporary Suspension of Additional Tariffs: The U.S. has temporarily suspended the additional 26% tariff on Indian goods for 90 days, until July 9, 2025, providing a window for diplomatic negotiations. ?
- Opportunity for Trade Reform: This pause offers India a chance to reassess and potentially reform its trade and foreign investment policies, which have been criticized for being restrictive and deterring foreign direct investment.?
- Demographic and Economic Potential: India's growing, educated workforce positions it as a viable alternative to China in global supply chains, making trade liberalization and economic reforms more pressing.?
Prospects of India-U.S. Bilateral Trade Agreement
- Ongoing Negotiations: India and the U.S. have agreed on the terms of reference for the first phase of a bilateral trade deal, aiming to finalize it by late 2025. ?
- Ambitious Trade Targets: The goal is to increase bilateral trade from the current $191 billion to $500 billion by 2030, indicating a significant deepening of economic ties. ?
- Strategic Alignment: A successful trade agreement could serve as a model for India's trade relations with other major economies, such as the UK and EU, and solidify its role as a key player in the global economy.?
Practice Question
Q. Discuss the implications of the recent U.S. tariff policies on India's trade and economic strategy. How can India leverage this situation to reform its trade and investment policies and strengthen its position in global supply chains?


Editorials
Context
The Beijing India Report 2024, marking 30 years of the Beijing Declaration, highlights India's progress in gender equality. However, it reveals a significant gap in integrating gender considerations into climate policies, particularly affecting rural women. This oversight presents an opportunity to enhance gender-responsive climate action in India.?
Gendered Impacts of Climate Change
- Health and Livelihoods: Climate change exacerbates health issues among women, including increased rates of anaemia and reproductive health problems due to food insecurity and extreme weather events.?
- Economic Vulnerability: Women in rural areas face income losses of up to 33% from non-farm livelihoods, compounded by climate-induced disruptions like droughts and floods.?
- Increased Unpaid Care Work: Resource scarcity leads to an additional 0.3 hours of unpaid care work daily for women, potentially rising to 8.3 hours by 2050 without mitigation efforts.?
Policy Gaps and Recommendations
- Inadequate Climate-Gender Integration: The Beijing India Report lacks a robust climate-gender framework, missing an opportunity to address the intersectional impacts of climate change on women.?
- Need for Gender-Responsive Climate Action: Implementing gender-responsive climate policies is crucial for achieving gender equality and sustainable development.?
- Recommendations for Policy Enhancement: Develop gender-responsive climate budgets, promote women's leadership in climate initiatives, and ensure inclusive participation in climate decision-making processes.?
Role of Women in Climate Adaptation
- Traditional Knowledge: Rural and indigenous women possess valuable traditional knowledge for sustainable agriculture and natural resource management, essential for climate resilience.?
- Leadership in Climate Initiatives: Women lead community-based climate adaptation efforts, such as seed preservation and ecosystem conservation, demonstrating effective local solutions.?
- Policy Inclusion: Integrating women's perspectives into climate policies enhances the effectiveness and inclusivity of adaptation strategies.?
Practice Question
Q. ?Critically analyze the gaps in India's Beijing India Report 2024 concerning the integration of gender perspectives in climate policies. Discuss the implications of these gaps on rural women's resilience to climate change and propose actionable policy recommendations.



