

14th May 2024 (13 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
Live-in relationships, although not explicitly recognized by Indian laws, have gained prominence in contemporary society. These relationships challenge traditional notions of marriage and cohabitation, raising important questions about morality, legality, and societal acceptance.
Societal Perspective on Live-in Relationships:
- In Indian society, the concept of live-in relationships has sparked debates and discussions regarding morality and social norms. While some view these relationships as progressive and reflective of individual freedom, others perceive them as immoral or culturally unacceptable.
- Despite legal recognition, live-in relationships continue to face societal stigma and disapproval, particularly in conservative communities. Social attitudes towards unmarried cohabitation lead to discrimination and ostracization of couples in such relationships.
- Responsible factor for growth: Urbanization, globalization, and exposure to Western values have contributed to greater acceptance of non-traditional relationship models, including live-in arrangements.
Implications of Live-in relationships on Society
- Changing Social Norms: Live-in relationships challenge traditional notions of marriage and family, leading to shifts in societal norms regarding relationships and cohabitation.
- Acceptance and Stigma: The social stigma may impact individuals' social standing and relationships with family and friends.
- Legal Ambiguity: In the absence of specific laws governing live-in relationships, legal rights and responsibilities concerning property, inheritance, and child custody can be uncertain.
- Impact on Children: Children born or raised in live-in relationships may face societal judgment and legal complications, particularly regarding inheritance and parental rights. Moreover, the stability and long-term prospects of such family structures may affect children's well-being and social integration.
- Impact on Marriage: The prevalence of live-in relationships may influence perceptions of marriage, leading some individuals to choose cohabitation over formal marriage or delay marriage altogether. This trend can have broader implications for family structures and social institutions.
- Positive implications: Personal Freedom and Autonomy, Compatibility Testing, Flexibility and Adaptability, Emotional Support and Companionship, Social Cohesion and Community Bonds
Fact Box: Constitutional Provisions for Live-in Relationships
|


Mains Issues
Context
India recently signed a significant 10-year agreement with Iran to develop and operate the Chabahar port, bolstering ties with this strategic Middle Eastern nation.
Background:
- India has been working on developing the Chabahar port in Iran as a vital route to transport goods to Iran, Afghanistan, and Central Asian countries.
- In 2016, India, Iran, and Afghanistan inked the Trilateral Agreement, solidifying Chabahar’s role as an International Transport and Transit Corridor.
- However, progress on the port's development was slowed due to U.S. sanctions on Iran (2019).
Key Highlights of the Agreement:
- The contract was signed between Indian Ports Global Limited (IPGL) and the Port & Maritime Organisation of Iran.
- IPGL will invest approximately $120 million, with an additional $250 million in financing, bringing the total contract value to $370 million. Since taking over operations in 2018, IPGL has handled significant container traffic and bulk cargo.
- The long-term contract is expected to significantly boost economic activities and enhance India's role in global trade and commerce.
Significance of Chabahar Port:
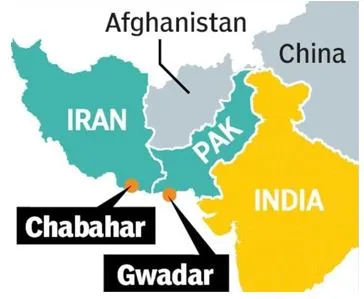
- Easy access to market: The port is an optimally located node for accessing Afghanistan, Central Asia, the Caucasus and Eurasian markets.
- Easy access to INSTC: Chabahar Port, located on Iran's southwestern coast, provides easy access to India's west coast and forms a crucial link in the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC). It connects India to Russia and Central Asia via the INSTC, facilitating the movement of goods between these regions.
- Reduced time and cost: This collaboration between India and Iran aims to reduce transportation costs and time, promoting trade in the region.
- Energy Security: It offers India a strategic advantage in securing its energy needs. With Iran holding substantial reserves of oil and natural gas, Chabahar provides India with direct access to these resources, bypassing maritime chokepoints like the Strait of Hormuz.
- Diversified routes: Chabahar Port offers strategic advantages to India's oil and gas sector by diversifying import routes, accessing new markets in Central Asia, and enhancing energy security. By bypassing Pakistan’s ports (Karachi and Gwadar), India will reduce its dependency on traditional routes (vulnerable to disruptions).
- Expanding footprints: By leveraging Chabahar Port, India can mitigate risks associated with traditional import routes, expand its energy footprint, and assert its presence in regional geopolitics.
PYQQ1: Mention the significance of straits and isthmus in international trade. (2022) Q2. What is the importance of developing Chabahar Port by India? (2017)
Solution: (c) |


Mains Issues
Context
The Smart Cities Mission (SCM) was launched as a flagship programme to adapt to global urban development trends. However, its progress and effectiveness have come under scrutiny.
What is the concept of Smart Cities?
- Smart cities emerged as a concept after the 2009 financial crash, aiming for urban centers integrated with advanced communication networks and infrastructure.
- However, there is no universal definition, with interpretations varying across regions.
- Genesis of SCM: The Smart Cities Mission (SCM) was initiated in June 2015, aiming to develop 100 cities over five years. It encompassed area-based development and pan-city solutions, with an allocation of Rs 2 lakh crore and emphasis on public-private partnerships (PPPs).
Need of smart cities (unprecedented urban expansion):
- Experts estimate that about two out of every three peoplein the world will live in cities by 2050
- India is home to three of world’s 21 megacities (Mumbai, Delhi, and Kolkata), each with populations exceeding 10 million.
- Despite this urban growth, the country faces significant challenges hindering urban development and economic growth.
- Migration from rural to urban areas for economic opportunities is increasing, but issues like poor local governance, inadequate infrastructure and services, and outdated urban planning pose major obstacles.
- As a result, the number of slums has reached record levels.
What is the status of SCM?
- As of April 2024, the SCM has seen a reduction in project outlay, with completion rates lower than expected. Many ongoing projects are unlikely to meet the extended deadline of June 2024, and PPP funding remains minimal.
- Exclusionary Approach: The selection process of cities lacked consideration for diverse urban realities, leading to exclusionary outcomes. The governance structure, centered around special purpose vehicles (SPVs), sidelined elected councils and faced objections for being top-down.
- Implementation Hurdles: The SCM's inadequate funding, compared to the estimated capital requirement for urban development, limited its impact. The SPV model conflicted with constitutional amendments and led to displacement of vulnerable populations, exacerbating issues like urban flooding.
- Successes:
- Awareness: The SCM raised awareness about the concept of smart cities and the need for urban modernization in India.
- Infrastructure Development: Some cities witnessed infrastructure development and improvement in basic services like waste management and water supply.
- Technological Integration: The emphasis on ICT solutions promoted technological integration in urban governance and service delivery.
Way forward
There is a need for a more inclusive approach to urban development that considers the diverse needs of urban populations and engages local communities in decision-making. Future urban development initiatives should focus on holistic planning, integrating social, economic, and environmental aspects for sustainable growth.
Overall, while the SCM raised awareness about urban modernization, its implementation faced significant challenges and criticisms. Moving forward, there is a need for a more inclusive, holistic, and sustainable approach to urban development in India.
PYQQ1: Economy (GS-III): What are ‘Smart Cities’? Examine their relevance for urban development in India. Will it increase rural-urban differences? Give arguments for ’Smart Villages’ in the light of PURA and RURBAN Mission. (2016) Q2: Society (GS-I): Discussion the various social problems which originated out of the speedy process of urbanization in India. (2013) |


Mains Issues
Context
The rhino and the cedar were the animal and plant species most affected by global illegal wildlife trade during 2015-2021, the 2024 World Wildlife Crime Report released by the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime.
Key-Takeaways:
The 2024 World Wildlife Crime Report highlights the significant impact of illegal wildlife trade on animal and plant species:
- Most Affected Species:
- Animal: Rhino horn market (29%), pangolin scales (28%), and elephant ivory (15%) are the most affected.
- Plant: Cedars and Sapindales (47%), rosewoods (35%), and agarwood and myrtales (13%) are the top affected.
- Diversity Among Seizures:
- Corals (16%), crocodilians (9%), elephants (6%), and bivalve molluscs (6%) are among the most seized animal species.
- Coral pieces (16%), live specimens (15%), and medicines from animal products (10%) are the most seized commodities.
- Despite efforts, wildlife trafficking persists globally, driven by adaptable traffickers.
- The report calls for strong international cooperation, investment in data capacity, and modernized criminal justice responses.
- Corruption and technology are identified as areas of concern, undermining regulation and enforcement.
- Prioritized and strategic interventions are needed to reduce wildlife trafficking, addressing organized crime as a whole.
- Overall, the report underscores the urgent need for comprehensive strategies to combat wildlife trafficking and protect biodiversity.
Why is India hub for wildlife crimes?
- Megadiverse Nature and Dense Population: With 8% of the world's wildlife, India serves as both a source and transit country for illegal wildlife and products due to its dense human population.
- Porous international borders with China, Myanmar, and other Southeast Asian countries facilitate illegal trade.
- Demand for raw materials (red sandalwood and ivory drives trafficking)
- Infrastructure and Technology:
- A growing aviation sector and expanding airport infrastructure provide avenues for smuggling.
- Social media platforms are exploited by traffickers for online trade.
Initiatives to Combat Wildlife Crimes in India:
- Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB): Constituted under the Director, Wildlife Preservation to combat wildlife-related crimes.
- Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972: Prohibits hunting and illegal wildlife trade.
- Conservation Projects:
- Project Elephant addresses human-elephant conflict and protects elephant habitats.
- Project Tiger conserves endangered tigers and their habitats.
- Operational Initiatives:
- Operation “Save Kurma” targets poaching, transportation, and illegal trade of turtles and tortoises.
- Operation Thunderbird intensifies enforcement with INTERPOL.
- Operation Wildnet tackles illegal trade on e-commerce platforms.
- India's participation in CITES regulates international trade in endangered species.
- International Organizations: World Wildlife Fund, Environmental Investigation Agency, TRAFFIC, and International Fund For Animal Welfare play roles in preventing and controlling wildlife crime.
PYQQ1. With reference to Indian laws about wildlife protection, consider the following statements: (2022)
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Solution: (b) Q2. Consider the following statements in respect of Trade Related Analysis of Fauna and Flora in Commerce (TRAFFIC): (2017)
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
Solution: (b) |


Prelims Articles
Context
The most significant G5 geomagnetic storm since 2003, recently hit the Earth and disrupted GPS, satellite navigation, and other technologies.
About Geomagnetic Storms
- Geomagnetic storms, like the recent G5 storm, are disturbances in the Earth’s magnetosphere caused by solar wind activity.
- These storms result from coronal mass ejections (CMEs) from the sun, which carry their own magnetic fields and can disrupt communications, power grids, and satellite operations on Earth and in near-Earth orbit.
- On a scale from G1 to G5, G5 is the strongest level of geomagnetic storm (as per NOAA).
- G1 - Minor
- G2 - Moderate
- G3 - Strong
- G4 - Severe
- G5 - Extreme
- While a G4 storm can cause widespread power issues, a G5 storm could lead to complete blackouts and power grid collapses.
- These storms can cause auroras in the sky and disrupt technologies like GPS and satellite navigation.


Prelims Articles
Context
The Supreme Court has taken steps to strengthen the Juvenile Justice Act (JJA), 2015, by addressing significant gaps in its implementation. These measures aim to streamline procedures for handling legal violations by minors, managed by the Juvenile Justice Board (JJB), and ensure proper adjudication of cases involving minors.
Key Changes and Implications:
- Definite Timelines for Appeals: The Court has mandated that appeals against JJB decisions must be filed within 30 days, addressing the absence of a defined deadline for such appeals.
- Clarity in Appellate Process: The Court clarified the appellate process, especially regarding the interchangeability of the "Children’s Court" and "Court of Sessions" mentioned in the Act.
- Inclusion of Critical Details in Judicial Orders: The Court emphasized the need for judicial orders to include essential information, such as the names of decision-makers and the attendance of involved parties and their legal representatives.
Fact Box: About Juvenile Justice Act (JJA), 2015
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The Indian government is planning to complete GIS mapping of all national highways to enhance planning, execution, and monitoring of road projects.
India’s Road Network
- India has the world's second-largest road network, covering approximately 66.71 lakh kilometers, with national highways constituting 2% and carrying over 40% of total traffic.
- There are currently 599 national highways spanning 1,46,145 kilometers (December 2023).
- Classification: These highways are classified into various categories such as
- North-South Corridors
- East-West Corridors
- Golden Quadrilateral (connecting Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, and Kolkata)
- 3-D Highways (highway with 3 digit number, secondary branch of the main highway)
- Key organizations involved: Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH), National Highways Authority of India (NHAI), Border Roads Organization (BRO), and National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd (NHIDCL).
- Government initiatives: Bharatmala Pariyojana and allowing 100% FDI in roads and highways under the automatic route
PYQQ: With reference to India's projects on connectivity, consider the following Statements: (2023)
How many of the above statements are correct?
Solution: (d) |


Prelims Articles
Context
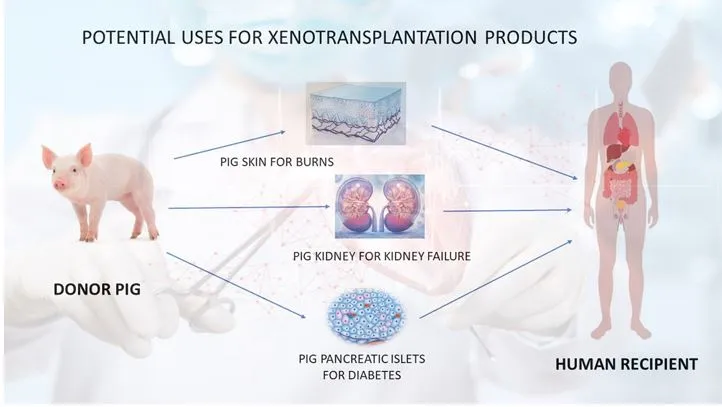
The first recipient of a modified pig kidney transplant (Xenotransplantation) passed away, around two months after the surgery was carried out. However, his death was not linked to the transplant operation.
About Xenotransplantation
- Xenotransplantation involves transplanting organs or tissues from nonhuman animals into humans to treat various medical conditions.
- It addresses the shortage of donor organs and aims to save lives by providing alternative sources for transplantation.
- Xenotransplantation encompasses procedures where live cells, tissues, or organs from nonhuman animals are transplanted into human recipients.
Fact Box: Organ donation in India
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Researchers at CSIR-Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology (CCMB) have discovered that the invasive armoured sailfin catfish has spread to 60% of the water bodies in the Eastern Ghats. This catfish, once introduced for its unique appearance and algae-cleaning abilities, has multiplied rapidly, damaging fishing nets and disrupting the local ecosystem.
About Armored catfish (Family: Loricariidae)
- Origin: The armoured sailfin catfish, known as the Rakashi or devil fish, come from South America.
- Feeding Habits: They mainly eat algae and are active at night. They have a distinct sucker on their underside.
- Invasion Impact: Once these catfish invade a new area and start reproducing, it's extremely difficult to get rid of them.
- Negative Effects: They harm native plants and animals by competing for resources, altering food chains, and causing water to become murky due to their burrowing. They also disrupt the feeding habits of large aquatic mammals like manatees.
Fact Box: About eDNA
Recent Interventions to control Invasive Species
|


Editorials
Context
There is growing restlessness and uncertainty in Nepal due to political and economic challenges, prompting discussions about the country's governance and future trajectory. Recent political developments, including shifts in alliances and foreign policy decisions, have heightened concerns about Nepal's stability and its relations with neighboring countries.
Political and Economic Uncertainty in Nepal:
- Questions on Governance: Nepal faces questions about the effectiveness of its transition to a secular federal democratic republic, with debates surrounding the rushed adoption of its Constitution and the loss of its Hindu identity.
- Foreign Policy Dynamics: Recent political shifts, including changes in coalition partners and diplomatic overtures to China, have raised concerns about Nepal's alignment and its implications for regional dynamics, particularly its relationship with India.
- Challenges for Stability: Political instability, governance issues, and concerns about corruption pose significant challenges for Nepal's stability and development, necessitating careful attention from both domestic and international stakeholders.
India's Role and Strategic Considerations:
- Strategic Dynamics with China: China's increasing influence in Nepal, marked by diplomatic engagements and infrastructure projects under the Belt and Road Initiative, presents strategic challenges for India and underscores the importance of managing bilateral relations effectively.
- India's Diplomatic Approach: India's approach to Nepal has been characterized by cautious engagement and respect for its sovereignty, with efforts to avoid interference in internal affairs while promoting shared developmental goals and mutual cooperation.
- Opportunities for Collaboration: India has the opportunity to strengthen its ties with Nepal through holistic development initiatives, fostering economic growth, promoting cross-border investments, and addressing shared challenges in areas such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
Mains Question:
Discuss the political and economic challenges facing Nepal and analyze the implications of recent developments in its foreign policy for regional dynamics, with a focus on India's strategic interests and diplomatic approach towards Nepal.


Editorials
Context
Chief Justice of India, Justice D.Y. Chandrachud, emphasizes the importance of mediation over litigation, aligning with the Mediation Act, 2023, which aims to revolutionize alternative dispute resolution in India.
Expanding Scope and Role of Mediation:
- Legislative Framework: The Mediation Act, 2023, formalizes mediation and introduces various forms, including pre-litigation and court-annexed mediation, to facilitate amicable settlements through neutral mediators.
- Recognition and Evolution: Former Supreme Court judge, Justice S.K. Kaul, acknowledges the evolving acceptance of mediation within the legal community, highlighting its synergistic role alongside established legal procedures.
- Philosophical Shift: Mediation, echoing Mahatma Gandhi's ethos, emphasizes reconciliation and healing, steering away from adversarial confrontation towards dialogue and understanding, thus fostering a democratic space for conflict resolution.
Challenges and Solutions in Mediator Skill Development:
- Barriers to Entry: Current guidelines mandate 15 years of professional experience for mediators, posing challenges for aspiring mediators transitioning from law school, where advocacy is emphasized.
- Integrated Learning Approach: There is a need for integrated legal education that allows legal professionals to seamlessly switch between advocacy and mediation roles, enhancing their effectiveness in both.
- Innovative Training Methods: Incorporating co-mediation and shadow mediation under the Mediation Act, 2023, provides practical exposure and dynamic learning experiences for emerging mediators, ensuring comprehensive skill development.
Mains Question:
Discuss the significance of the Mediation Act, 2023, in transforming dispute resolution in India.


Editorials
Context
Analysis of NSSO data from 1983 to 2023 reveals nuanced insights into employment figures, challenging prevalent narratives and highlighting the need for robust research in understanding employment dynamics.
Trends in Employment Growth:
- Consistent Growth: Principal employment has consistently grown since 1983, with no period showing jobless growth, emphasizing the resilience of the employment landscape.
- Fastest Growth Period: The period from 2017-18 to 2022-23 witnessed the fastest increase in employment, with approximately 80 million additional jobs, spread across rural and urban sectors, manufacturing, agriculture, construction, and services.
- Inclusive Growth: Employment growth during this period has been well-distributed among various demographics, including women and older citizens, suggesting diverse factors driving workforce participation.
Factors Influencing Employment Dynamics:
- Changing Demographics: Increased workforce participation among women and older individuals may reflect shifting socio-economic dynamics, including improved access to resources and changing family structures.
- Role of Government Initiatives: Government schemes like the PMMY (Mudra) have likely contributed to the growth of self-employment, but the sustainability and desirability of this trend warrant further analysis.
- Wage Stagnation: Despite employment growth, there has been relative stagnation in aggregate wages and salaries, highlighting potential challenges in maintaining living standards and labor productivity.
Mains Question:
Analyse the trends in employment growth revealed by the analysis of NSSO data from 1983 to 2023, focusing on factors influencing employment dynamics.



