30th July 2024 (10 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
India faces a growing mismatch between the rising demand for employment and the lack of a suitably skilled workforce. Despite a significant increase in the number of job seekers, the skills possessed by the workforce often do not align with the requirements of the modern job market.
Severity of the Problem (Economy Survey 2024)
- Sixty-five per cent of India’s fast-growing population is under 35, and many lack the skills needed by a modern economy.
- Estimates show that about 51.25 per cent of the youth is deemed employable.
- In other words, about one in two are not yet readily employable, straight out of college. However, it must be noted that the percentage has improved from around 34 per cent to 51.3 per cent in the last decade.
- Significance of Skilling:
- Skilling equips the workforce with the necessary competencies to meet industry demands, fostering innovation and productivity.
- Employment not only ensures economic stability but also empowers individuals, enhancing their quality of life and contributing to overall societal progress.
- With one of the youngest populations, a median age of 28, India can harness its demographic dividend by nurturing a workforce that is equipped with employable skills and prepared for the needs of the industry.
What are the reasons behind India’s Skill Gap?
- Inadequate Educational Systems
- Outdated Curricula: Many educational institutions offer outdated curricula that do not keep pace with industry advancements.
- Limited Practical Training: There is insufficient focus on practical skills and vocational training, leaving graduates unprepared for real-world job requirements.
- Mismatch Between Industry Needs and Educational Output
- Industry Evolution: Rapid technological changes and evolving job roles demand new skills that are not always covered by traditional education systems.
- Curriculum Gap: Educational programs often fail to align with current industry standards and needs.
- Insufficient Vocational Training
- Neglect of Vocational Education: Vocational training and technical education are less emphasized compared to academic education.
- Underfunded Institutions: Many vocational training institutions, like Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs), suffer from outdated facilities and inadequate resources.
Challenges
- Lack of Skills: Graduates and job seekers frequently lack the specific skills required for available jobs, leading to high unemployment or underemployment.
- Skill Gaps in Emerging Sectors: New industries and sectors require specialized skills that are not adequately addressed by existing training programs.
- Cost of Training: High costs associated with training and skill development can be a barrier for both individuals and companies.
- Infrastructure Issues: Poor infrastructure in training institutes limits the effectiveness of skill development programs.
- Access to Opportunities: There is often a lack of access to quality education and training facilities in tier-II and tier-III cities compared to metropolitan areas.
- Regional Imbalances: Unequal distribution of training resources exacerbates skill deficits in less developed regions.
How does it impact?
- Productivity Issues: Companies face difficulties in finding skilled employees, which can impact productivity and growth.
- Economic Inefficiencies: A mismatch between skills and job requirements can lead to inefficiencies in the labor market and economic stagnation.
- Unemployment and Underemployment: Persistent skill gaps contribute to higher rates of unemployment and underemployment, affecting economic stability.
- Reduced Aspirations: Lack of proper training and job opportunities can dampen the aspirations of the youth, limiting their career prospects.
Fact Box: Government Measures for Skill Development
|


Mains Issues
Context
Three students drowning in the flooded basement of Rau's IAS Study Circle in central Delhi's Rajender Nagar has once again brought to fore the water challenge faced by Indian metros. Most big cities in India, and particularly the metros, keep lurching from water shortage to floods. While this twin water challenge in urban areas, made worse by climate change, makes cities unliveable, it also does not bode well for India's economy.
What is the root of India's urban problem?
- Dysfunctional organisations: The root of India's urban problem is the dysfunctional organisations that characterise urban governance with no clear public accountability, and the nature of master plans of cities.
- No accountability: Instead of blaming the design and planning errors, everyone blames the rising population.
- As per World Bank, by 2036, India's towns and cities will be home to 600 million people, or 40 percent of the population, up from 31 percent in 2011, with urban areas contributing almost 70 percent to GDP.
- Cramped spaces: The high population density is forced upon people by planning that promotes highly regulated low FSI, resulting in cramped living spaces or pushing people into slums.
- Inequity: Little land is released for urban habitats, leading to extreme inequity in access to land and high unit costs of built-up spaces.
- Waterlogging is caused by expansion of planned and unplanned urban areas without regard for space for circulation; drying up and destruction of lakes, tanks and water bodies due to dumping of construction and demolition waste; and inclusion of areas occupied by lakes and other water bodies in habitation zones.
How does it impact?
- Economic loss: Flooding of urban areas disrupt the economy as vital economic centres, such as Bengaluru, come to a sudden halt.
- The World Meteorological Organisation's (WMO) State of the Climate in Asia 2021 report said that India suffered a loss of $3.2 billion due to flooding that year. Much of this loss can be attributed to urban areas incapacitated by waterlogging.
- Reducing expansion: Over time, it brings down productivity and the scope of future expansion and investment.
How to tackle India's urban explosion?
- Implement and Update Plans: Urban plans like Delhi’s MPD-2041 must be rigorously implemented. This includes integrating blue-green development and efficient waste management systems.
- Improve Drainage Systems: Cities need better drainage plans. For example, resolving waterlogging issues in Delhi’s ITO area requires updating sewage networks to align with water levels.
- Community Engagement: Engage local communities in removing encroachments and maintaining public spaces to ensure effective drainage and sanitation.
- Rainwater Harvesting: Incorporate rainwater harvesting systems in both new and existing buildings to capture and store rainwater.
- Groundwater Recharge: Refurbish and build lakes to help recharge groundwater levels. The government is working on a project to refurbish at least 75 lakes in each district.
- Waste Water Recycling: Increase efforts in wastewater recycling. The government aims to triple the current recycling rate by the end of the decade.
- Investment: A 2022 World Bank report says that India's cities require an estimated capital investment of $840 billion in urban infrastructure and municipal services in the 15 years till 2036 (in 2020 prices), equivalent to 1.18% of estimated GDP.


Mains Issues
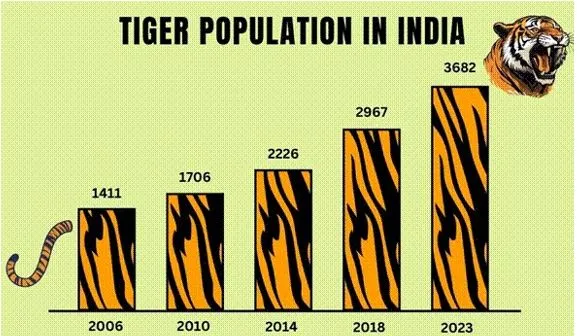
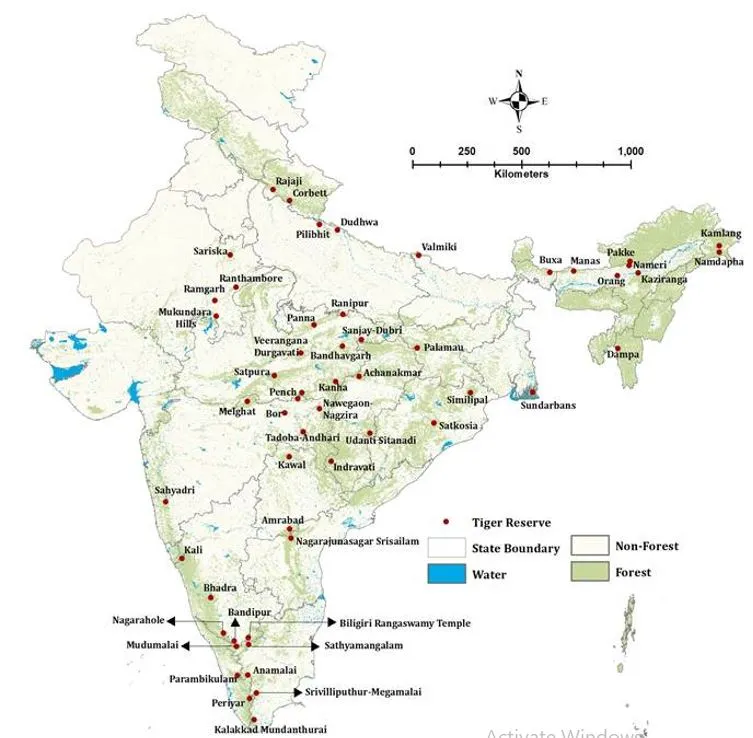
On International Tiger Day, a report titled "India's Tiger Reserves: Tribals Get Out, Tourists Welcome” reveals significant concerns regarding the displacement of indigenous communities and the impact of conservation measures on local populations and wildlife.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Massive Displacement of Tribals: The report estimates that approximately 5,50,000 Scheduled Tribes and other forest dwellers have been displaced due to the creation and expansion of Tiger Reserves.
- Breakdown:
- Pre-2021: 2,54,794 persons were displaced from 50 Tiger Reserves up to 2017.
- Post-2021: An additional 2,90,000 persons are projected to be displaced from six new Tiger Reserves created after 2021.
- Increase in Displacement: The report highlights a dramatic 967% increase in displacement per Tiger Reserve in the post-2021 period compared to previous years.
- Impact of Displacement:
- Loss of Livelihood: Displaced communities often lose access to traditional resources such as hunting grounds, fishing areas, and sacred sites.
- Human Rights Violations: The report details severe human rights violations, including forced evictions, destruction of homes, and legal abuses against those resisting displacement.
- Criticism of Conservation Practices:
- Non-Compliance: The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) has criticized non-compliance with the Forest Rights Act and the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972, particularly regarding the forced relocation of tribes without proper consent.
- Uncontrolled Activities: The report notes uncontrolled commercial and eco-tourism activities within Tiger Reserves, including the establishment of petrol pumps, rest houses, and resorts. These activities often contribute to tiger deaths through electrocution and other hazards.
- Specific Cases and Statistics (Major Tiger Reserves Impacted)
- Srivilliputhur-Megamalai Tiger Reserve (Tamil Nadu): About 4,000 people.
- Ramgarh Vishdhari Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan): Approximately 4,400 persons.
- Ranipur Tiger Reserve (Uttar Pradesh): Around 45,000 persons.
- Nauradehi Wildlife Sanctuary (Madhya Pradesh): At least 72,772 persons.
- Dholpur-Karauli Tiger Reserve (Rajasthan): About 4,000 persons.
- Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary (Rajasthan): Around 160,000 persons.
Important Conservation Initiatives:
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Australia is taking significant steps to protect an Indigenous site within Kakadu National Park, known as Jabiluka. This site is notable for having one of the world's largest high-grade uranium deposits.
About
- It is the largest national park in Australia and one of the largest in the world’s tropics.
- Kakadu preserves the greatest variety of ecosystems on the Australian continent including extensive areas of savanna woodlands, open forest, floodplains, mangroves, tidal mudflats, coastal areas and monsoon forests.
- Kakadu has been home to Aboriginal people for more than 50,000 years, and many of the park’s extensive rock art sites date back thousands of years.
- In 1981, it was declared as a UNESCO world heritage site.


Prelims Articles
Context
An international team of biologists has made a groundbreaking discovery about the Charles Darwin’s frog (Minervarya charlesdarwini), an endangered species native to the Andaman Islands. This research reveals fascinating and previously unknown aspects of this frog's reproductive behavior.
Key Highlights
- Upside-Down Spawning: The Charles Darwin’s frog lays its eggs in a unique upside-down position on the inner walls of tree cavities or root buttresses filled with water. This is different from other frogs, which lay eggs in a more traditional position.
- Egg Development: Once the eggs are laid, they eventually fall into the water below, where they hatch into tadpoles.
- Male Calls: Male Charles Darwin’s frogs use three types of calls to attract females: advertisement calls, aggressive calls, and combat calls.
- Physical Confrontations: If vocal calls do not deter rival males, physical fights involving kicking, boxing, and biting occur.
- Mating Disruptions: Unpaired males often try to interrupt the mating pairs, leading to intense battles. The upside-down position of the mating pair might help prevent rivals from disturbing them.
- Use of Trash: Due to habitat loss, these frogs are increasingly found breeding in discarded containers like plastic and metal trash. This shift from natural breeding sites to human waste is a growing concern.
- Implications: Researchers are worried about the long-term effects of this behavior on the frogs’ survival and are calling for efforts to protect their natural habitats.
Fact Box: About Charles Darwin’s frog (Minervarya charlesdarwini)
|


Prelims Articles
Context
The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) reviewed and approved amendments to the deal for 31 MQ-9B High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) from general Atomics of the US.
Key Decisions
- The DAC approved amendments to the deal for 31 MQ-9B High Altitude Long Endurance (HALE) Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) from General Atomics, USA.
- Details: The amendments are related to indigenous content and other aspects. The deal includes 15 Sea Guardians for the Indian Navy and 16 Sky Guardians (eight each for the Indian Army and Air Force).
- Cost: Estimated at $3.99 billion.
- Global Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) Facility: General Atomics is expected to establish a maintenance facility in India as part of the MQ-9B UAV deal, which will contribute to offset obligations.
- The MQ-9B drones are planned to be deployed at four places, including INS Rajaji near Chennai and Porbandar in Gujarat, by the Indian Navy, while the other two services will keep them jointly at two bases in Sarsawa and Gorakhpur in Uttar Pradesh at Air Force bases due to long runway requirements.
Fact Box: MQ-9B drones
|


Prelims Articles
Context
Scientists have developed an improved genome-editing tool. This tool, called enhanced FnCas9, offers more precise and efficient DNA modifications compared to current CRISPR technologies.
Key Findings
- Enhanced FnCas9 cuts target DNA more effectively than the original FnCas9.
- It has fewer off-target effects, making it more reliable for precise gene editing.
- The enhanced FnCas9 can identify and correct single-nucleotide changes more effectively, potentially improving genetic diagnostics.
- Therapeutic Applications
- Testing for Blindness: The team tested enhanced FnCas9 on cells with a mutation causing Leber congenital amaurosis type 2 (LCA2), a form of inherited blindness. The tool successfully corrected the mutation in iPSCs (induced pluripotent stem cells) derived from a patient’s skin cells.
- Results: Most corrected iPSCs showed normal levels of the protein RPE65, which is crucial for vision. The editing was highly efficient, with some colonies showing complete correction of the mutation.
Fact Box: About CRISPR-Cas9
|


Editorials
Context
Indian authorities have acknowledged a significant skill gap between Chinese and Indian technicians, impacting productivity in various sectors. Despite the need for Chinese expertise, visa restrictions have hindered their entry, exacerbating India's challenges in bridging this gap and advancing its manufacturing sector.
Current Visa and Skill Gap Challenges
- Visa Restrictions: Indian officials have sharply reduced visas for Chinese nationals from 200,000 in 2019 to just 1,000 this year due to security concerns and political tensions. This decline affects various industries reliant on Chinese technical expertise.
- Skill Deficit: Indian businesses, including those in footwear and solar manufacturing, struggle with underutilized Chinese machinery due to insufficient local expertise. Chinese technicians are noted for their productivity and ability to maximize resources.
- Education Shortcomings: India’s education system lags behind China’s, with only about 15% of Indian students having basic international skills compared to 85% of Chinese students. This education gap underscores the urgent need for foreign expertise to fill technical roles.
Historical and Comparative Insights
- China’s Approach: China leveraged foreign expertise and improved its education system over decades, successfully transitioning from a weaker educational base to a global manufacturing leader. This strategy combined international knowledge with local educational advancements.
- Korean Model: In the 1980s, South Korea used foreign technology alongside its strong educational foundation to advance rapidly. This example illustrates how essential a solid educational base is for effectively utilizing foreign expertise.
- Indian Education Limitations: India has expanded school infrastructure but struggled with educational quality, resulting in low skill levels among students. This problem hampers India’s ability to benefit from advanced technologies and foreign knowledge.
Future Implications and Recommendations
- Economic Impact: India’s potential for labor-intensive manufactured exports remains constrained by its limited human capital and strict visa policies. This reduces its competitiveness compared to countries like Vietnam and Mexico, which have capitalized on similar opportunities.
- Missed Opportunities: India’s restrictive visa policies and educational inadequacies risk missing out on global manufacturing and technology trends. This could further isolate India from significant economic advancements and investment opportunities.
- Need for Reform: To avoid further economic setbacks, India must address its educational deficiencies and reconsider visa restrictions for foreign experts. Enhancing domestic capabilities and integrating foreign knowledge is crucial for future growth.
Mains Question
Q: What are the challenges faced by India in bridging its skill gap and advancing its manufacturing sector?


Editorials
Context
A recent tragedy at an IAS coaching centre in New Delhi, where flooding resulted in the deaths of three IAS aspirants, highlights the increasing issue of urban flooding exacerbated by human errors and inadequate infrastructure.
Regulatory and Safety Concerns
- Basement Usage Regulations: Building regulations in India generally restrict the use of basements for habitation, allowing them for storage, parking, and utility purposes. However, mixed-use buildings often see basements used for activities like coaching classes, which may not comply with these regulations.
- Permits and Permissions: The Delhi Master Plan 2021 mandates that basement usage for coaching centres requires clearance from fire authorities and other statutory bodies. There is uncertainty whether the coaching centre in question had the necessary approvals and if any changes in basement use were duly notified.
- Inspection and Compliance Issues: Often, users avoid notifying authorities about changes to avoid bureaucratic hurdles and potential bribe demands. This non-compliance contributes to unsafe conditions, as seen in recent urban flooding incidents.
Infrastructure and Flood Management
- Impact of Urban Flooding: Localized flooding in cities like New Delhi is becoming more common due to both natural topography and poor urban planning. Flooding often damages critical infrastructure, as seen in past incidents like the 2015 Chennai floods.
- Building Vulnerabilities: Basements are particularly vulnerable during floods due to limited access and poor ventilation. Effective flood management for such spaces requires specialized pumping systems and other mitigation measures to prevent water ingress.
- Resilience Measures: To enhance flood resilience, buildings should include features such as concrete walls, flood barriers, and non-return valves. These measures can prevent water from entering basements and other critical areas up to a height of 1.5 meters.
Mains Question
Q. In the light of the recent New Delhi coaching centre tragedy, analyze the impact of urban flooding on building safety and infrastructure.


Editorials
Context
The rise of complex Machine Learning (ML) models and Large Language Models (LLMs) has introduced challenges related to data privacy, AI bias, and misinformation, particularly during sensitive events like elections. Machine Unlearning (MUL) has emerged as a potential solution to address these issues by enabling AI systems to forget specific data, thus mitigating the problems associated with data management and bias.
Concept and Challenges of Machine Unlearning
- Machine Unlearning (MUL): Machine Unlearning involves incorporating algorithms into AI models to delete specific types of data, such as false or sensitive information. This concept is designed to counteract the difficulties in removing data due to the complex data lineage created by LLMs.
- Challenges in Data Management: The continuous processing of data in ML models creates a tangled web of information, making it difficult to track and remove specific data. This complexity increases the risk of data manipulation and adversarial outputs.
- Comparative Approaches: Simply deleting and retraining the entire dataset (data pruning) is costly and time-consuming, leading to reduced accuracy. MUL offers a more efficient alternative, and is being explored by companies like IBM to improve accuracy and reduce costs.
Approaches to Implementing MUL
- Private Approach: In the private model, data fiduciaries independently test and implement MUL algorithms on their AI systems. This voluntary method allows for innovation but may be limited by the resources and expertise of smaller companies.
- Public Approach: Governments can mandate MUL implementation through regulatory frameworks, such as the European Union’s AI Act, which addresses data poisoning. This approach could involve issuing guidelines or creating a standardized MUL model to be adopted by data fiduciaries.
- International Approach: An international framework for MUL could be developed by global standard-setting organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission. Uniform standards across countries would facilitate global governance of AI, though geopolitical frictions may pose challenges.
Prospects and Implementation
- Current Status: MUL is still in the early stages of development, with ongoing research and testing to refine its effectiveness. The need for technical and regulatory adjustments is crucial for its successful deployment.
- Regulatory Considerations: As AI and data privacy regulations evolve, MUL could become a key component in addressing privacy concerns. Effective implementation will require careful balancing of technical feasibility and regulatory requirements.
- Future Directions: Stakeholders must collaborate to address both technical challenges and regulatory gaps to ensure MUL's successful integration into AI systems. Continued research and policy development will be essential for advancing MUL and enhancing data privacy.
Mains Question
Q. Evaluate the concept of Machine Unlearning (MUL) as a solution to address data privacy and bias issues in AI systems. Discuss the potential approaches for implementing MUL and the challenges associated with each approach.