

25th March 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
A parliamentary panel on agriculture in its report, tabled in Parliament recently, noted that the government is far from its 2022 goal of doubling the income of farmers which the Centre had announced six years ago.
About
Key Findings:
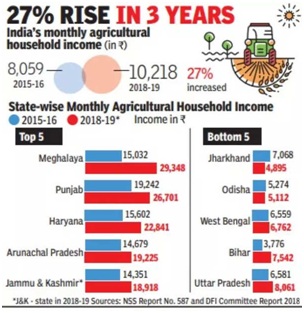
- Between 2015-16 and 2018-19, nationwide farm income rose 27%, which is still well short of the trajectory needed to achieve the goal of doubling income this year.
- Between 2015-16 and 2018-19, Jharkhand saw a drop in monthly income by 30%.
- The Doubling Farmers’ Income (DFI) committee had calculated the 2015-16 baseline by extrapolating the National Statistical Organisation’s (NSO) survey data from 2012-13, calculating that the national average monthly income of a farm family in that year was Rs.8,059.
- By the time the next NSO survey was conducted in 2018-19, monthly income had risen 27% to Rs.10,218.
- In Jharkhand, however, a farm family’s average income fell from Rs.7,068 to Rs.4,895 over the same period.
- In Madhya Pradesh, it fell from Rs.9,740 to Rs.8,339,
- in Nagaland, from Rs.11,428 to Rs.9,877, and
- for Odisha, it dipped marginally from Rs.5,274 to Rs.5,112
About Doubling Farmer Income Initiative:
- The reference year for farmer income is 2015-16 and target year is 2022-2023.
- The aim is to double the Real Income of farmer and not the nominal income.
- According to NITI Aayog, farmers’ income in 2015-16 was Rs. 44027 in real terms.
- In order to achieve the aim, an annual growth of 10.41% is required in farmers’ income.
|
Initiatives
|


