

10th July 2024 (9 Topics)
Context
An estimated $3.8 trillion could be generated by Earth observation (EO) data by 2030, according to a new World Economic Forum (WEF).
What is Earth Observation Data?
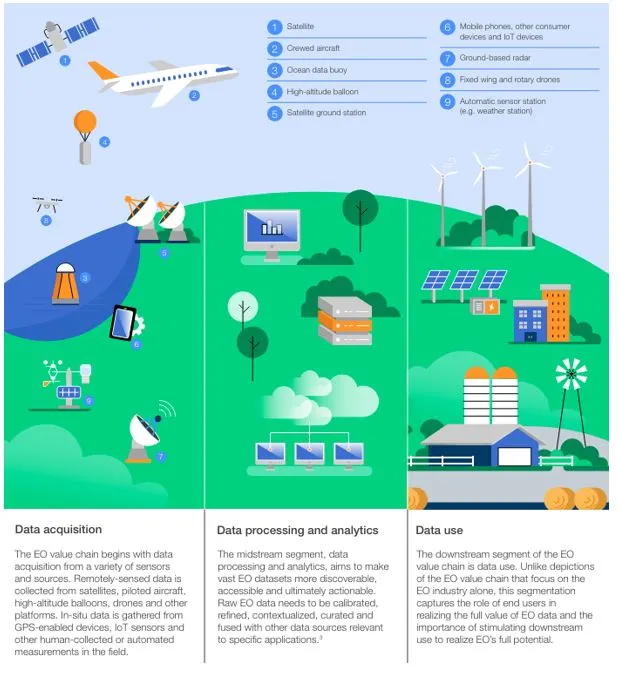
- Earth observation (EO) data refers to information gathered about Earth's physical, chemical, and biological systems using various sensor technologies.
- These include satellites, aircraft, underwater devices, and even people equipped with specialized equipment.
- Applications in Environmental Protection:
- Monitoring Natural Ecosystems: EO data monitors variables like soil moisture, atmospheric conditions, and temperature changes on land and sea. It tracks changes in land cover and detects the presence of chemicals and radiation levels.
- Protecting Ecosystems: EO plays a crucial role in safeguarding ecosystems like mangroves and coral reefs.
- Mangroves, vital for marine life and carbon storage, are monitored to prevent loss from human activities and natural disasters.
- Disaster Prevention and Response: EO data aids in early warning systems for wildfires and helps identify illegal deforestation. It detects gas leaks from pipelines and other sources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Optimizing Resource Use: EO optimizes shipping routes to save fuel and minimize emissions. It monitors crop health, allowing for efficient use of fertilizers and water.
- Environmental Impact Reduction: By applying EO technologies, global greenhouse gas emissions could potentially be reduced by 3.6% annually, equivalent to 2 gigatonnes.
More Articles


