13th May 2024 (15 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
Amidst the diverse issues facing the nation, one recurrent issue is the housing crisis in India. With million homeless individuals, and concerns persisting even among those with homes regarding quality, congestion, and insufficient amenities and infrastructure, housing emerges as a pressing concern for the public.
Status of India’s Housing Crisis
- India has about 1.7 million homeless people, as per the 2011 Census. Even those with homes face issues like poor quality, overcrowding, and lack of amenities.
- A 2012 government report estimated a need for around 18.78 million more houses in India.
- A 2020 study by ICRIER found that India's urban housing shortage increased by 54% from 2012 to reach 29 million in 2018.
- This shortage includes homeless individuals, inadequate housing, obsolete homes, and crowded households.
- Reasons for the Crisis:
- Inadequate housing conditions, reduced land entitlements, rapid urbanization. Issues like high land costs, escalating construction material prices, and lack of affordable housing options contributed to the problem.
- India’s housing crisis in India reflects systemic challenges in urban planning, infrastructure development, and policy implementation.
- Impact of Housing Shortage:
- Urban congestion and the proliferation of slums are direct consequences of the housing shortage.
- Slum dwellings account for a significant portion of the urban population
Significance of the sector for Economy
- Housing is important for the Indian economy.
- The real estate sectoris responsible for about 50% of the economic output in the country.
- The Ministry of Statistics notes thatmore than one-third of all gross fixed capital formation in 2021-22 could be attributed to housing and building construction.
Fact Box:
Government Interventions
|
PYQQ: What is the meaning of the term ‘tax expenditure’? Taking the housing sector as an example, discuss how it influences the budgetary policies of the government. (2013) |


Mains Issues
Context
The National Institute of Nutrition (NIN) under the apex health research body released revised "Dietary Guidelines for Indians (DGIs)" to meet the requirements of essential nutrients and prevent non-communicable diseases (NCD).
17 Dietary Guidelines for Indians (DGIs)
- Eat a variety of foods to ensure a balanced diet
- Pregnant women and new mothers should have access to extra food and healthcare
- Ensure exclusive breastfeeding for the first six months; continue breastfeeding till two years and beyond
- After six months of age, the infant should be fed homemade semi-solid complementary foods
- Ensure adequate and appropriate diets for children and adolescents in health and sickness
- Eat plenty of vegetables and legimes
- Use oil/fats in moderation; choose a variety of oil seets, nuts etc. to meet daily needs of fats and essential fatty acids
- Obtain good equality proteins and essential amino acids; avoid protein supplements to build muscle mass
- Adopt a health lifestyle to prevent abdominal obesity, overweight and overall obesity
- Be physically active, exercise regularly
- Restrict salt intake
- Consume safe and clean foods
- Ensure appropriate pre-cooking and cooking methods are used
- Drink plenty of water
- Minimise the consumption of ultra-processed foods and high fat, sugar, salt
- Prioritise nutrient-rich foods in the diets of elderly people
- Read information on food labels
Need of the guidelines
- Changes in dietary habits have led to increased prevalence of non-communicable diseases alongside persisting undernutrition issues.
- Unhealthy diets contribute to 56.4% of India's disease burden.
- 34% of children aged 5-9 have high triglycerides.
- Healthy diets and physical activity can reduce a significant portion of coronary heart disease, hypertension, and prevent up to 80% of type 2 diabetes.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle can prevent premature deaths.
Significance of the guidelines
- The guidelines emphasize balanced diets, breastfeeding, and healthy lifestyle habits to address the prevalence of non-communicable diseases and undernutrition issues.
- Prioritizing nutrient-rich foods and minimizing consumption of ultra-processed foods are crucial for overall health.
- Special attention to pregnant women, infants, children, adolescents, and the elderly ensures their nutritional needs are met at different life stages.
- Promoting physical activity alongside dietary changes further contributes to overall health and disease prevention.
- Education on reading food labels empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices.
PYQQ: The increase in life expectancy in the country has led to newer health challenges in the community. What are those challenges and what steps need to be taken to meet them? [150 Words] [10 Marks] [2022] |


Mains Issues
Context
The development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) chatbots, known as 'deadbots', designed to mimic deceased loved ones, has raised ethical concerns. While these chatbots may offer comfort to individuals grieving the loss of a loved one, researchers warn of potential psychological distress if not developed with safety in mind.
Understanding Deadbots:
- Deadbots, also known as griefbots, are AI-enabled digital representations of departed loved ones.
- They simulate the language patterns and personality traits of the deceased using their digital footprint, including emails, social media posts, and voice recordings.
- The concept of conversing with a digital version of a lost loved one may provide solace to individuals coping with grief and loss.
Potential Risks and Ethical Concerns:
- There are potential risks associated with deadbots, including psychological distress.
- While the intention behind deadbots may be to provide comfort, their use could lead to emotional dependency and hinder the grieving process.
- There are concerns about the ethical implications of using AI to simulate conversations with the deceased, raising questions about the authenticity of these interactions and the impact on individuals' mental health.
Ethical Analysis:
- The development and use of deadbots raise ethical questions related to privacy, consent, and the manipulation of emotions.
- There is a need for clear guidelines and regulations to govern the development and use of deadbots, ensuring that they prioritize the well-being of users and respect the dignity of the deceased.
- Ethical considerations must also address the potential for exploitation, as deadbots could be used for malicious purposes or to profit from individuals' grief.
Fact Box: Case Study: Microsoft's Deadbot Patent:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Aurora lights in red hues were recently observed from Ladakh's clear skies. Astronomers from the Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bengaluru (IIA) captured these auroras using all-sky cameras located around the Indian Astronomical Observatory (IAO) in Hanle, Ladakh.
Aurora Lights and Their Origin:
- Aurora lights are typically seen in high-latitude regions near the North and South Poles.
- When observed near the North Pole, they are called Aurora Borealis, and near the South Pole, Aurora Australis.
- These colorful lights result from the interaction between charged solar winds and the Earth's magnetosphere.
- Solar winds, consisting mainly of protons and electrons, interact with the Earth's magnetic field, causing collisions with atoms and molecules in the upper atmosphere.
- These collisions produce light, similar to how electrons in a neon light create different colors when colliding with gases.
Why Auroras were visible in Ladakh?
- The auroras visible from Ladakh were attributed to increased solar flare activity in space, particularly due to Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs).
- CMEs are large ejections of magnetic particles and plasma from the Sun's corona.
- Originating from an active region on the Sun, AR13664, these CMEs reached the Earth's atmosphere, following intense solar flares.
- These storms caused auroras in red, violet, and blue colors, visible even from lower-latitude regions like Ladakh, the US, and the UK.
Impact of Solar Storms:
- Intense solar storms, like the recent CMEs, can disrupt satellite operations in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), which includes navigation, military, and communication satellites.
- The energetic particle environment created by these storms can induce heating in the upper atmosphere, posing radiation hazards and increasing friction on satellites.
- Excessive friction can lead to satellite malfunction or even ignition and burning in extreme cases, jeopardizing their operations.
PYQQ. If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Solution: (c) |


Prelims Articles
Context
The government plans to construct roads along the China border in Uttarakhand and Sikkim under the Vibrant Village Programme (VVP). Each kilometer of road construction is estimated to cost over Rs 2 crore.
Key-highlights (Implementation Status)
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has sanctioned 113 roads in Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, and Sikkim under the VVP to improve connectivity along the China border.
- Arunachal Pradesh has received the majority of these sanctions, with Uttarakhand and Sikkim also receiving approvals.
- The MHA has mandated the installation of GPS-enabled tracking devices on machinery used for road construction. This ensures efficient monitoring of construction activities.
Fact Box: Vibrant Village Programme
|


Prelims Articles
Context
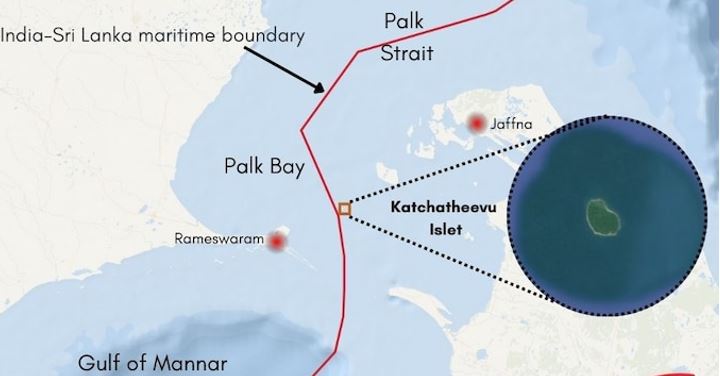
Talks between fishing communities of Tamil Nadu and the Northern Province in Sri Lanka are being considered to address the fisheries dispute in the Palk Bay.
Root Cause of the Conflict:
1. Disagreements over Kachchatheevu:
- A key issue is the disagreement over Kachchatheevu, an islet in the Palk Strait (north of Sri Lanka's Jaffna peninsula).
- Ownership history: Initially owned by the Raja of Ramnad, it later became part of the Madras Presidency during British rule.
- Transfer to Sri Lanka: In 1974, India ceded Kachchatheevu to Sri Lanka under a bilateral agreement
- The International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) was born out of a bilateral agreement signed back in 1974 and 1976 under the United Nations Convention on Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
2. Poaching by Indian Fishers through Bottom Trawling:
- The main cause of conflict is bottom trawling, a fishing method banned in Sri Lanka.
- Bottom trawling involves scouring sea beds, causing damage to the marine ecosystem.
- Indian fishers cross into Sri Lankan waters due to depleted catch on the Indian side.


Prelims Articles
Context5. China Surpasses US in Trade with India
In the fiscal year 2023-24, China emerged as India's largest trading partner, surpassing the US, with a two-way commerce of USD118.4 billion. This slightly edged past the US, whose bilateral trade with India stood at USD118.3 billion during the same period.
Key-highlights:
- Trade Figures with China: India's exports to China rose by 8.7% to USD16.67 billion in the last fiscal year, driven by sectors like iron ore, cotton yarn/fabrics/madeups, handloom, spices, fruits and vegetables, plastic, and linoleum. However, imports from China increased by 3.24% to USD101.7 billion.
- Trade Figures with the US: In contrast, India's exports to the US dipped by 1.32% to USD77.5 billion in 2023-24, while imports decreased by about 20% to USD40.8 billion. However, imports from the US grew by 14.7%, resulting in an expanded trade surplus for India, which grew from USD16.86 billion to USD36.74 billion.
- Trends in Trade Surplus: The significant growth in imports from the US contributed to India's trade surplus expansion, which increased from USD16.86 billion to USD36.74 billion in the fiscal year 2023-24.
- Historical Context: China was India’s top trading partner from 2013-14 till 2017-18 and also in 2020-21. The UAE, followed by the US, held the position before China became the top trading partner again.
- In 2023-24, the UAE ranked as India’s third-largest trading partner, with a trade volume of USD83.6 billion.
- Other Major Trading Partners: Apart from China and the US, other major trading partners of India in 2023-24 included Russia (USD65.7 billion), Saudi Arabia (USD43.4 billion), and Singapore (USD35.6 billion).


Prelims Articles
Context
The recent research findings regarding the inheritance of knowledge in Caenorhabditis elegans worms are significant because they shed light on the potential transmission of behavior-modifying molecules across generations. This breakthrough has garnered attention due to its implications for understanding biological mechanisms and their relevance to human health and behavior.
Key-highlights of Research Findings:
- Researchers discovered that C. elegans worms inherit knowledge to avoid disease-causing bacteria for up to four generations.
- This phenomenon raises questions about similar abilities in humans.
- Mechanism of Transmission: Pseudomonas vranovensis, a disease-causing bacterium, produces a small RNA molecule (sRNA) that alters the worm's feeding behavior. The learned avoidance behavior is passed down to subsequent generations of worms through RNA interference.
- Role of sRNA in Behavior Modification:
- Worms absorb sRNA from bacteria, reducing the expression of the maco-1 gene, which plays a role in neurological function.
- Worms trained to avoid pathogenic bacteria pass on this behavior to their offspring.
- Implications for Human Health: The study prompts speculation about whether humans can absorb sRNA from microbes and modify behavior across generations.
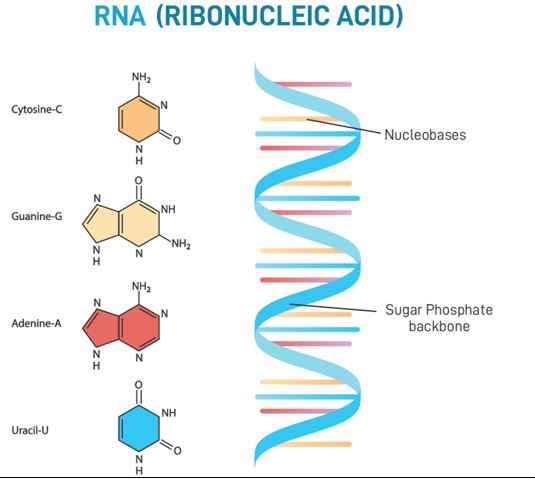
Fact Box:About Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans )
Understanding RNA:RNA molecules are like half-ladders with ribose sugar and four bases: A, C, G, and U.
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Apple introduced the M4 chip with the iPad Pro, boasting significant improvements in performance, notably the inclusion of a 16-core Neural Engine, Apple's version of a Neural Processing Unit (NPU).
What is Neural Processing Unit?
- An NPU is a specialized processor designed to accelerate neural network processes, which are the basis for AI-related tasks like speech recognition, natural language processing, and photo/video editing.
- In consumer gadgets like smartphones and tablets, the NPU is integrated within the main processor, while in data centers, it might be a separate processor.
- Different from CPU and GPU
- Central processing unit (CPU) execute instructions sequentially, while NPUs employ parallel computing for simultaneous execution of multiple calculations, making them efficient for AI tasks.
- Graphics processing unit (GPU) also have parallel computing capabilities but are mainly used for graphic rendering. NPUs are dedicated to AI tasks, making them more efficient and less power-consuming.


Prelims Articles
Context
The Indian Army is set to enhance its surveillance capabilities with the acquisition of the Hermes-900 Starliner drones, also known as Drishti-10, from Adani Defence Systems.
About Hermes-900 Starliner Drones:
- The drones are state-of-the-art unmanned aerial vehicles equipped with high-performance sensors.
- They have proven instrumental in detecting ground or maritime targets across a wide spectral range and can execute ground target attacks.
Fact Box: Additional Procurements:The army will also acquire a Very Short Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS) and a UAV-launched Precision Guided Munition (ULPGM) to bolster its capabilities further. About VSHORADS (Very Short Range Air Defence System)
About ULPGM (UAV Launched Precision Guided Munition):
|


Editorials
Context
India recently concluded a significant trade deal with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), comprising Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland, amid ongoing parliamentary elections and stalled negotiations with other countries like the United Kingdom and the European Union.
Breakthrough Investment Chapter:
- Incorporation of Detailed Investment Provisions: The FTA includes a comprehensive investment chapter, distinguishing it from recent Indian FTAs lacking such provisions.
- Specific Investment Targets: Notably, the agreement sets investment targets for EFTA nations, indicating a commitment to bilateral economic growth.
- Introduction of Obligation of Conduct: The FTA introduces an obligation of conduct, emphasizing sincere efforts toward investment goals, rather than guaranteeing outcomes.
Integration of Trade and Investment:
- Recognition of Intrinsic Linkage: The FTA underscores the inherent connection between trade and investment, challenging India's previous approach of separating negotiations.
- Comprehensive Economic Treaty: The India-EFTA agreement sets a precedent for a holistic economic treaty, potentially offering India greater negotiation leverage.
- Strategic Bargaining Stance: The combined approach enables a more strategic stance in negotiations, facilitating concessions in one area in exchange for benefits in another.
Implications for India's Trade Policy Approach:
- Shift in Trade Policy Strategy: India's pivot towards integrating trade and investment in the FTA signifies a departure from its FTA 2.0 strategy of decoupling agreements.
- Impact on Future FTAs: The agreement's approach may influence future FTAs, indicating a potential return to the integrated trade-investment model of the early 2000s.
- Need for Comprehensive FTA Policy: Emphasis on a clear and comprehensive FTA policy underscores the necessity for India to align its trade and investment laws for optimal economic growth.
Mains Question:
Examine the significance of India's recent trade agreement with the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), particularly focusing on the innovative investment provisions.


Editorials
Context
Malaysia's commodities minister Johari Abdul Ghani has proposed gifting orangutans to trade partners who purchase the country's palm oil, drawing inspiration from China's successful "panda diplomacy" using giant pandas for diplomatic outreach.
Use of Animals in Diplomacy:
- Historical Significance: Throughout history, animals have been utilized in diplomacy to symbolize nations' values and intentions, such as the use of dogs, horses, and ermines in royal portraits to convey fidelity, power, and purity, respectively.
- China's Panda Diplomacy: China's "panda diplomacy" has been a notable example, leveraging the appeal of giant pandas to foster diplomatic relations and improve international perceptions, particularly during periods of strained relations with other nations.
- Malaysia's Orangutan Diplomacy: Malaysia's proposal to gift orangutans as a diplomatic gesture aims to mitigate accusations of unsustainability surrounding palm oil plantations, echoing China's use of pandas to soften diplomatic tensions and promote its interests.
Challenges and Ironies:
- Unintended Consequences: Despite the symbolic value of diplomatic animal gifts, history shows that they do not always yield the desired outcomes, as seen in the case of Soliman the elephant, whose arrival as a wedding gift led to strain in the recipient's marriage.
- Environmental Concerns: Malaysia's proposal to gift orangutans comes at a time when the country faces scrutiny from environmental groups over deforestation linked to palm oil production, potentially overshadowing the diplomatic gesture with unintended irony.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of animals in diplomacy raises ethical questions regarding their welfare and exploitation, highlighting the need for careful consideration of the consequences of such gestures.
Mains Question:
Discuss the historical significance of using animals in diplomacy.


Editorials
Context
The Delhi High Court's observations emphasized the need to equip minors with knowledge and tools to navigate online interactions safely, extending beyond traditional concepts of child protection to address risks in cyberspace.
Challenges of Online Protection:
- Technological Evolution Outpacing Understanding: The rapid evolution of technology has surpassed society's understanding of its impact, particularly on children and young adults, who have grown up as "digital natives."
- Exposure to Various Online Dangers: Children are increasingly exposed to various online dangers, including child sexual abuse, cyberbullying, harassment, and blackmail.
- Limitations of Existing Legislation: While legislation like the POCSO Act and DPDP Act address some concerns, their effectiveness is limited due to the dynamic nature of the internet and its threats.
Holistic Approach to Child Protection Online:
- Promoting Education and Awareness: Effective protection efforts should start with home and school environments, fostering open conversations between children and adults about online safety.
- Teaching Appropriate Online Behavior: Education should focus on teaching children appropriate online behavior, recognizing signs of predatory behavior, and understanding privacy settings and boundaries.
- Balanced Approach to Internet Access: While safeguarding children online is crucial, it's essential to maintain a balanced approach that respects their right to access the internet, considering its significance in education, entertainment, socializing, and self-realization.
Mains Question:
What measures can be implemented to ensure effective online protection for children while respecting their right to access the internet?


Editorials
Context
The consumer affairs ministry is taking action against advertisements promoting illegal betting and gambling, which violate the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) guidelines. These ads, often indirect or surrogate, are on the rise during cricket and election seasons.
India's Gaming Market
- Despite regulations, online betting platforms continue to advertise their services, raising concerns about their impact, especially on the youth, and the socio-economic consequences.
- India's gaming market is growing rapidly, expected to reach USD 3.1 billion in FY23 and projected to reach USD 7.5 billion by FY28.
- India ranks as the second-largest gaming market globally, with 15.4 billion game downloads in FY23, second only to China.
- Risks associated with excessive gaming: addiction, health issues from prolonged screen time, social isolation, financial loss from in-game purchases, privacy and security concerns, cyberbullying, and negative effects from violent or aggressive games.
Fact Box:Regulation of Gaming Industry
|