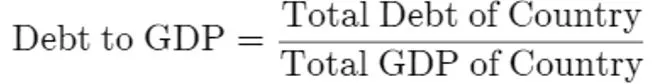29th July 2024 (12 Topics)
Context
The Indian government's fiscal policy has traditionally aimed to limit the fiscal deficit (difference between what the government spends and what it earns) to a specific percentage of GDP. However, in a recent budget speech, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a shift in focus from a fixed fiscal deficit target to managing the ratio of government debt to GDP.
What Is Changing in Fiscal Policy?
- Current System: Traditionally, the Indian government set a target for the fiscal deficit as a percentage of GDP (Gross Domestic Product). For instance, the target for 2024-25 is 4.5% of GDP.
- Future Change: From 2026-27, the government will focus on reducing the ratio of government debt to GDP, rather than strictly aiming for a specific fiscal deficit percentage. This means that instead of just lowering the fiscal deficit, the priority will be to ensure that the overall debt compared to the size of the economy is decreasing.
- Reason for Change:
- Criticism of Old Target: The 3% fiscal deficit target, which many consider a standard, doesn't have a solid scientific basis. It originally came from the 1992 Maastricht Treaty in Europe. The new approach will still reduce the deficit but will emphasize managing debt more effectively.
How Will These Changes Affect?
- Over time, the focus on reducing debt relative to GDP should help in managing the country's overall economic health, but specific targets for fiscal deficit might not be strictly followed.
- The new approach aims to ensure that while the fiscal deficit might not meet a specific percentage, the overall debt-to-GDP ratio is on a declining path. This shift is intended to make fiscal policy more flexible and responsive to economic conditions.
Fact Box: What is the Debt-to-GDP Ratio?
|
More Articles