6th August 2024 (8 Topics)
Mains Issues
Context
The recent downfall of the government in Dhaka and the resignation of Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina will affect growing trade ties, restricting the movement of people and goods, and stalling a potential free trade agreement (FTA) between the two countries.
What is the matter behind Bangladesh Protests?
- The student protests, initially focused on abolishing quotas in civil service jobs, have now grown into a broader anti-government movement.
- The mass protests in Bangladesh began as student demonstrations demanding reforms to the civil service quota system.
- A Supreme Court ruling against reintroducing job quotas did not fully satisfy the protesters, who continue to demand the abolition of all job reservations for children of "freedom fighters”.
- The situation intensified when former army chief General Ikbal Karim Bhuiyan criticized the government’s handling of the protests and called for troop withdrawal.
About India-Bangladesh recent developments:
- In Trade: In October 2023, India and Bangladesh began discussions on an FTA during a meeting of the Joint Working Group on Trade in Dhaka.
- FTA would reduce or eliminate customs duties on goods traded between India and Bangladesh, and ease norms to help promote further trade and investments.
- Export-Import data: A 2012 working paper published by the World Bank estimated that a full FTA for goods would increase Bangladesh’s exports to India by 182%, whereas a partial FTA could lead to a 134% increase.
- Infrastructure and connectivity: Infrastructure and connectivity has been a growing part of India-Bangladesh ties, according to the Minister of External Affairs.
- India has extended three lines of credit to Bangladesh since 2016 amounting to $8 billion for the development of road, rail, shipping and port infrastructure.
- In November 2023, two joint projects – the Akhaura-Agartala cross-border rail link and Khulna-Mongla Port rail line – were inaugurated.
- Ports and Marine connectivity: In 2023, the countries had agreed to operationalise the agreement for the usage of the Chittagong and Mongla ports to ease the movement of cargo between mainland India and the Northeast.
India-Bangladesh Trade Relations:
- Bangladesh is India’s biggest trade partner in the subcontinent, and India is Bangladesh’s second biggest partner in Asia after China.
- Their total bilateral trade amounted to 13 billion dollars in the financial year 2023-24, according to the Union Ministry of Commerce.
- India exports a variety of goods to Bangladesh, including cotton, machinery and food products, while imports goods like jute and fish.
- Bangladesh is the biggest export destination for India’s cotton, accounting for 34.9% of India’s total cotton exports (some $2.4 billion in FY24).
- Other major Indian exports to Bangladesh are Petroleum products and cereals.
- India’s top imports from Bangladesh are readymade garments, amounting to $391 million in FY24. In recent years, Bangladesh has emerged as a major global hub for textiles.
Concerns related to downfall in Bangladesh
- Long border sharing with North-east India: A disruption in Indo-Bangladesh ties could thus restrict India’s access to the Northeast, which will be connected to mainland India only through the narrow “Chicken’s Neck” Between West Bengal and Assam.
- Trade disruptions: According to exporters, they are already facing disruptions in exports to Bangladesh due to a shortage of foreign exchange in that country.
- India's exports of perishable goods are facing challenges at the border.
- Impacts on Global Economy: Bangladesh poses several risks to India's trade, proactive measures and regional cooperation can help mitigate these impacts and ensure continued economic stability and growth.


Mains Issues
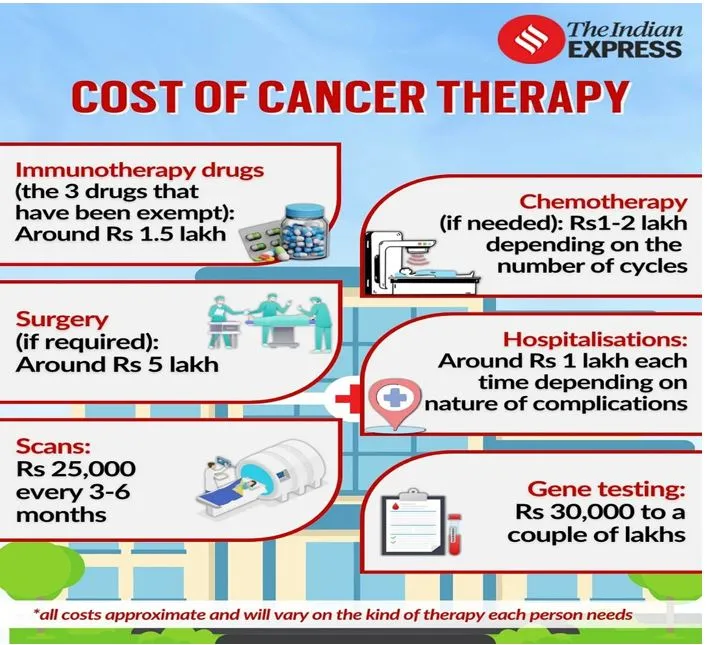
A new cancer drug, promising fewer side effects and better outcomes, is now a ray of hope for cancer patients in India. However, this hope comes at a high price. The cost of drugs curing cancer is too high to access and afford by normal people.
Making Affordable Cancer Treatment in India:
- In her Budget 2024-25 speech, the finance minister announced customs duty (which was earlier ~10%) exemptions on 3 targeted cancer drugs - trastuzumab deruxtecan, osimertinib, and durvalumab.
- The decision is likely to make these drugs more accessible to Indian patients and reduce the overall cost of cancer therapies.
About Cancer:
- It is a complex and broad term used to describea group of diseases characterized by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body.
- These abnormal cells, known as cancer cells,could invade and destroy healthy tissues and organs.
- In a healthy body, cells grow, divide, and die in a regulated manner, allowing for the normal functioning of tissues and organs.
- However, in the case of cancer, certain genetic mutations or abnormalities disrupt this normal cell cycle,causing cells to divide and grow uncontrollably.
Cancer profile in India:
- The number of cancer cases in India is on the rise. According to the National Cancer Registry data,
- An estimated 6 lakh new cancer cases were detected in 2022, up from 14.2 lakh in 2021 and 13.9 lakh in 2020.
- The number of deathsdue to cancer increased to an estimated 08 lakh in 2022, up from 7.9 lakh in 2021 and 7.7 lakh in 2020.
- The incidence of cancer cases in India:
- According to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), 1 in 9 Indians will develop cancer during their lifetime.
- The incidence is higher among women- 103.6 per 100,000 population in 2020 compared to 94.1 among men.
- The most common cancersamong men were of the lung, mouth, prostate, tongue and stomach; for women, they were breast, cervix, ovary, uterus and lung.
Regulation of Prices of these Cancer Drugs in India:
- Trastuzumab Injection is a scheduled drug under the National List of Essential Medicines (NLEM) 2022 and the National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) has fixed the ceiling price (Rs. 54725.21 per vial) of the same.
- The other two medicines i.e., Osimertinib and Durvalumab are non-scheduled medicines under Drug Prices Control Order (DPCO), 2013.
- Hence, NPPA monitors the maximum retail price (MRP) of the non-scheduled formulation to ensure that the same does not increase by more than 10% of MRP during the preceding 12 months.


Mains Issues
Context
In the recent Union budget, the government hiked customs duty on laboratory chemicals from 10 per cent to 150 percent, increasing concerns for the scientists’ community in India.
About the update:
- Generally, chemicals attract duty of 2.5 percent, 5 percent, 7.5 percent or 10 percent.
- Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs has reinstated a 10% import duty on chemicals for laboratory use, reversing a previous hike announced in the Union budget for FY25.
Chemical’s import dependence:
- Laboratory chemicals (Harmonised System Code 9802) include fine chemicals and pure compounds used by the pharmaceutical and biotech industry and researchers for lab analysis and synthesis. These chemicals are niche in nature and mostly imported.
- Analysis of trade under this HS Code shows that the value of imports has been sharply rising each year. It was ?104 crore in FY21, ?181 crore in FY22, ?416 crore in FY23, and zoomed to ?701 crore in FY24.
Key Exclusions and Compliance by CBIC:
- Ethyl Alcohol: Undenatured ethyl alcohol is excluded from the 10% duty and is subject to a 150% duty due to misuse concerns.
- Compliance Requirement: Non-compliance with end-use declarations will result in ineligibility for the concessional rate.
Tariff Classification:
- Current Tariffs: Chemicals generally attract import duties ranging from 2.5% to 10% under the Customs Tariff Act.
- Special Classification: Chemicals imported in packages not exceeding 500ml or 500g for laboratory use are specifically classified with a 10% duty.
Impacts on the increase in Custom Duty:
- Pharmaceutical companies and research labs might face soaring costs for critical imported chemicals, potentially driving up research expenses and end-product prices.
- Almost 95 per cent of research labs use imported lab chemicals, and most of this experimentation work needs to be reproduced globally.
- Thus, the focus must be on quality-oriented moves rather than raising government revenue.


Prelims Articles
Context
In a recent finding it was found that the Higgs boson is responsible for the mass and interactions of all the particles making elementary particles interacting with a field and dubbed the Higgs field.
About Higgs Boson:
- The Higgs boson is the fundamental force-carrying particle ofthe Higgs field, which is responsible for granting fundamental particles their mass.
- This field was first proposed in the mid-sixties by Peter Higgs, for whom the particle is named.
- The particle was finally discovered onJuly 4, 2012, by researchers at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the most powerful particle accelerator in the world, located at the European particle physics laboratory CERN, Switzerland.
- The LHC confirmed the existence of the Higgs field and the mechanism that gives rise to mass and thus completed the standard model of particle physics.
- It is one of the 17 elementary particles that make upthe Standard Model of particle physics, which is scientists' best theory about the behaviors of the universe's most basic building blocks.
- Higgs boson plays such a fundamental role in subatomic physics that it is sometimes referred to as the "God particle."
- Features:
- The Higgs boson has a mass of 125 billion electron volts, meaning it is 130 times more massive than a proton.
- It is also chargeless with zero spin, a quantum mechanical equivalent to angular momentum.
- It is the only elementary particle with no spin.

- What is a Boson?
- A boson is a "force carrier" particlethat comes into play when particles interact with each other, with a boson exchanged during this interaction. For example, when two electrons interact, they exchange a photon, the force-carrying particle of electromagnetic fields.
- Because quantum field theory describes the microscopic world and the quantum fields that fill the universe with wave mechanics, a boson can also be described as a wave in a field.
- So, a photonis a particle and a wave that arises from an excited electromagnetic field, and the Higgs boson is the particle or "quantized manifestation" that arises from the Higgs field when excited.
- This mass-granting phenomenon also only applies to fundamental particles like electrons and quarks. Particles like protons, made up of quarks, get most of their mass from the binding energy that holds their constituents together.


Prelims Articles
Context
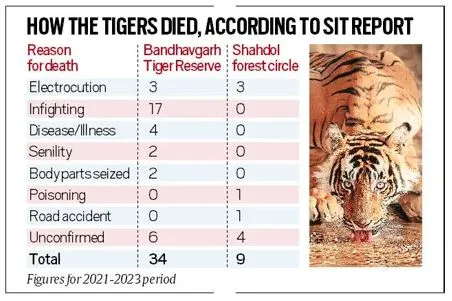
Recently, concerns were raised by a Special Investigation Team (SIT) that was looking into the deaths of 43 tigers between 2021 and 2023 in Madhya Pradesh’s Bandhavgarh Tiger Reserve (34 deaths) and Shahdol Forest Circle (9 deaths) regarding medical ignorance of department.
About SIT Report:
- According to the report, there was a “lack of interest by higher authorities and Forest Range Officers in discharging their duties, resulting in arrests in only two out of five cases where unnatural causes of death”.
- In many cases where tigers were found dead due to electrocution and there was a lack of information on revenue, and private land ownership in the region.
Tiger Population and Conservation:
- The number of tigers in Madhya Pradesh has increased from 526 to 785 in the last four years. It is followed by Karnataka (563) in second place and Uttarakhand (560) in third place.
- Project Tiger:
- Project Tiger is a wildlife conservation initiative in India that was launched in 1973.
- The primary objective of Project Tiger is to ensure the survival and maintenance of the tiger population in their natural habitats by creating dedicated Tiger Reserves.
- Starting with only nine reserves covering 9,115 sq. km, the project marked a paradigm shift in wildlife conservation efforts.


Editorials
Context
The present Uttar Pradesh government's response to its electoral loss in the Lok Sabha elections by amending the Prohibition of Unlawful Conversion of Religion Act. The changes make the law more stringent, affecting interfaith relationships and conversions, and raise concerns about state interference and religious freedom.
Stricter Penalties and Broader Scope
- Increased Penalties: Imprisonment and fines are significantly raised for conversion offenses, with second-time offenders facing up to life imprisonment and fines reaching one lakh rupees.
- Broader Scope: The amended law includes threats, marriage promises, and overseas funding in its purview, expanding the definition of unlawful conversions.
- Third-Party FIRs: Amendments allow any third person to file complaints, inviting potential misuse by vigilantes and local leaders to target interfaith relationships.
Constitutional Concerns and Political Motivations
- Intrusive Law: The law presumes all conversions are suspicious, undermining constitutional religious freedom and enabling widespread state interference in personal choices.
- Interfaith Relationship Impact: The amendments make interfaith live-in relationships illegal, disproportionately affecting minority communities and fueling societal intolerance.
- Political Motive: The stringent law diverts attention from governance issues like development and employment, using intolerance to gain political advantages for the ruling party.
Mains Question:
Q. “Critically examine the implications of the amended Prohibition of Unlawful Conversion of Religion Act in Uttar Pradesh on religious freedom and interfaith relationships. Discuss the constitutional challenges it poses.”


Editorials
Context
India is hosting the 32nd International Conference of Agricultural Economists (ICAE) in Delhi from August 2-7, 2024.
India's historical and current role in agricultural development and global food security. India's contributions to agricultural revolutions and the importance of South-South collaboration are significant especially between India and Africa, to address food and nutritional security challenges.
Historical Significance and ICAE's Roots
- ICAE's Origin in India: Founded by Lord Elmhirst with Rabindranath Tagore's support to aid village development in Santiniketan in 1921.
- First ICAE in India: India hosted the ICAE in 1958, with PM Jawaharlal Nehru as the chief guest, marking its global agricultural significance.
- Tagore's Vision: Tagore aimed to free villages from ignorance and inspire scientific training, forming the foundation of ICAE’s goals.
Agricultural Challenges and South-South Collaboration
- Nutritional Security Issues: India and Africa struggle with child malnutrition, needing global and South-South collaboration for sustainable solutions.
- ICAE Study Findings: High-debt service ratios and underfunding in agriculture hamper productivity and efforts to reduce child malnutrition in India and Africa.
- Public Spending and R&D: Enhancing investment in agricultural R&D and infrastructure is crucial for growth and improved nutrition outcomes.
Global Food Security and G20 Leadership
- Global Hunger Goals: Achieving Zero Hunger by 2030 requires an additional $21 billion annually in agriculture and rural investment.
- G20 Impact: India's and Brazil's G20 presidencies focus on food security, bioeconomy, and supporting the African Union for global food systems transformation.
- Climate Resilience Investment: Building a bio-economy and investing in climate resilience can transform food systems, benefitting the global South.
Mains Question:
Q. Discuss the role of South-South collaboration in addressing food and nutritional security challenges in India and Africa. Analyze the impact of G20 leadership on global food systems transformation.


Editorials
Context
The recent assassinations of Fuad Shukr, a senior Hezbollah commander, and Ismail Haniyeh, the political chief of Hamas, by Israel. It highlights the escalating tensions in West Asia and the potential for a wider conflict involving Israel, Iran, and possibly the United States.
Rising Tensions in West Asia
- Killings of Key Figures: Fuad Shukr and Ismail Haniyeh were killed, escalating regional tensions.
- Israel's Military Actions: Israel claimed responsibility for Shukr's killing but remained ambiguous about Haniyeh’s assassination.
- Conflict-driven instances: Hezbollah responded with rocket attacks, heightening the risk of broader conflict.
Potential Consequences
- Iran's Expected Retaliation: Iran may retaliate against Israel, risking a confrontation.
- S. Involvement: A direct Iran-Israel war could drag the U.S. into the conflict.
- Netanyahu's Policies: Netanyahu's actions suggest a preference for continued conflict over peace negotiations.
Mains Question:
Q. Analyse the implications of Israel's recent assassinations of Hezbollah and Hamas leaders on the geopolitical stability of West Asia. Discuss the potential role of the U.S. in mitigating the conflict.